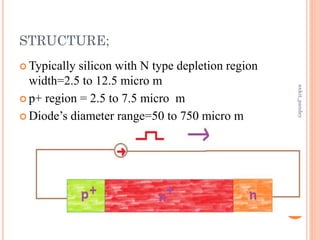
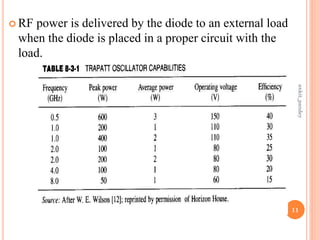
The document discusses the TRAPATT diode, which is a type of p-n junction diode that generates microwaves. It operates by forming a trapped plasma within the junction region when a high electric field propagates through. Key points:
- It was first reported in 1967 and can generate power over 1 kW at frequencies up to 50 GHz with efficiencies up to 75%
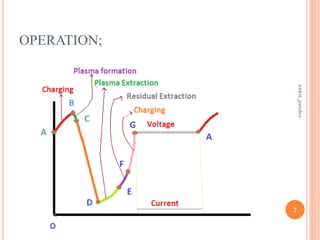
- It operates by inducing avalanche breakdown to generate a dense plasma of electrons and holes within the depletion region, which becomes trapped and oscillates the voltage and current
- Applications include low power Doppler radars, radio altimeters, and radar transmitters due to its pulsed operation capabilities between 3-50 GHz