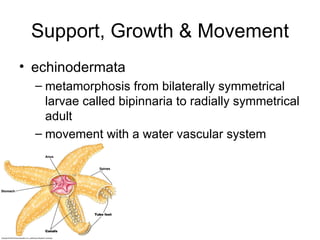
This document summarizes the circulation, support, growth, movement, neural control, and sensory organs of various invertebrate phyla. It describes that mollusks have open or closed circulatory systems, annelids have closed circulatory systems with aortic arches, and arthropods and echinoderms have a variety of circulatory approaches. Support and movement is enabled through muscles, appendages, shells, and water vascular systems. Neural control systems include nerve cords, ganglia, sensory hairs and various eye structures.