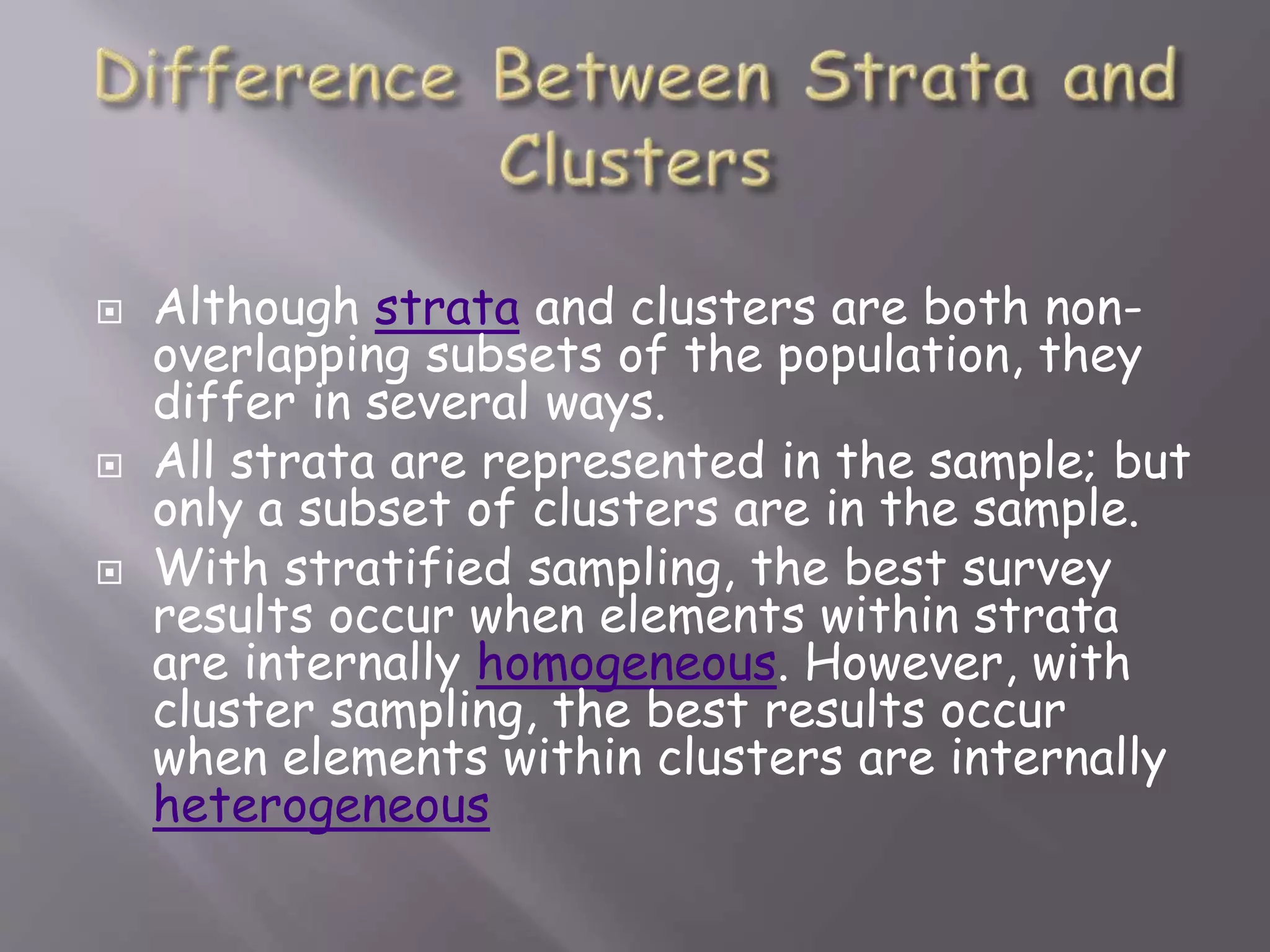
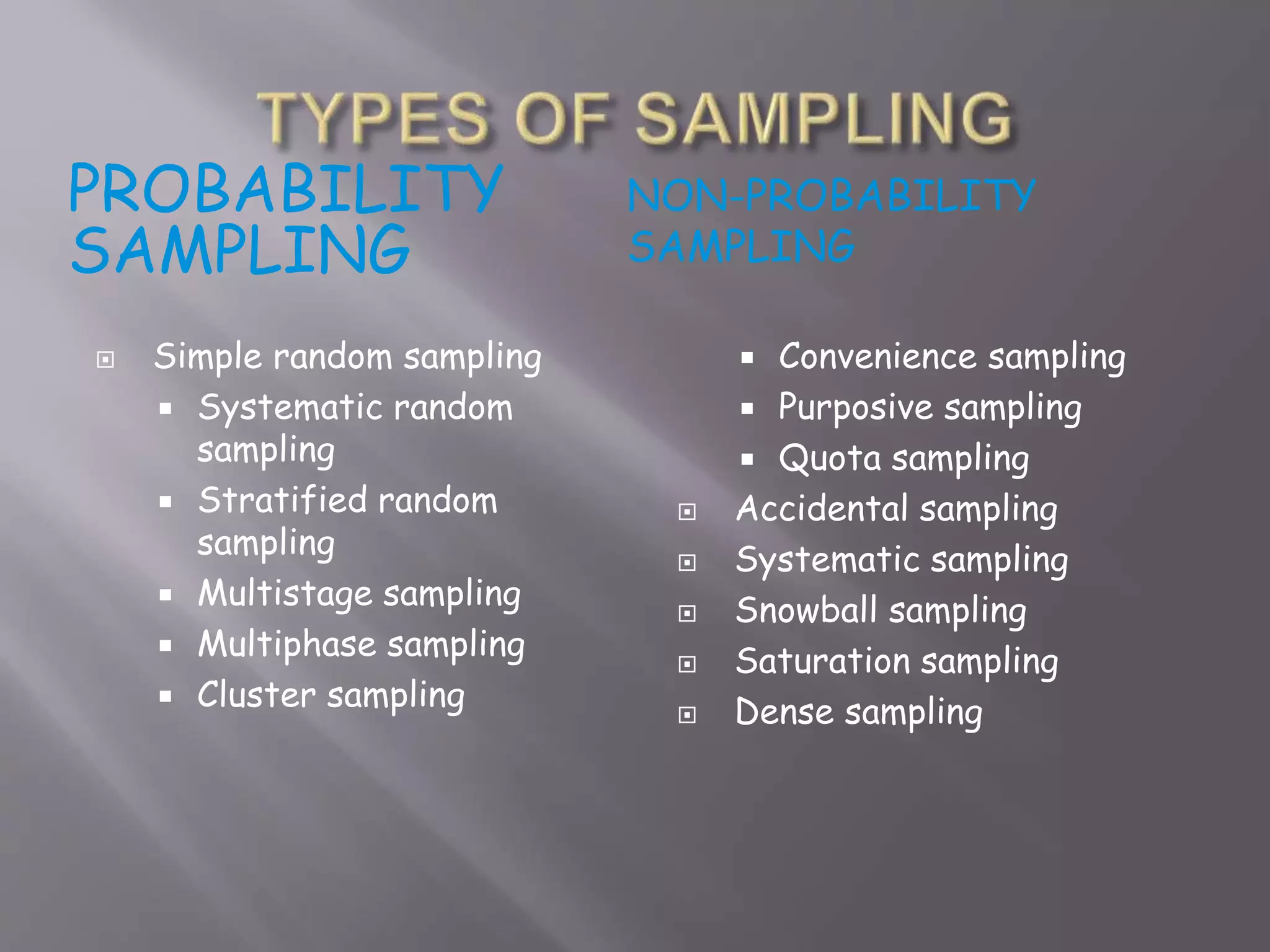
This document discusses sampling methods and their key aspects. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of individuals from a population to make inferences about the whole population. Probability sampling methods aim to give all population elements an equal chance of selection, while non-probability methods do not. Some common probability methods described include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. The document also discusses sampling frames, statistics versus parameters, confidence levels, and evaluating different sampling techniques.




























![ Cons
Larger sampling error
[variation in score
form sample to
sample]
Typically “requires”
larger sample
Pros
Saves time
Saves money
Should allow for
closer supervision in
the field
Requires enumerating
only part of the
population](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampling1-160114042341/75/Sampling-30-2048.jpg)