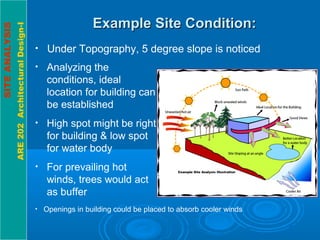
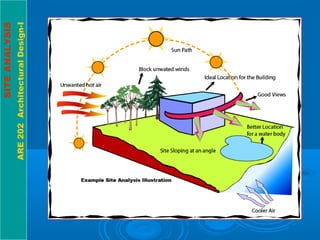
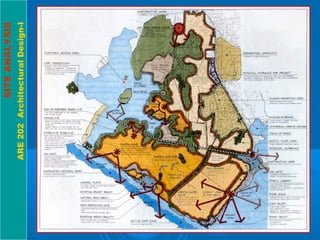
This document discusses the importance of site analysis for architectural design. It explains that site analysis involves taking an inventory of various site elements, including topography, climate, vegetation, and analyzing how they relate to the client's needs. The inventory should gather information about subsurface features like geology and hydrology, natural surface features like slopes and wildlife, and cultural/man-made features like utilities, land use, and circulation. Understanding these site conditions through analysis is crucial for establishing an ideal building location and incorporating local features into a successful design.