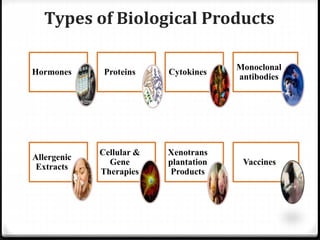
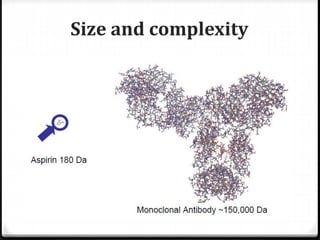
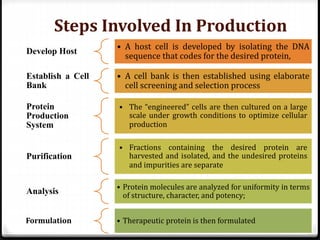
Biological products, or biologics, are medical products made from sugars, proteins, nucleic acids, or living entities like cells and tissues. They are used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose diseases. Biologics are made from natural sources through complex production processes involving cell culture, purification, analysis, and formulation. Examples include vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and products for cancer, arthritis, and skin/nerve conditions. Their production requires tightly controlled conditions to consistently produce safe, pure, and potent products.