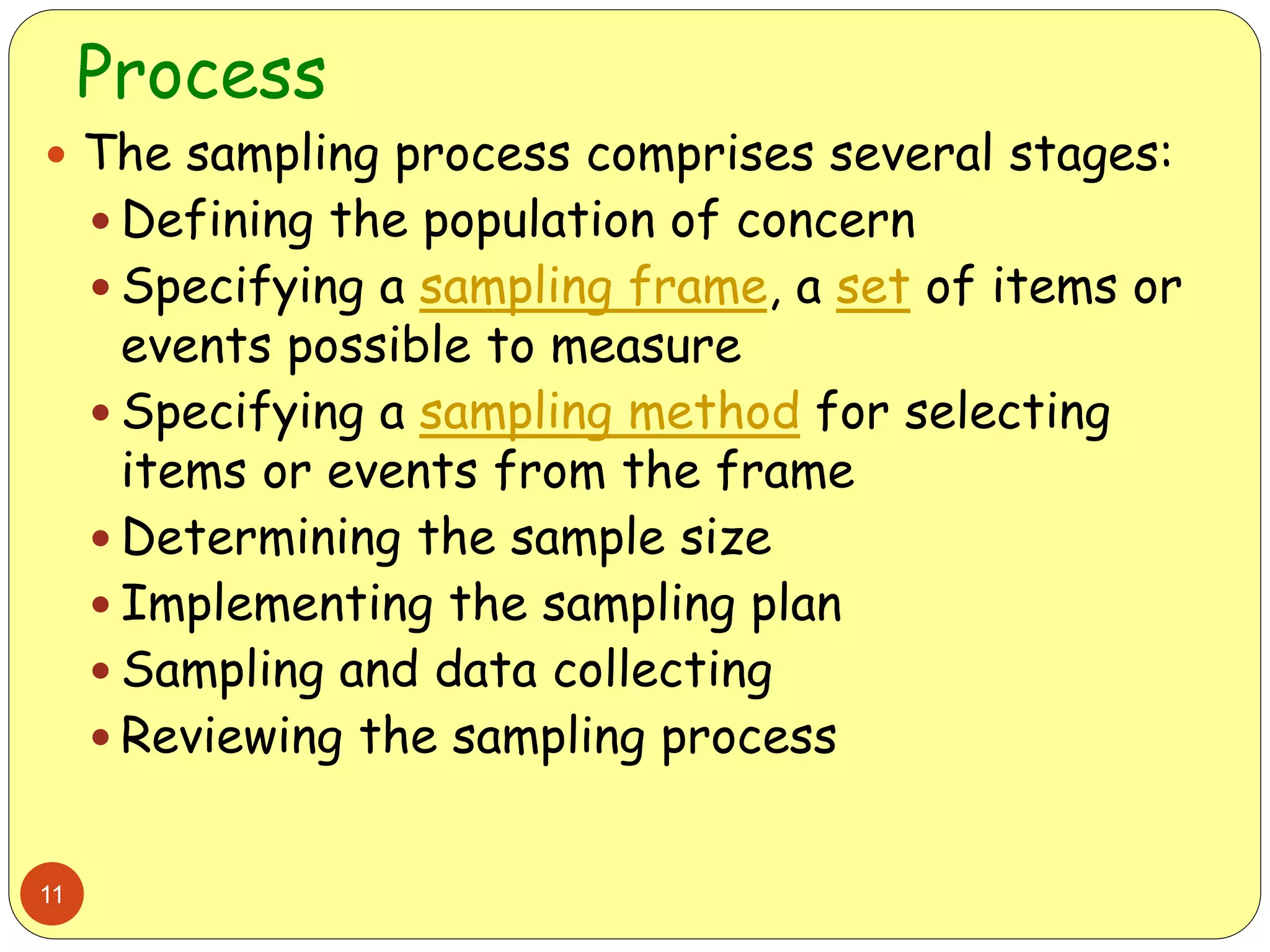
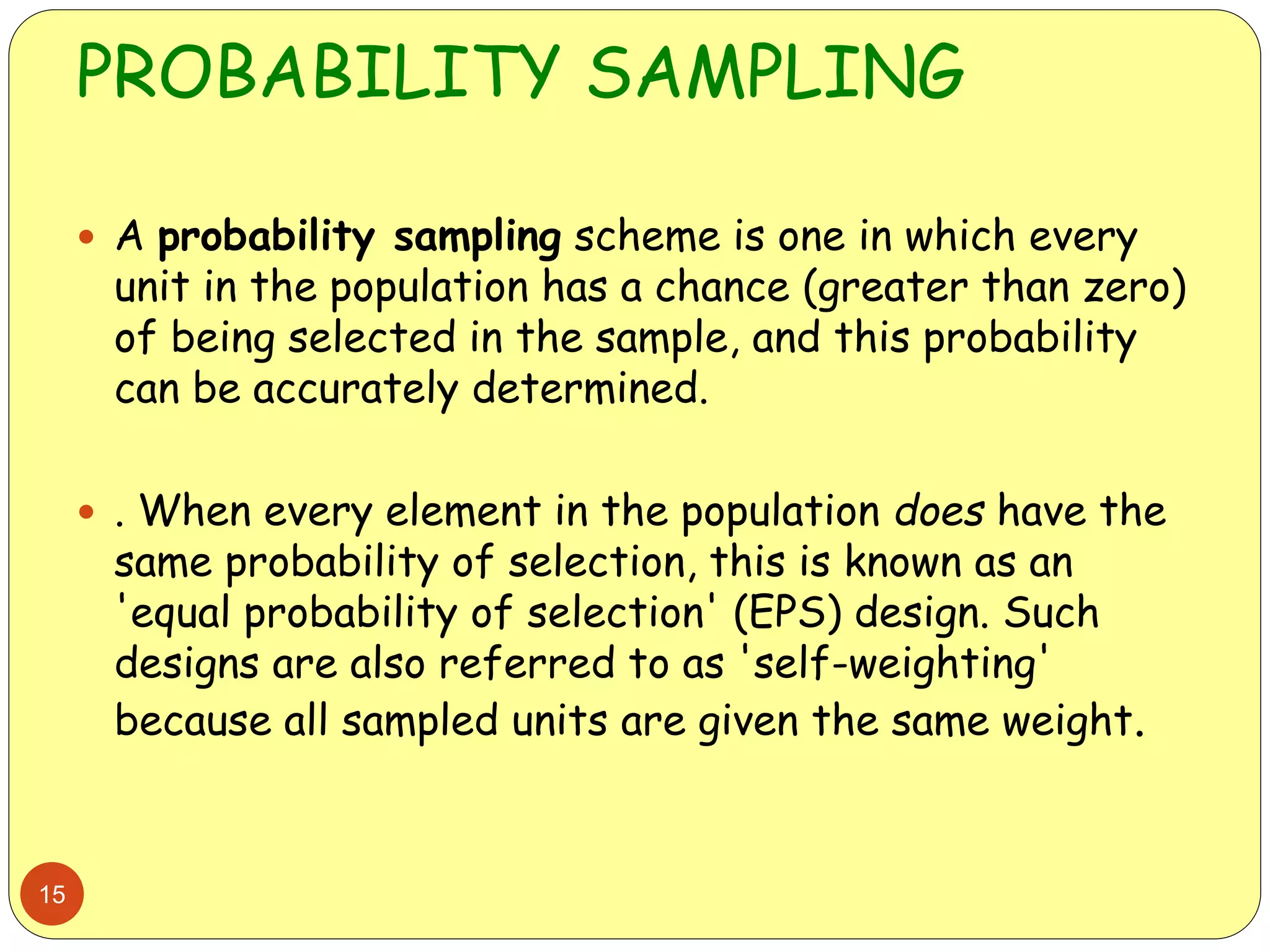
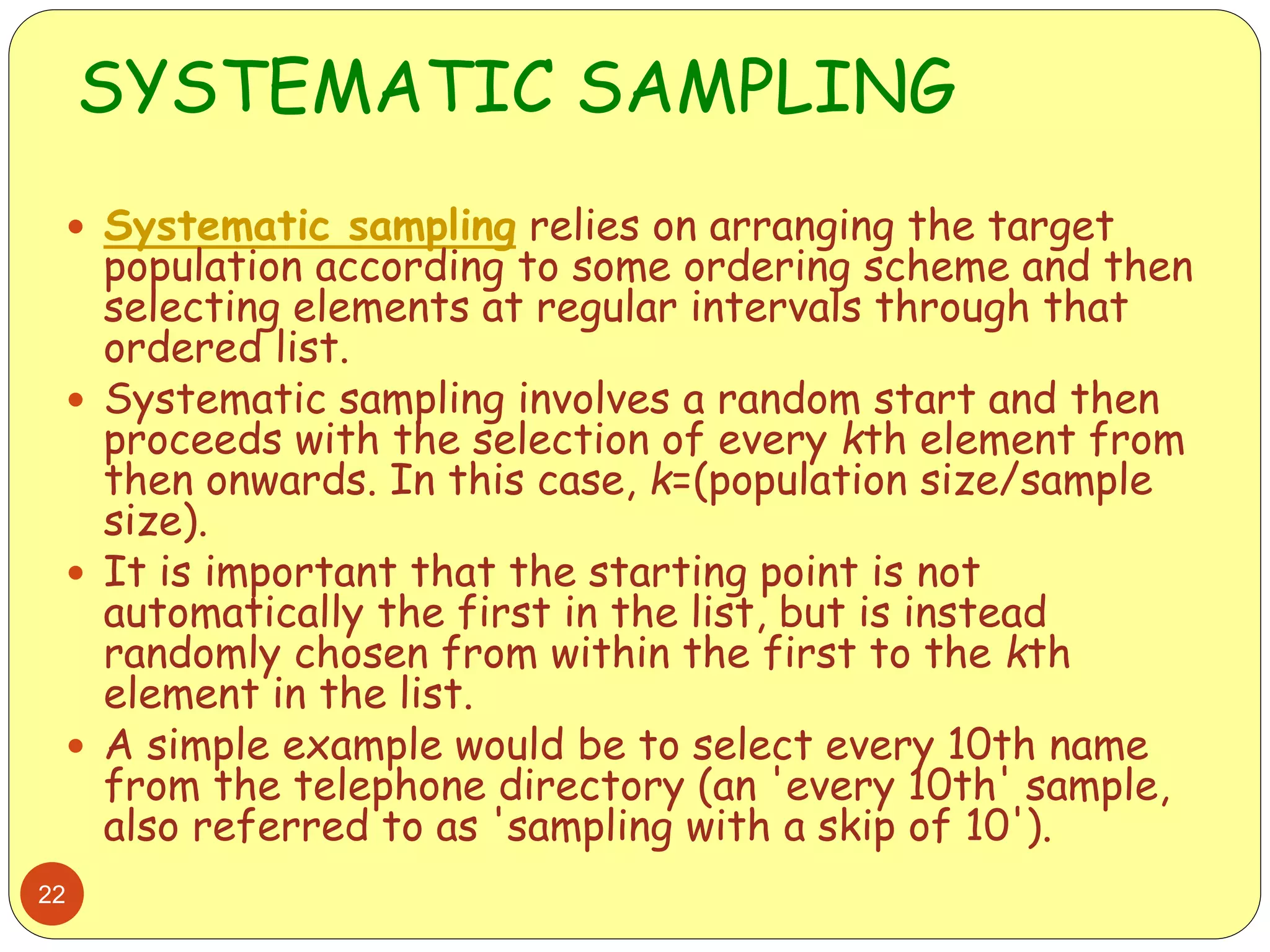
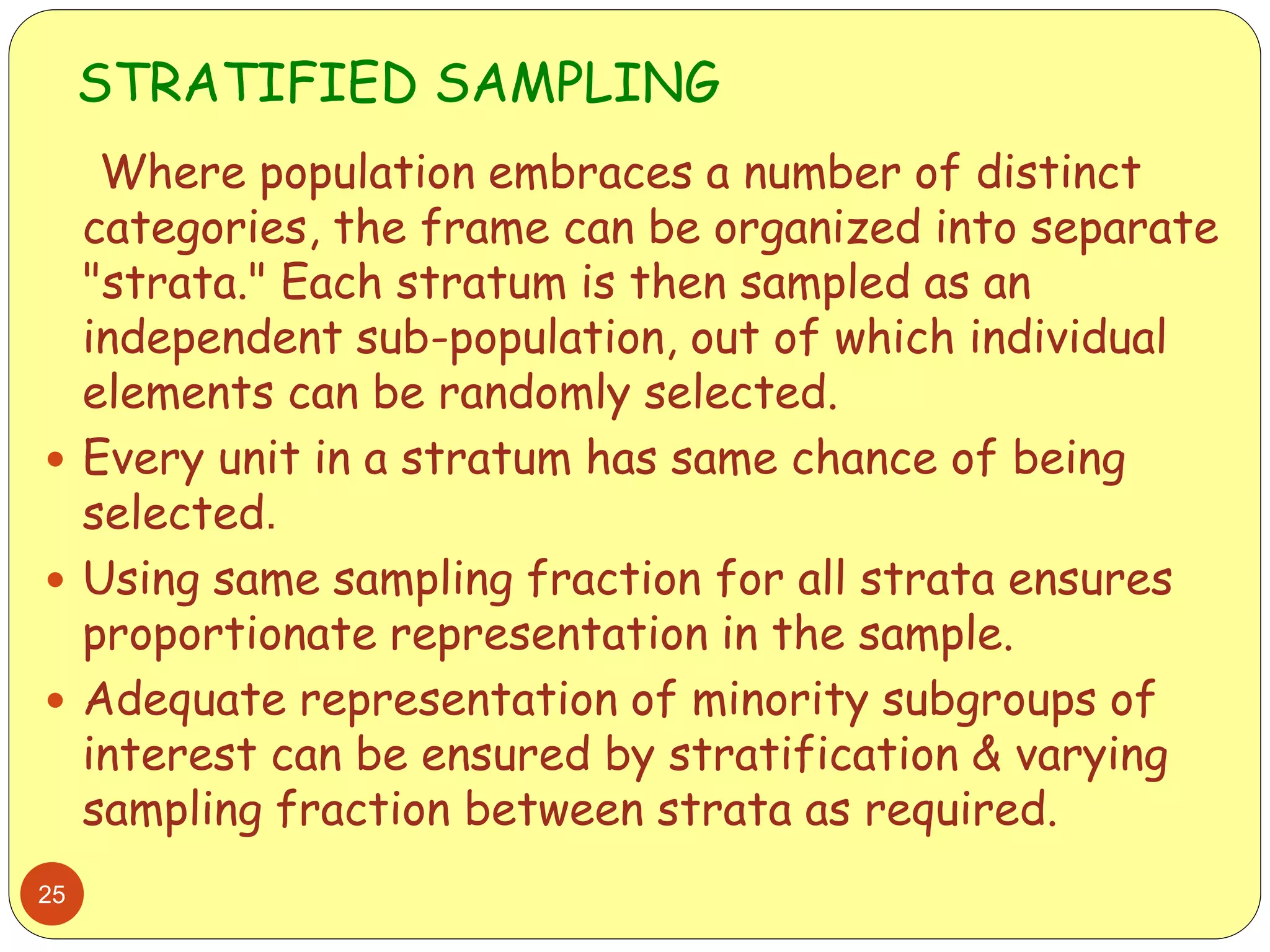
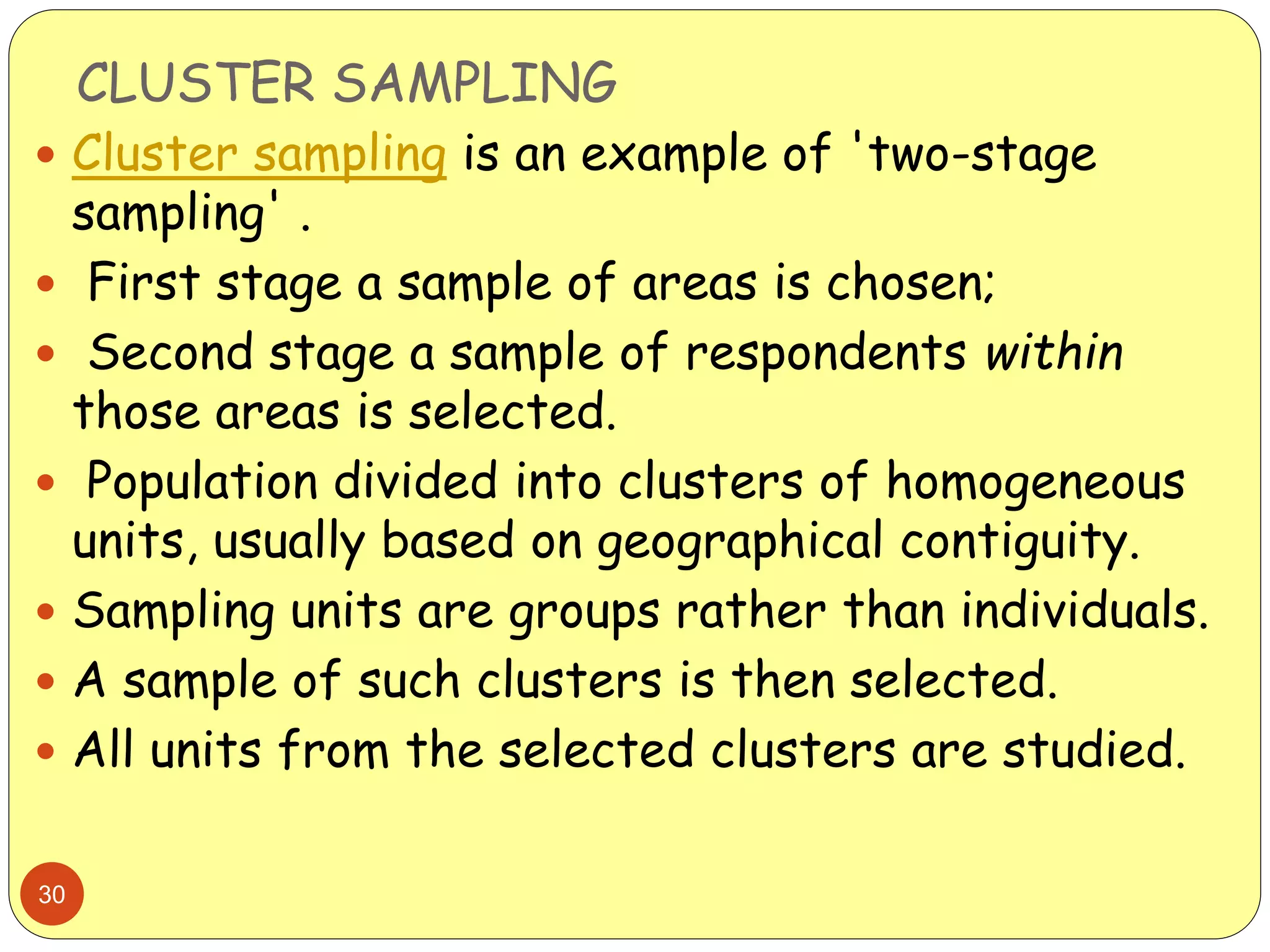
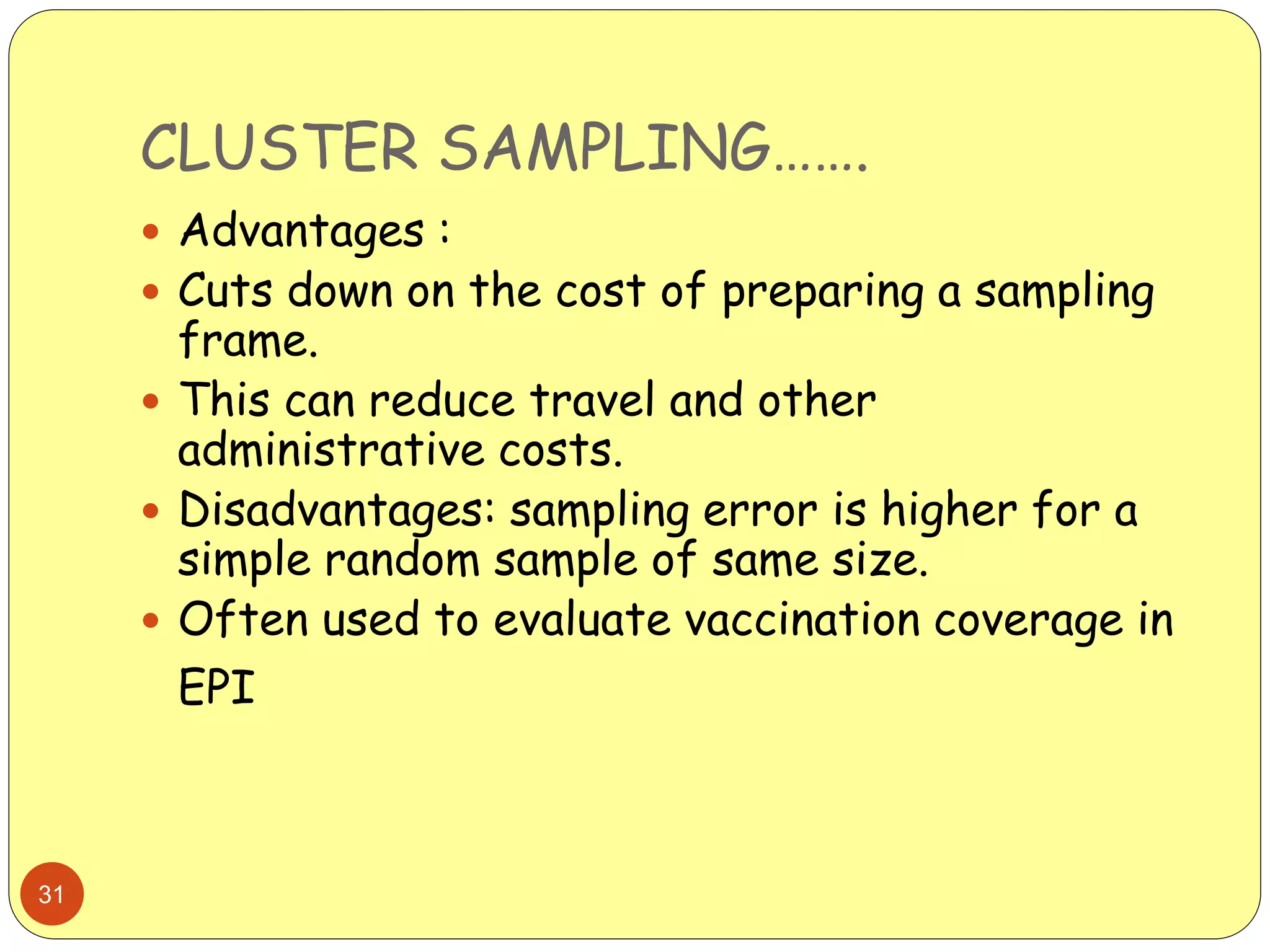
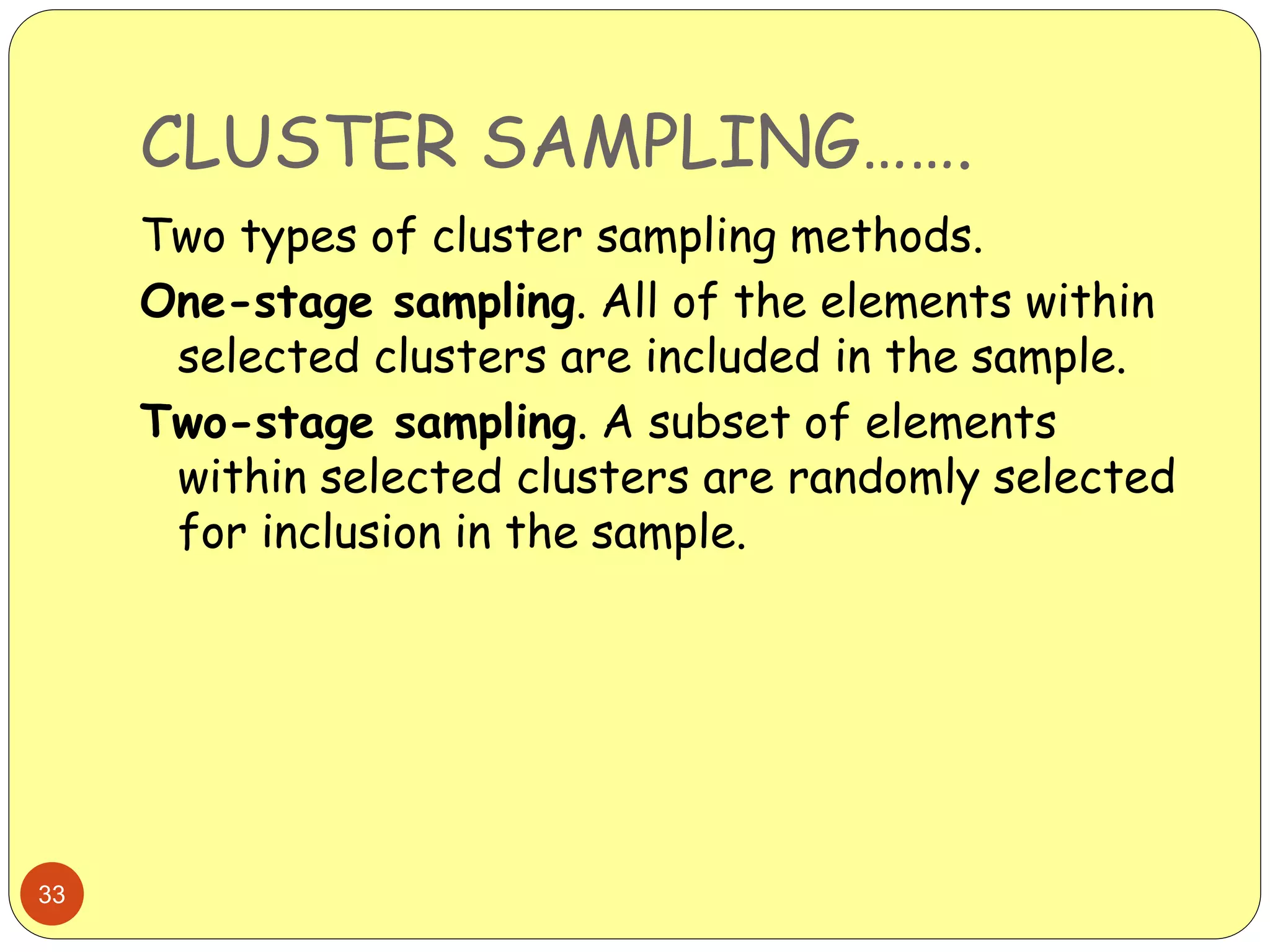
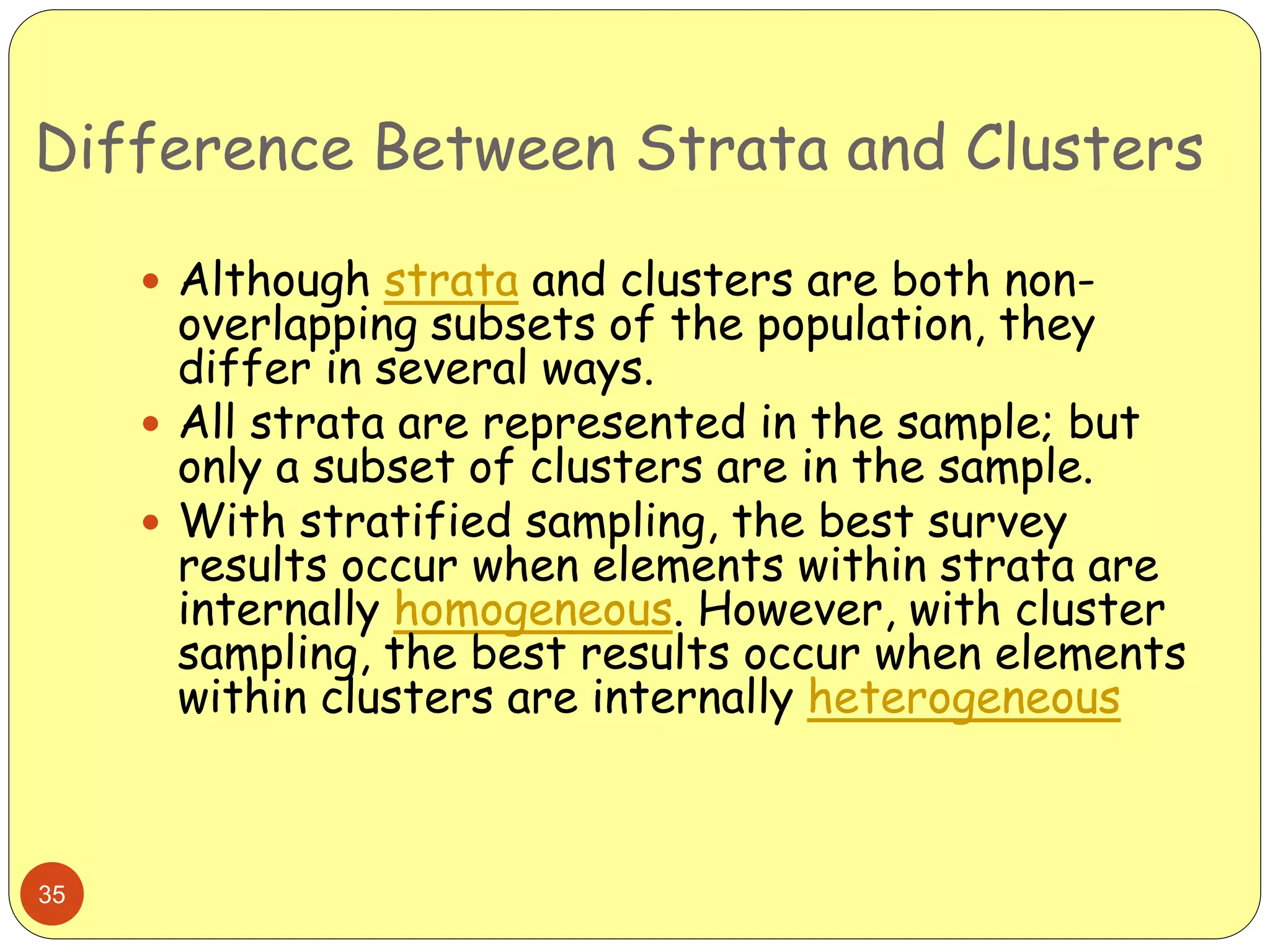
This document discusses various sampling methods used in research. It begins by defining key terms like population, sample, and sampling frame. It then explains the difference between probability sampling methods, like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling, and non-probability sampling methods, like convenience sampling. For each method, it provides details on how to implement the method and discusses their relative advantages and disadvantages. The goal is to help readers understand different approaches to drawing sample populations from a target population in a way that limits bias.