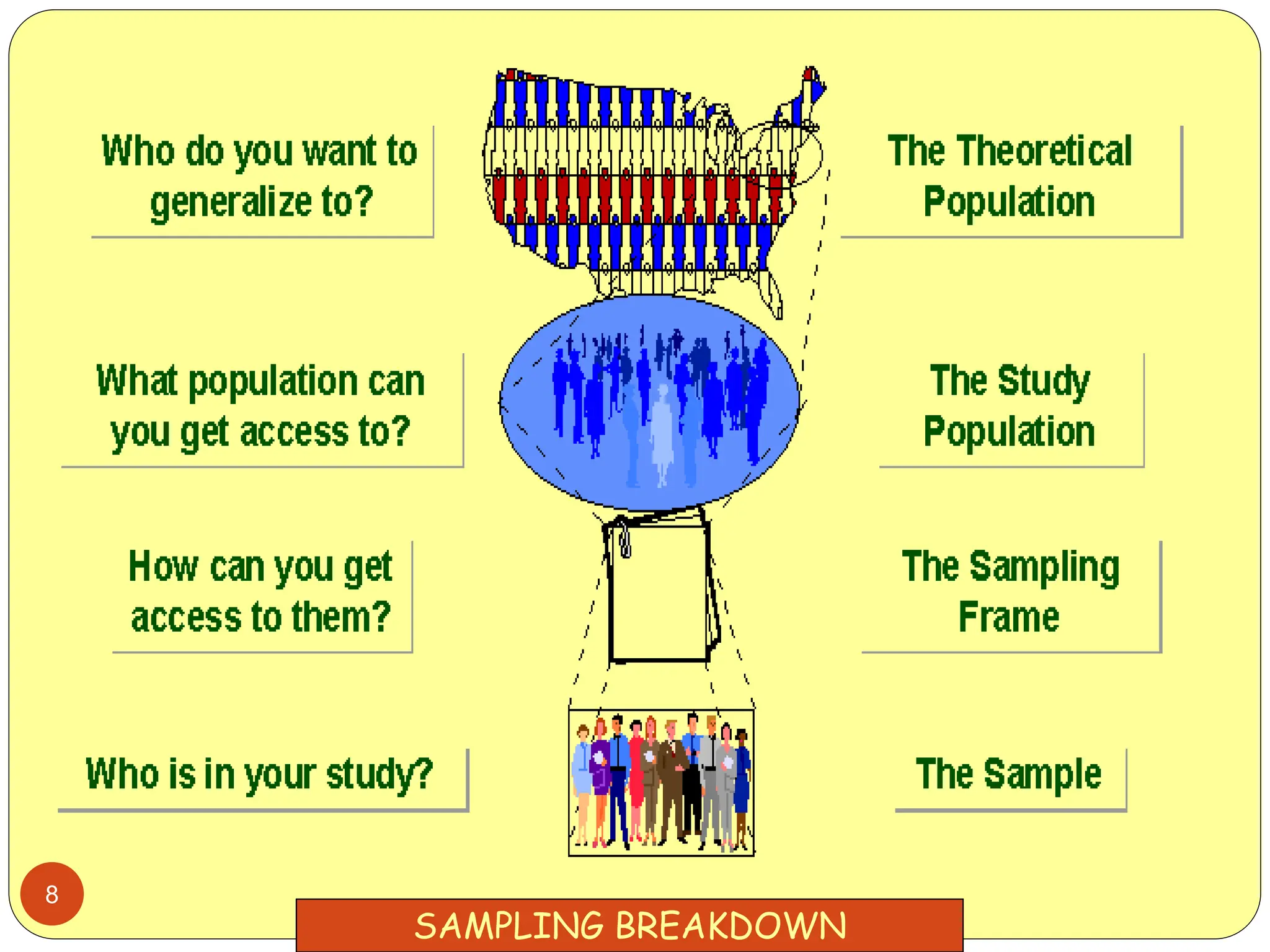
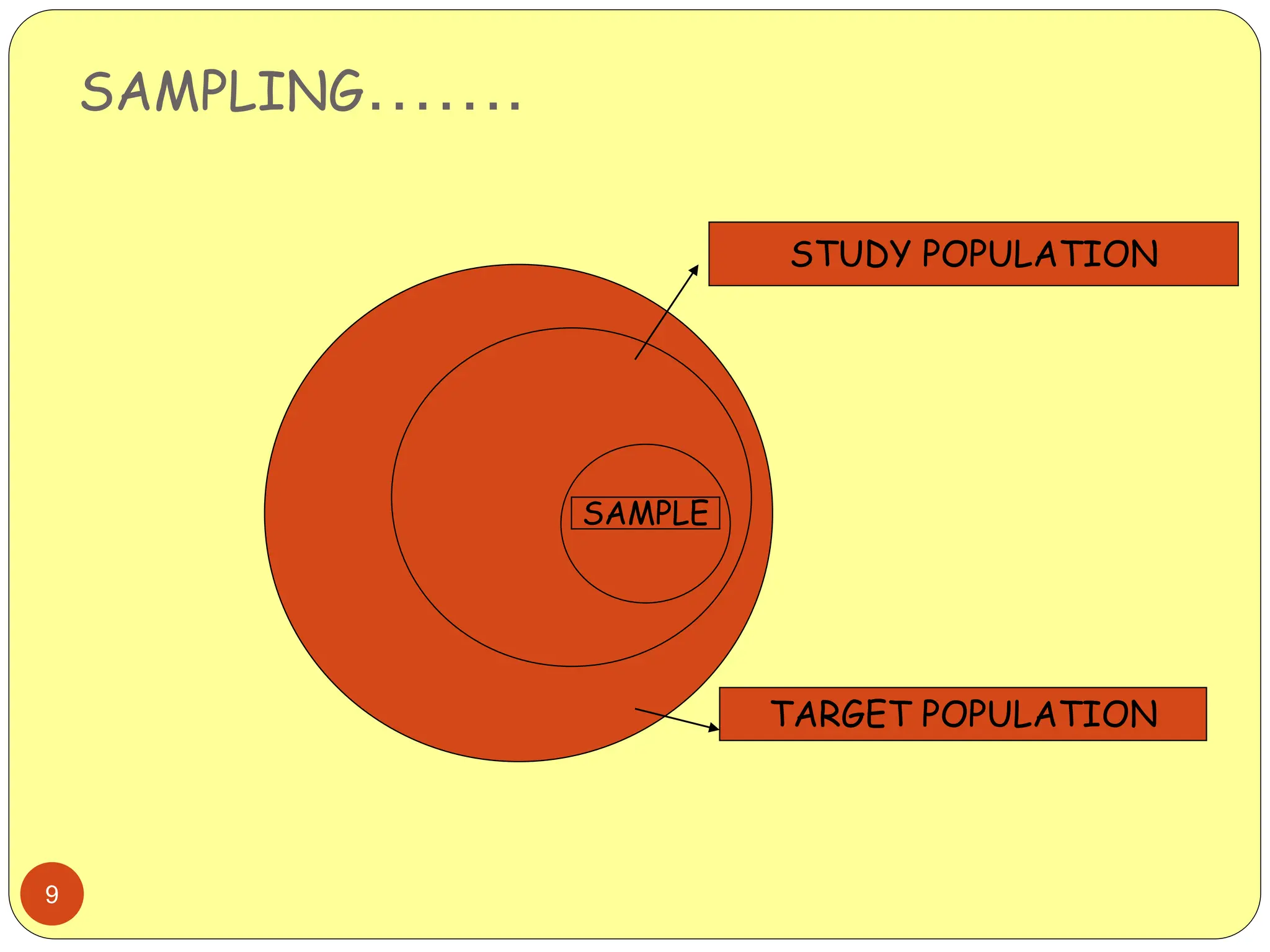
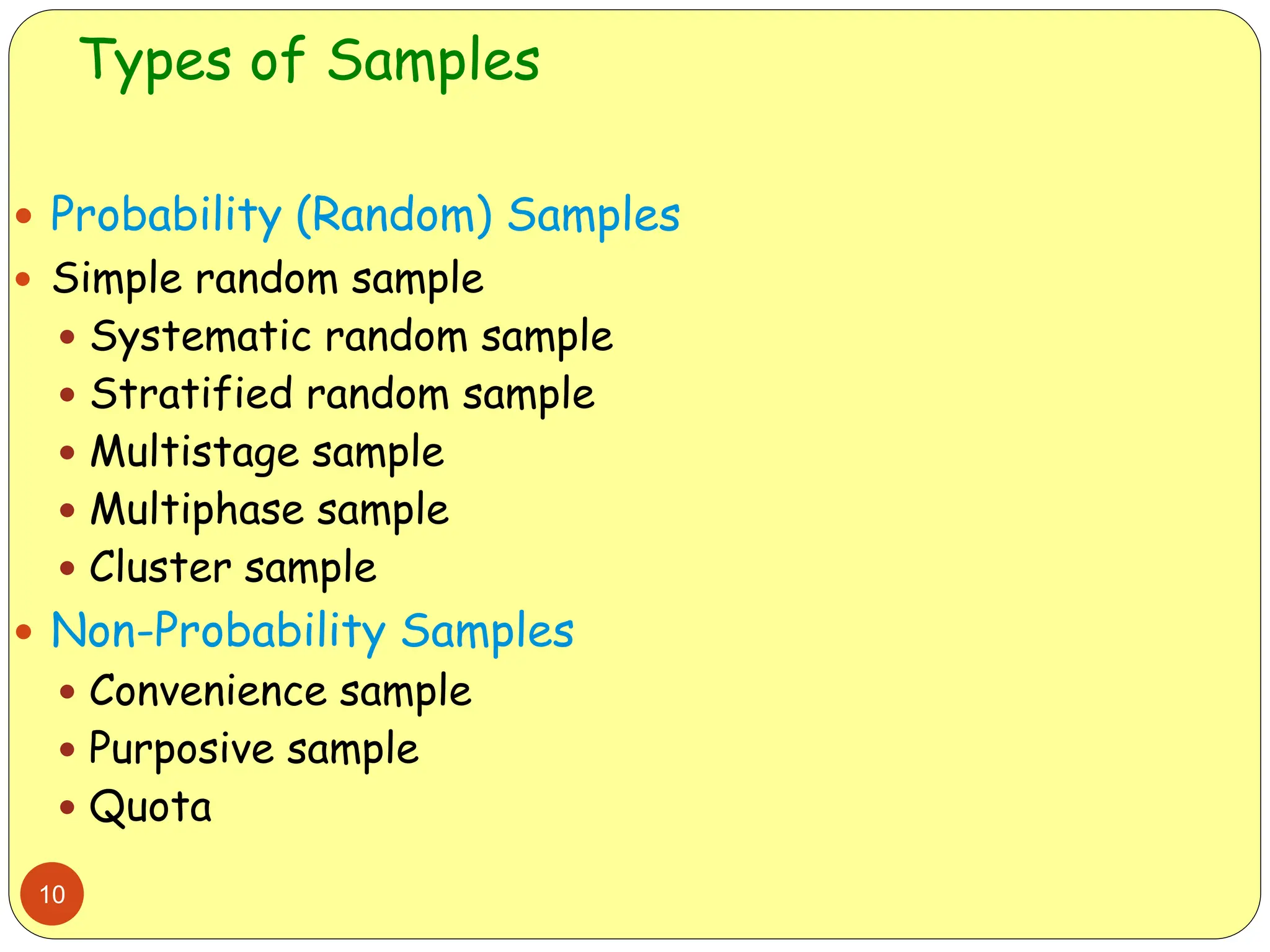
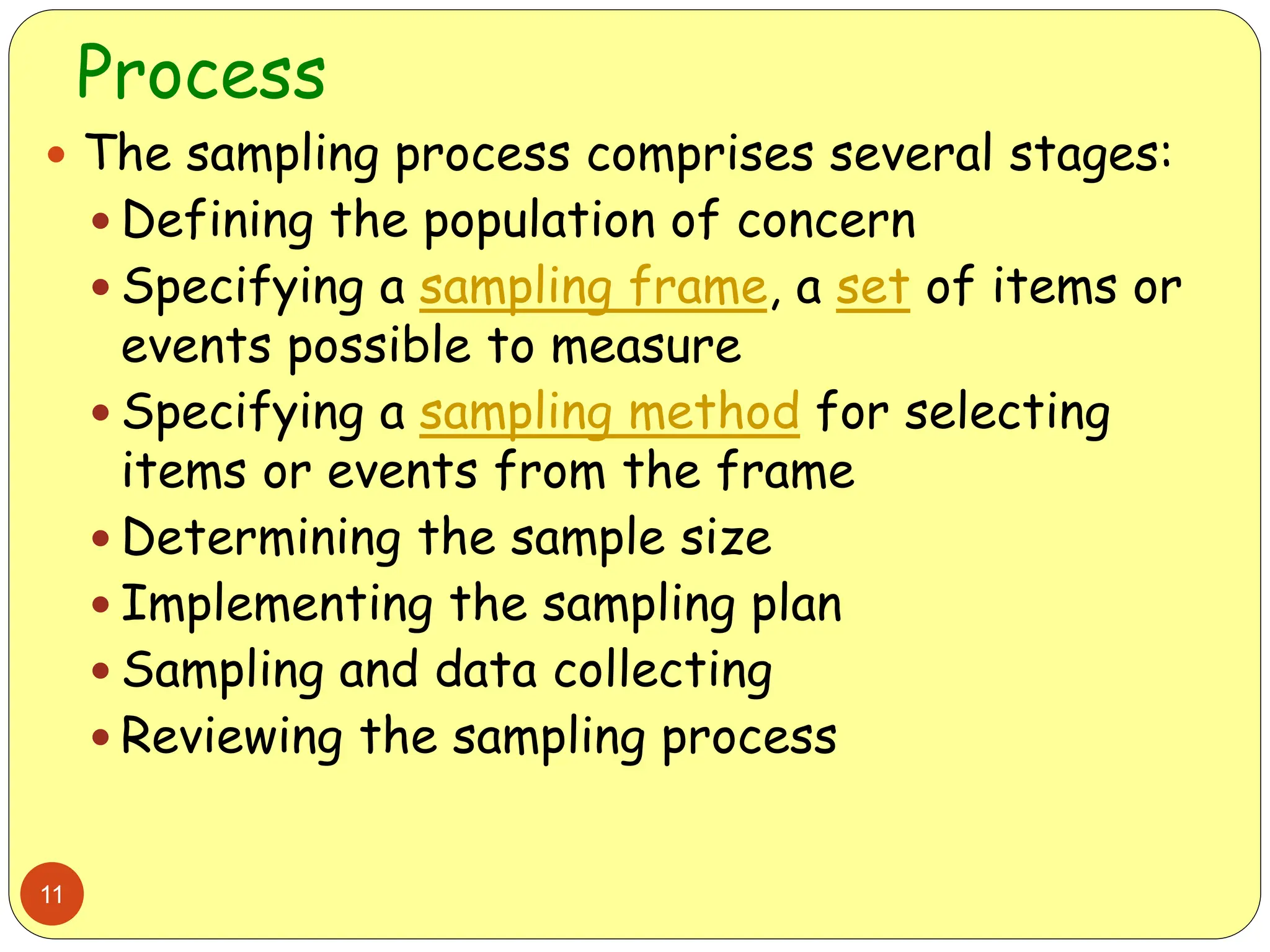
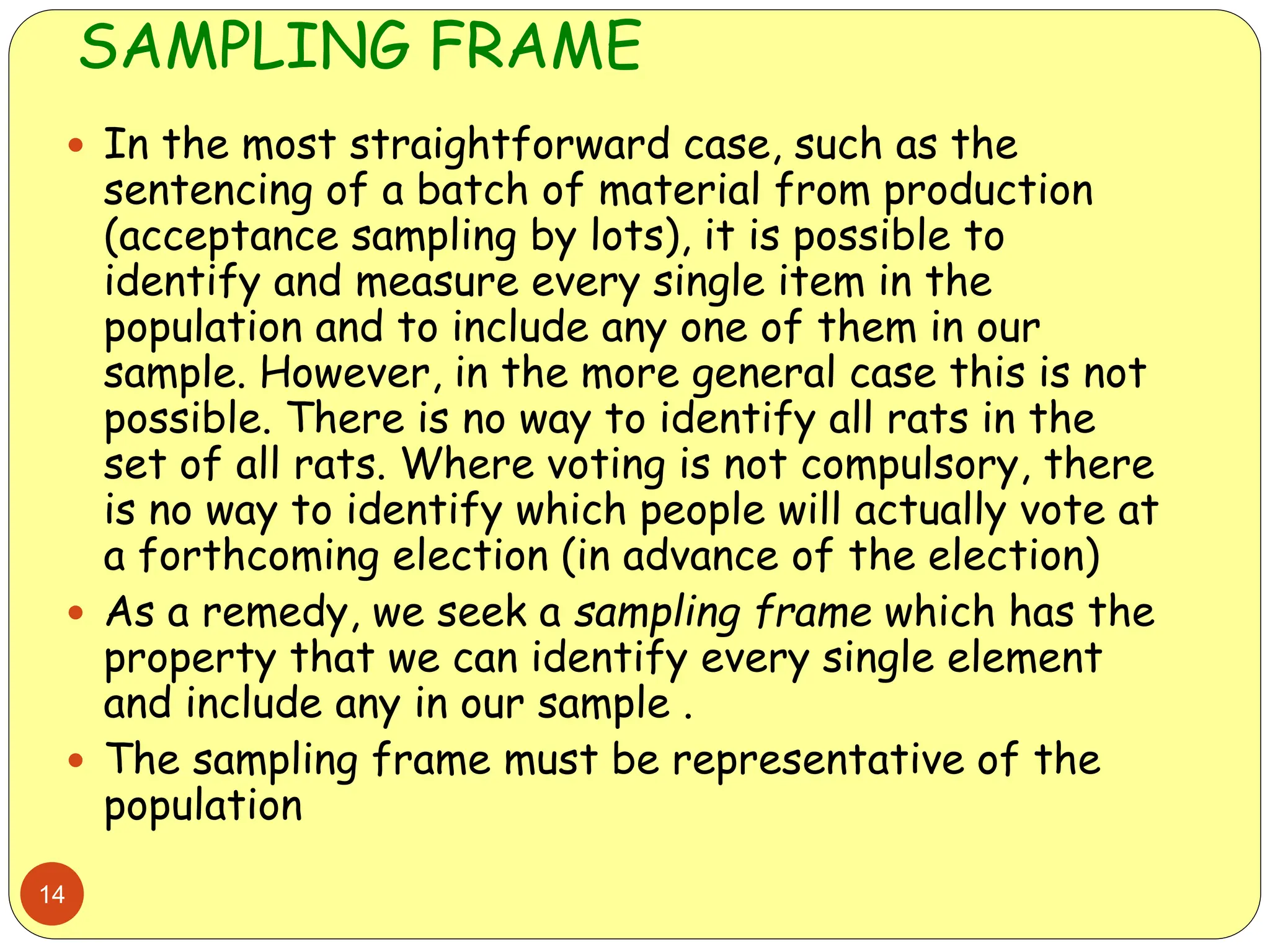
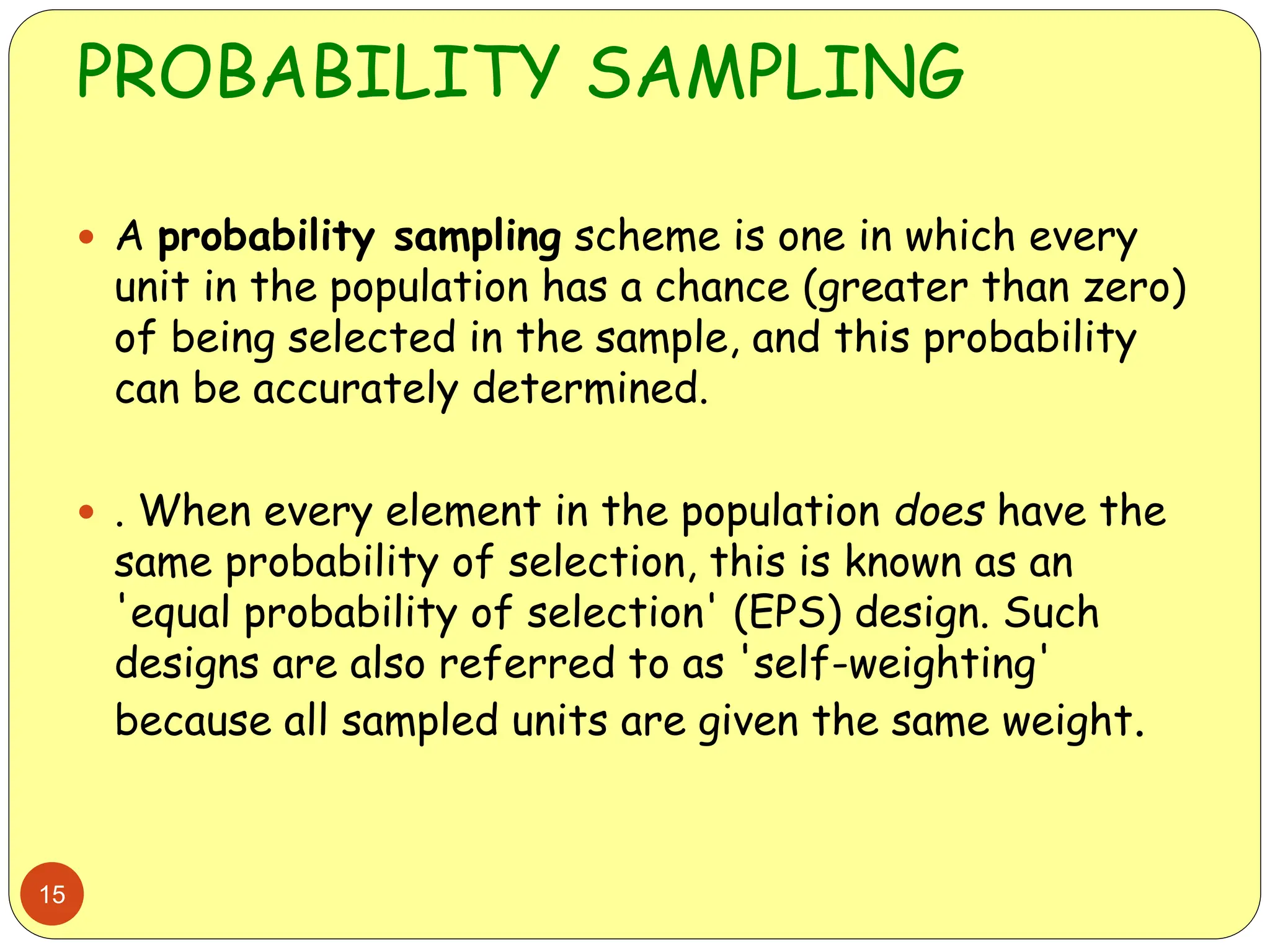
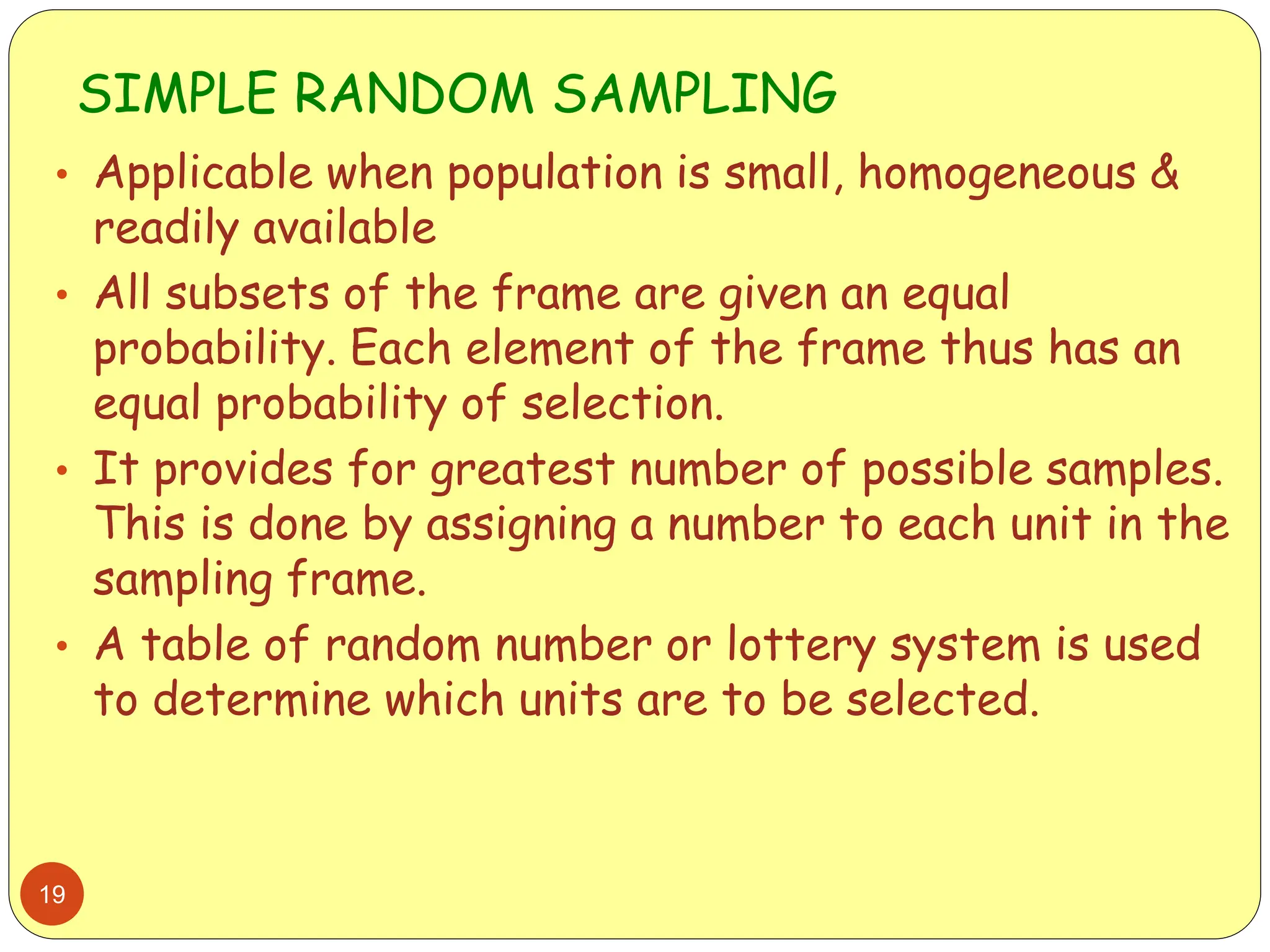
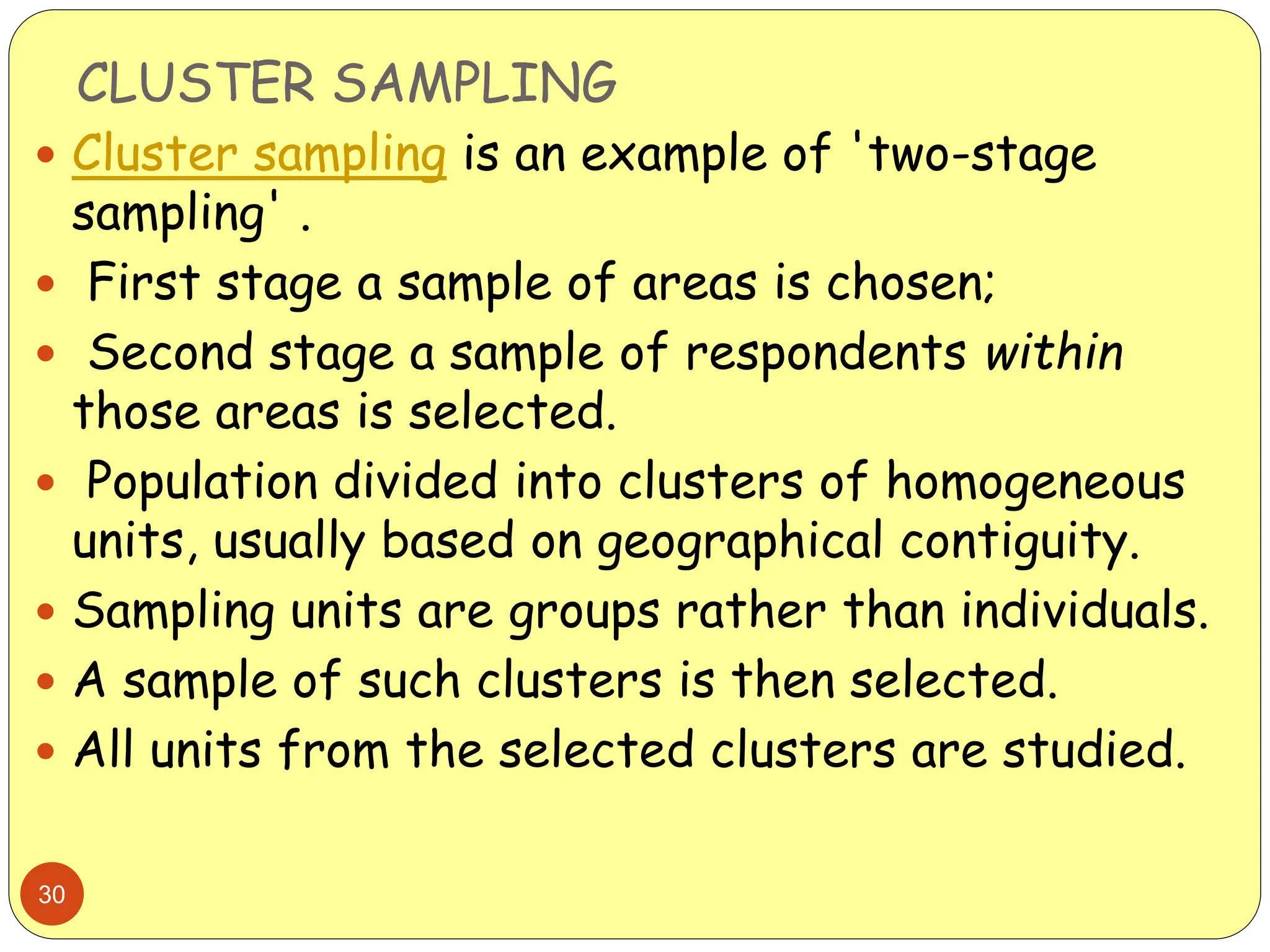
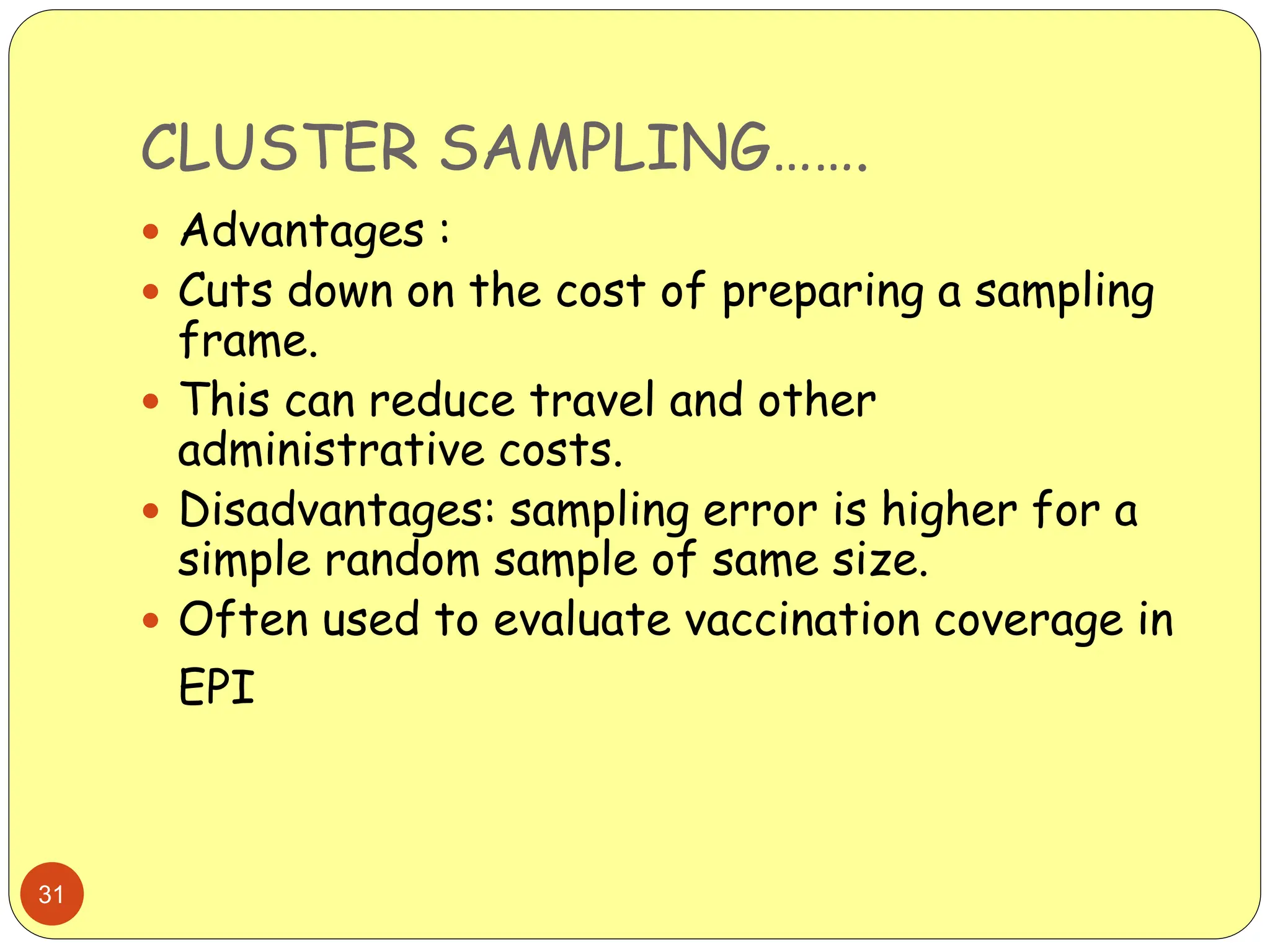
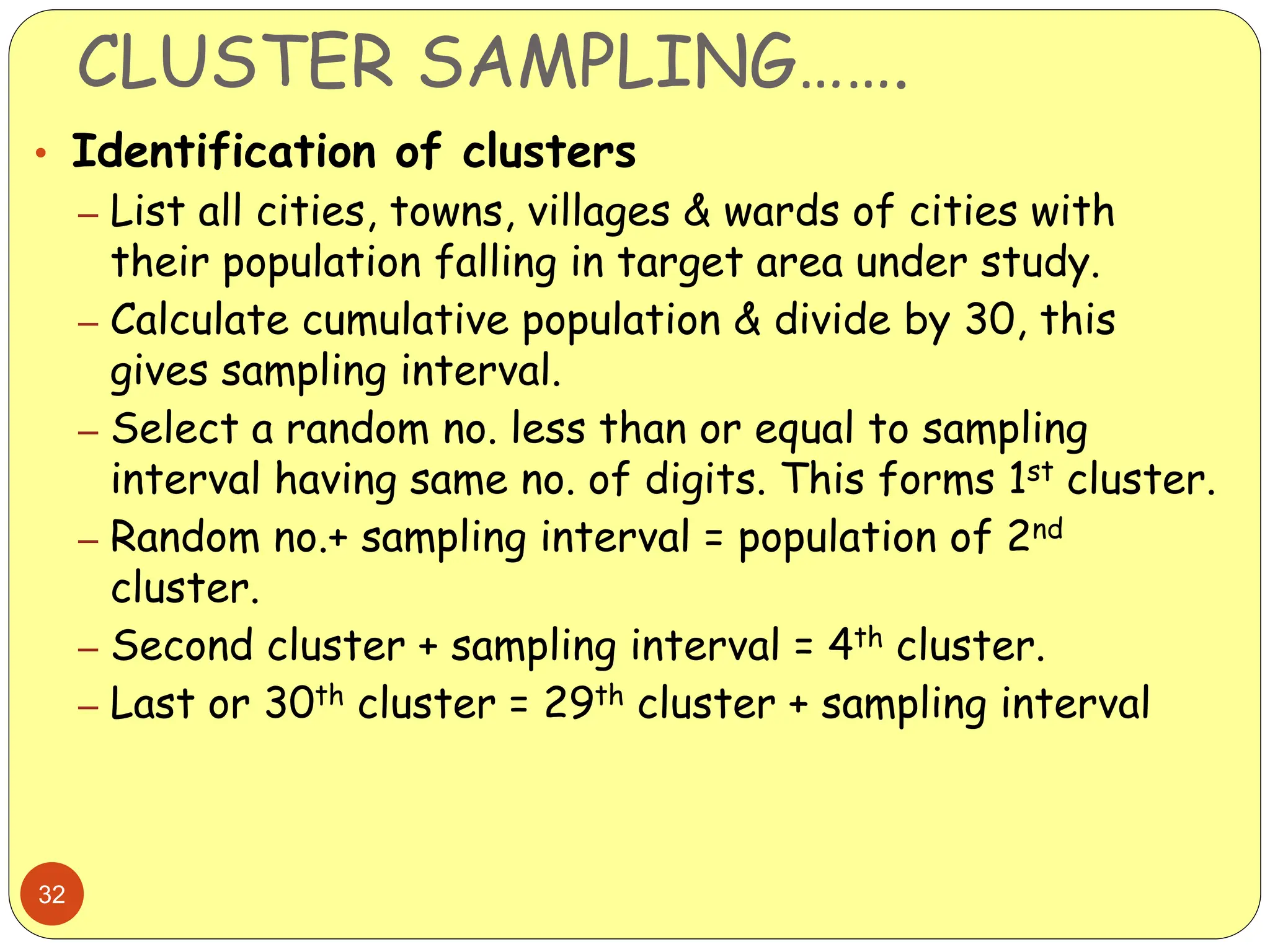
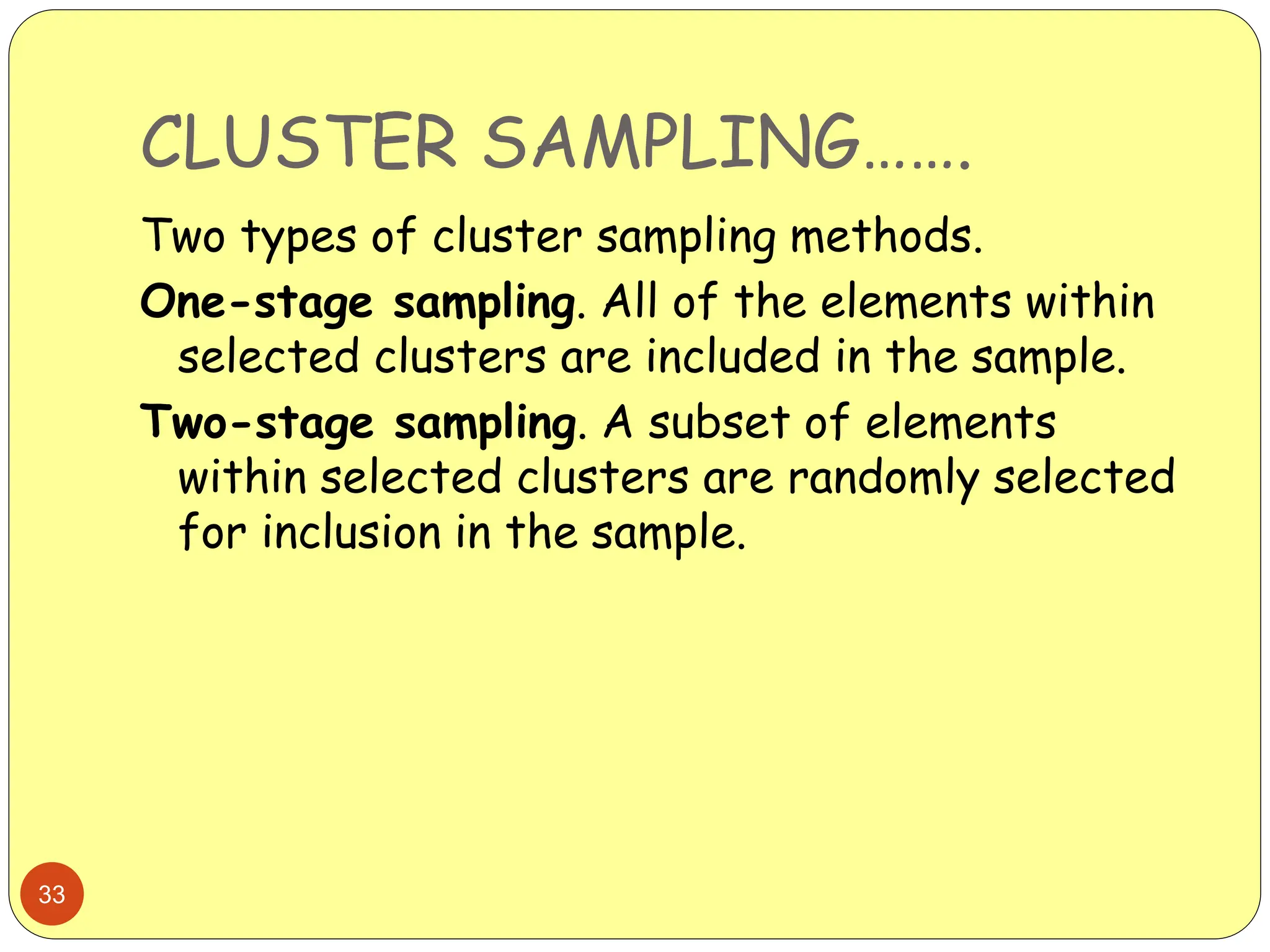
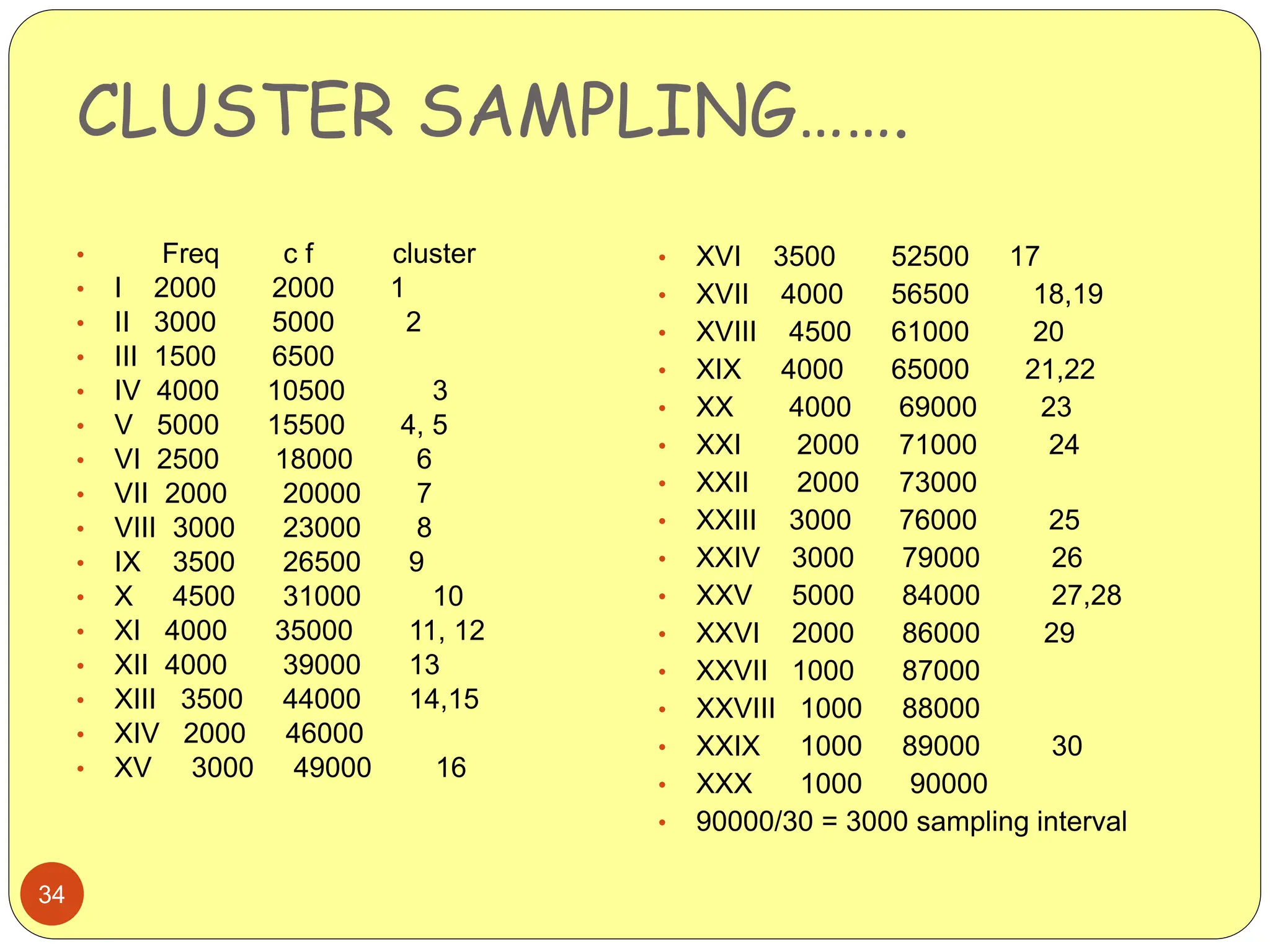
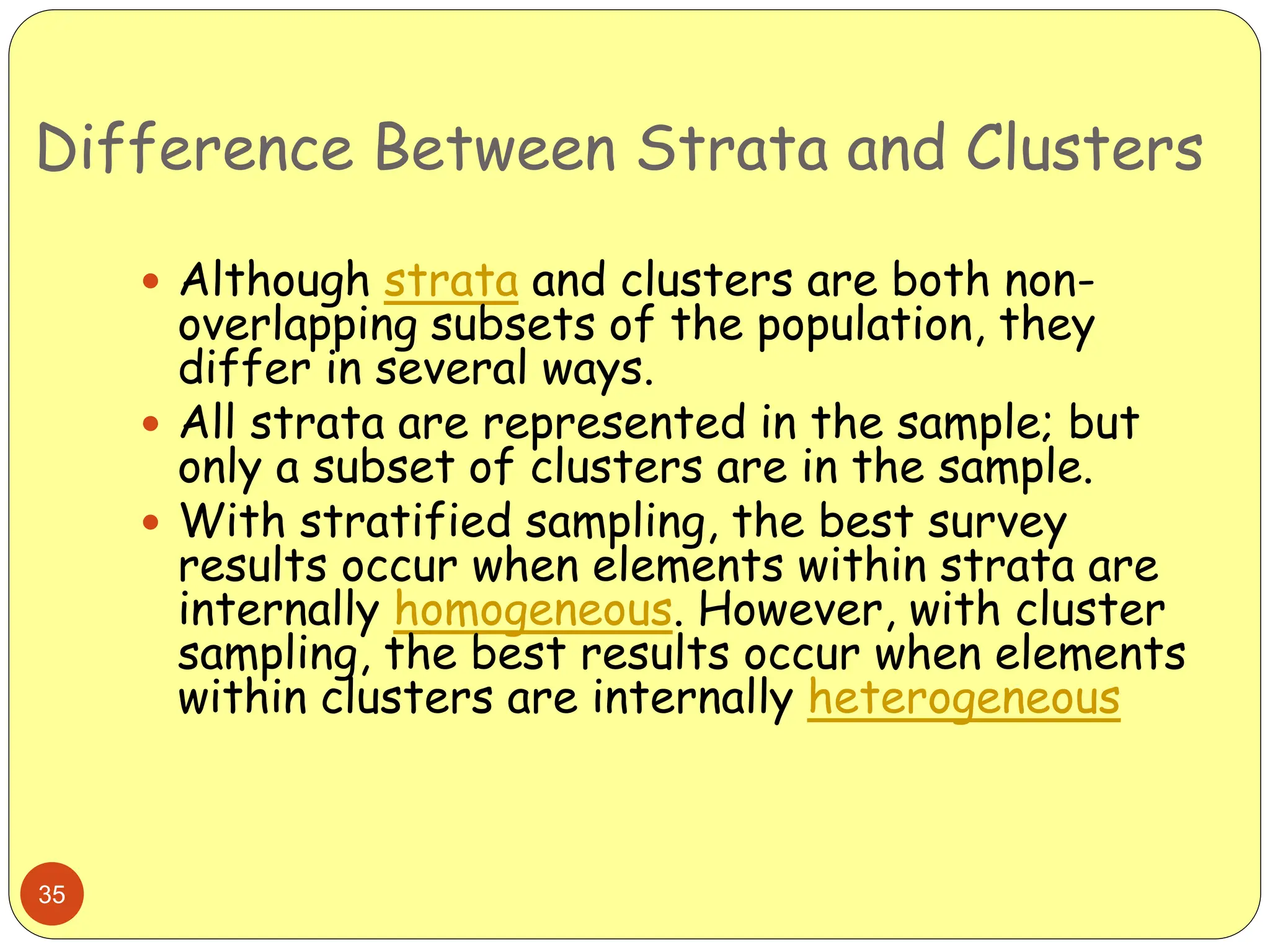
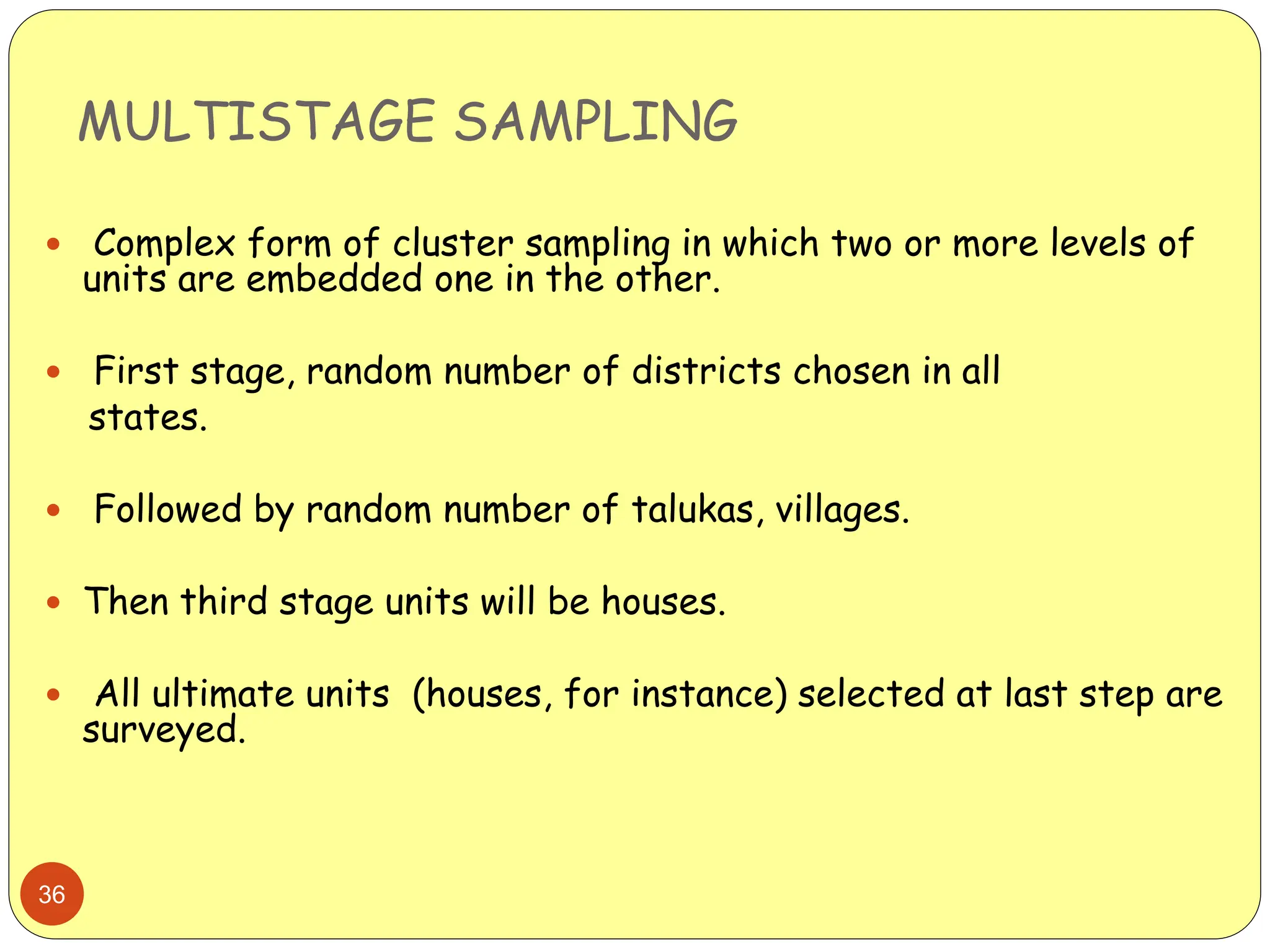
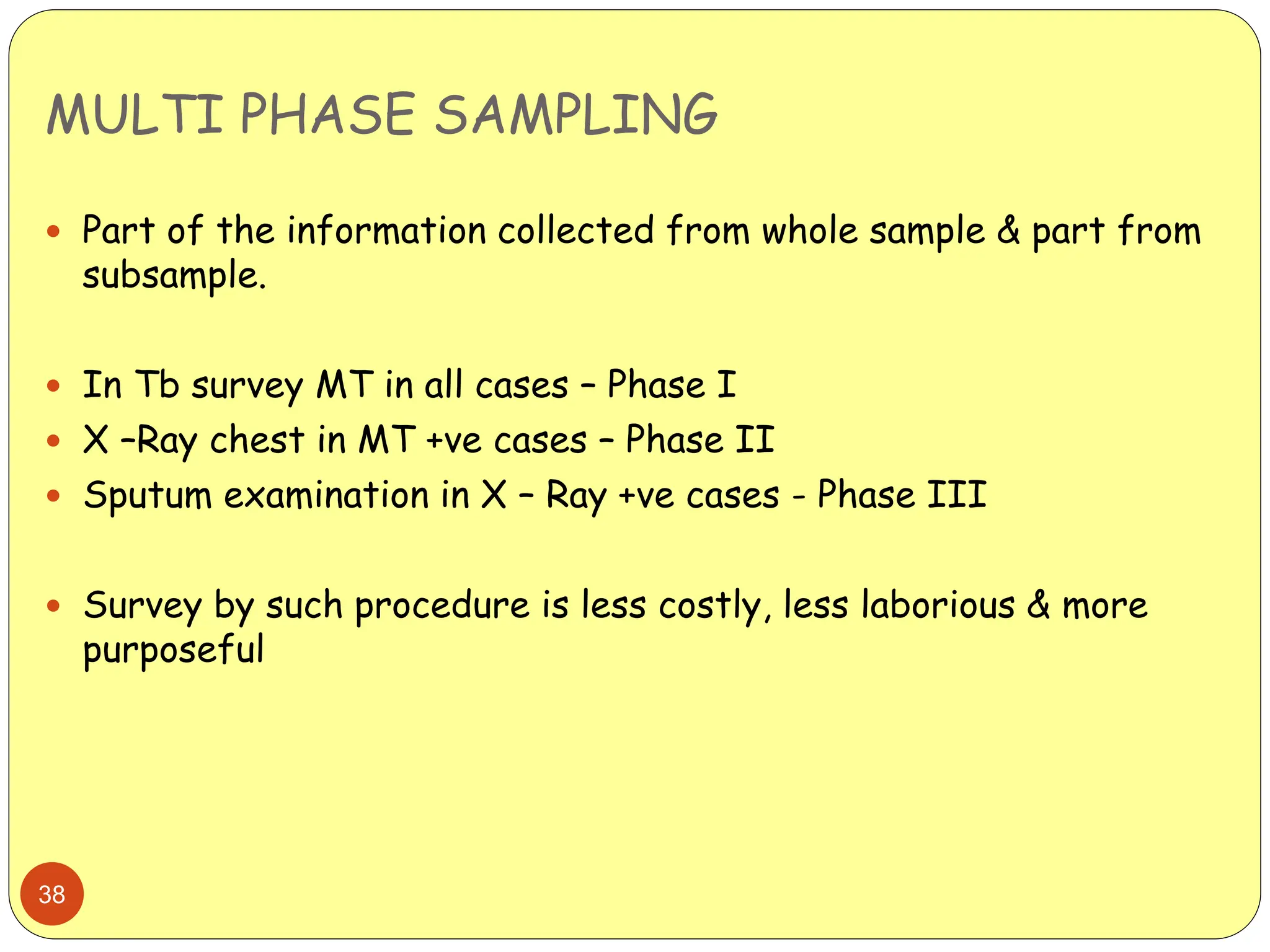
This document discusses different sampling methods used in research. It begins by defining sampling as selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole population. The document then covers various probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. It also discusses non-probability sampling and compares the advantages and disadvantages of different sampling techniques. Key factors that influence sample representativeness like sampling procedure, sample size, and response rate are also highlighted.