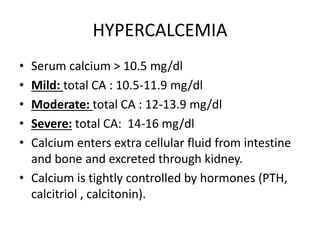
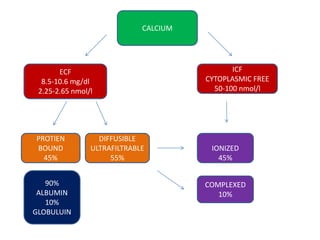
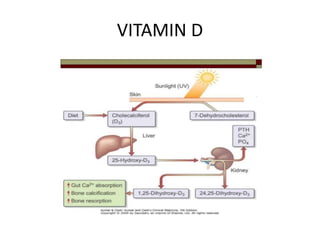
This document discusses hypercalcemia, which is defined as a serum calcium level above 10.5 mg/dl. It outlines the various causes of hypercalcemia including primary hyperparathyroidism, certain cancers, granulomatous diseases, and certain medications. The clinical presentation of hypercalcemia can include symptoms affecting the stones, bones, abdominal organs, psyche, and other nonspecific symptoms. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure calcium and PTH levels along with imaging tests. Treatment focuses on rehydration, bisphosphonates, glucocorticoids, calcitonin, surgery, and dialysis depending on the severity and underlying cause of the hypercalcemia.