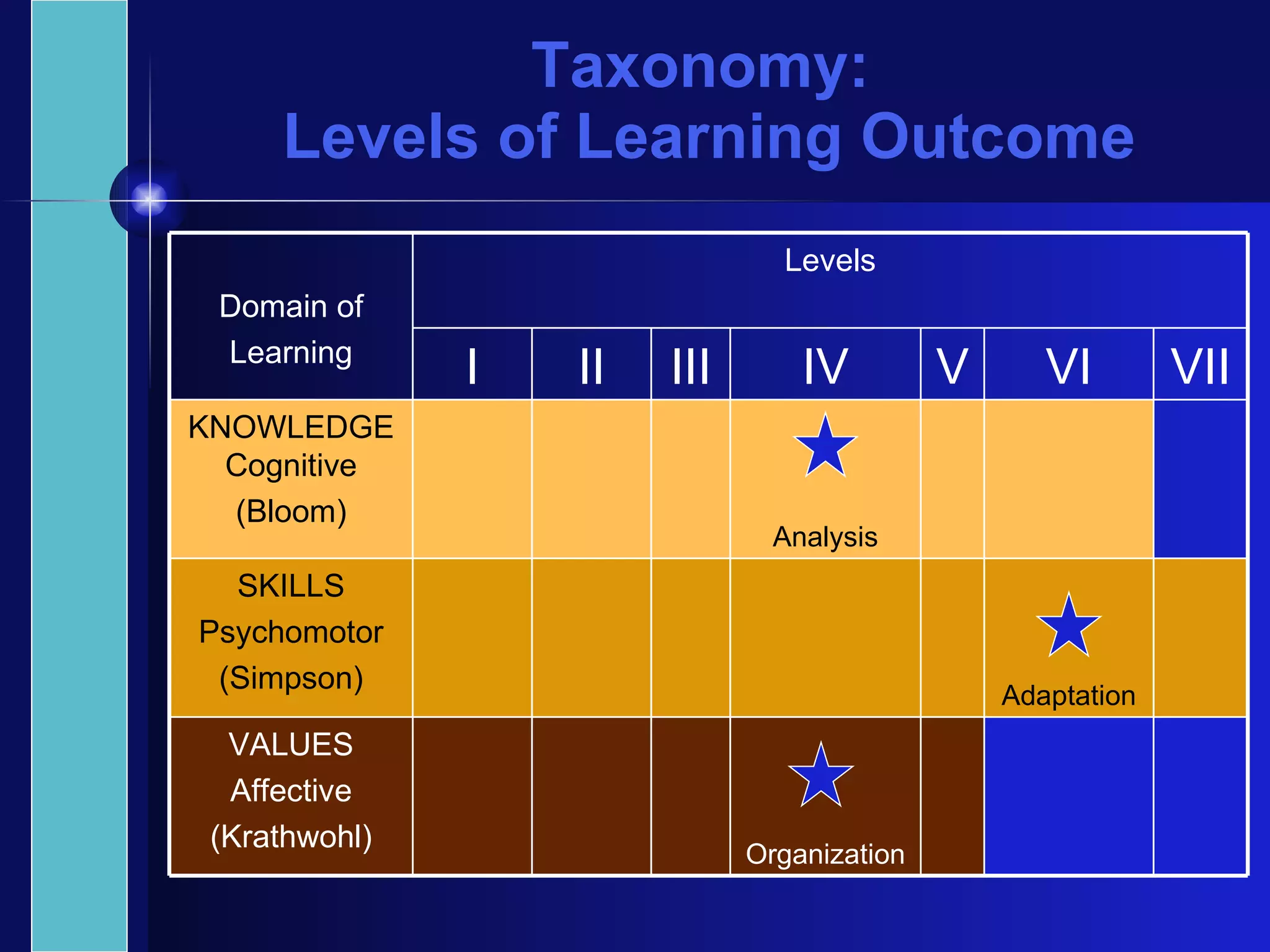
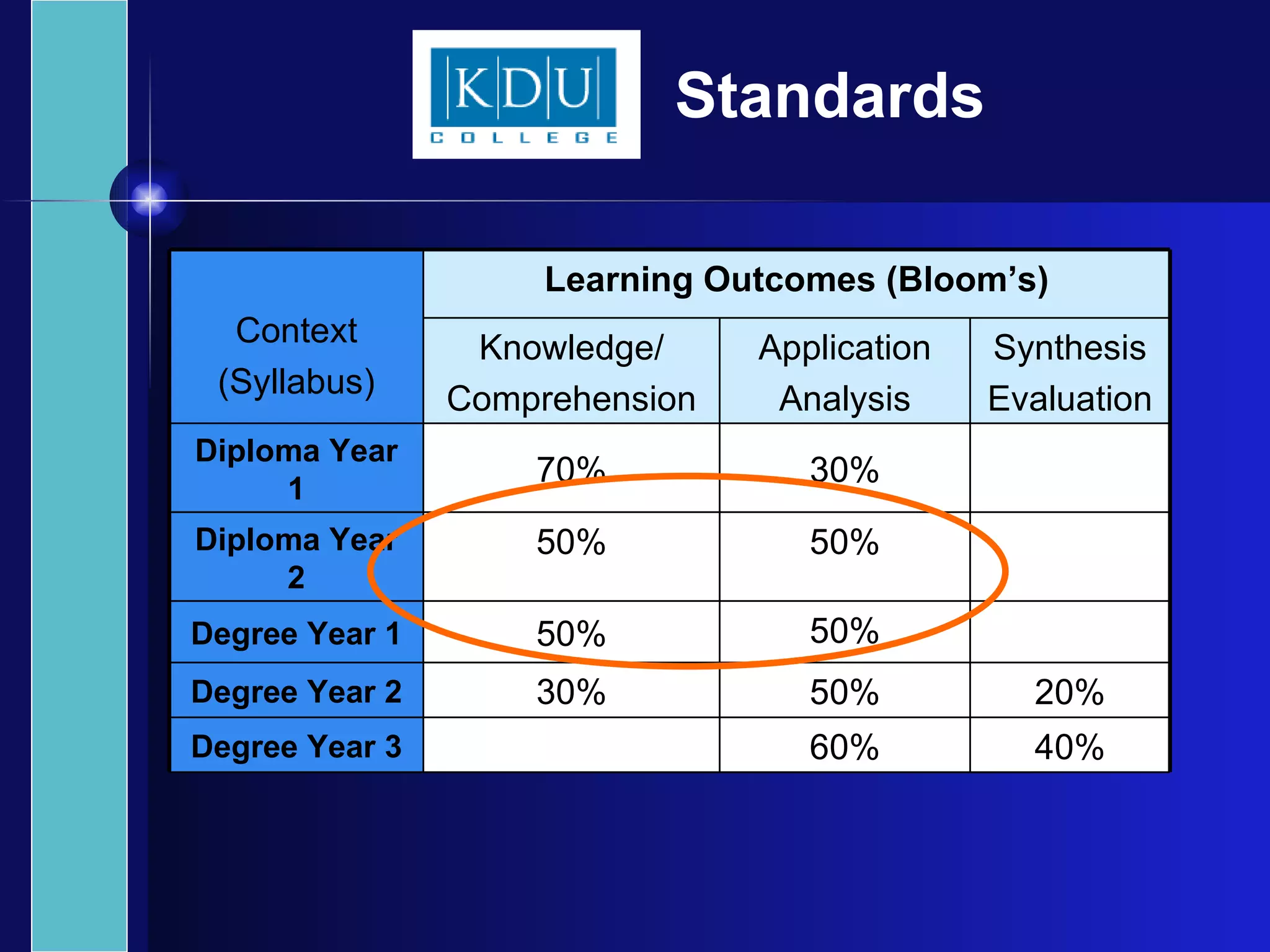
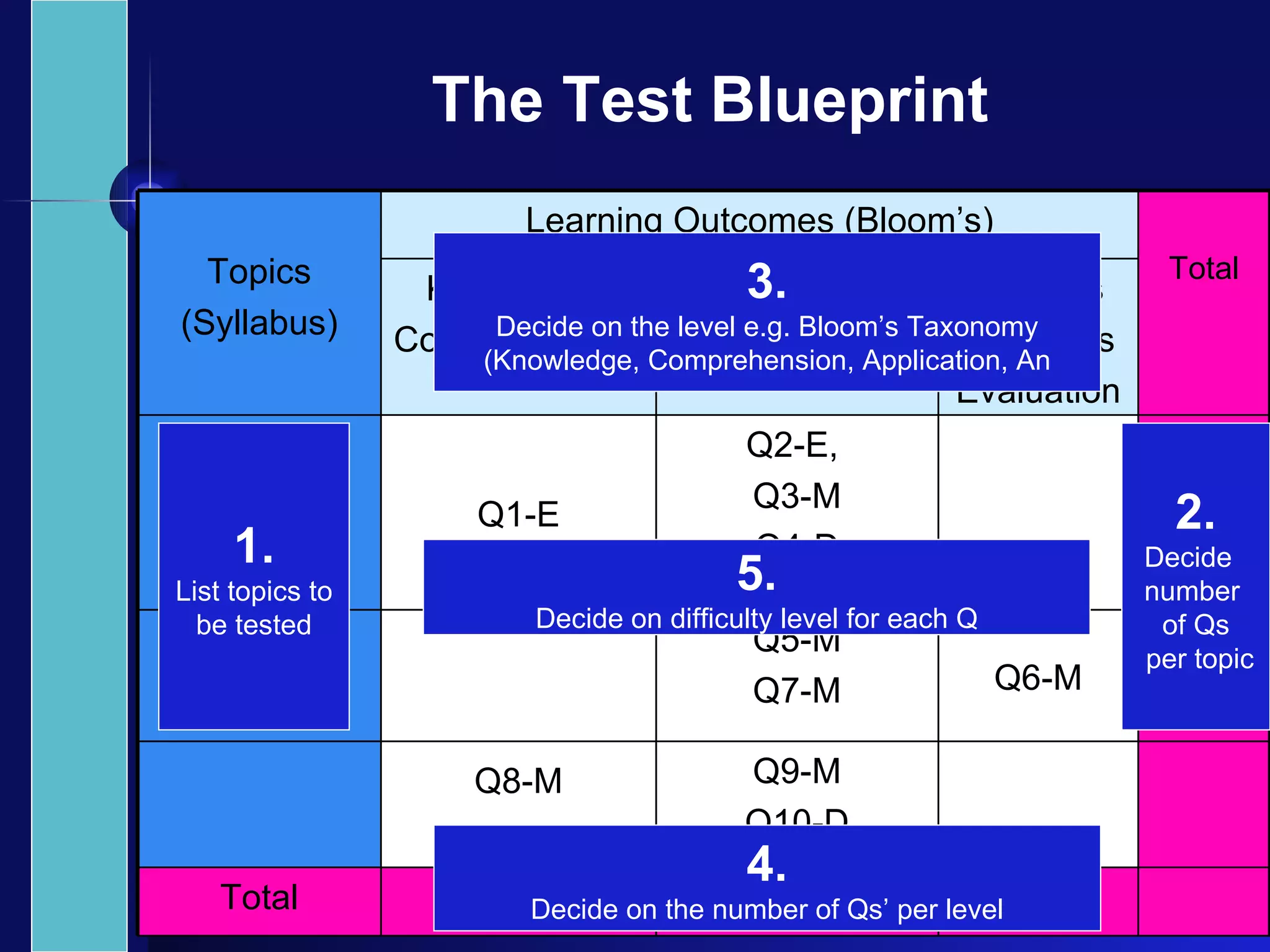
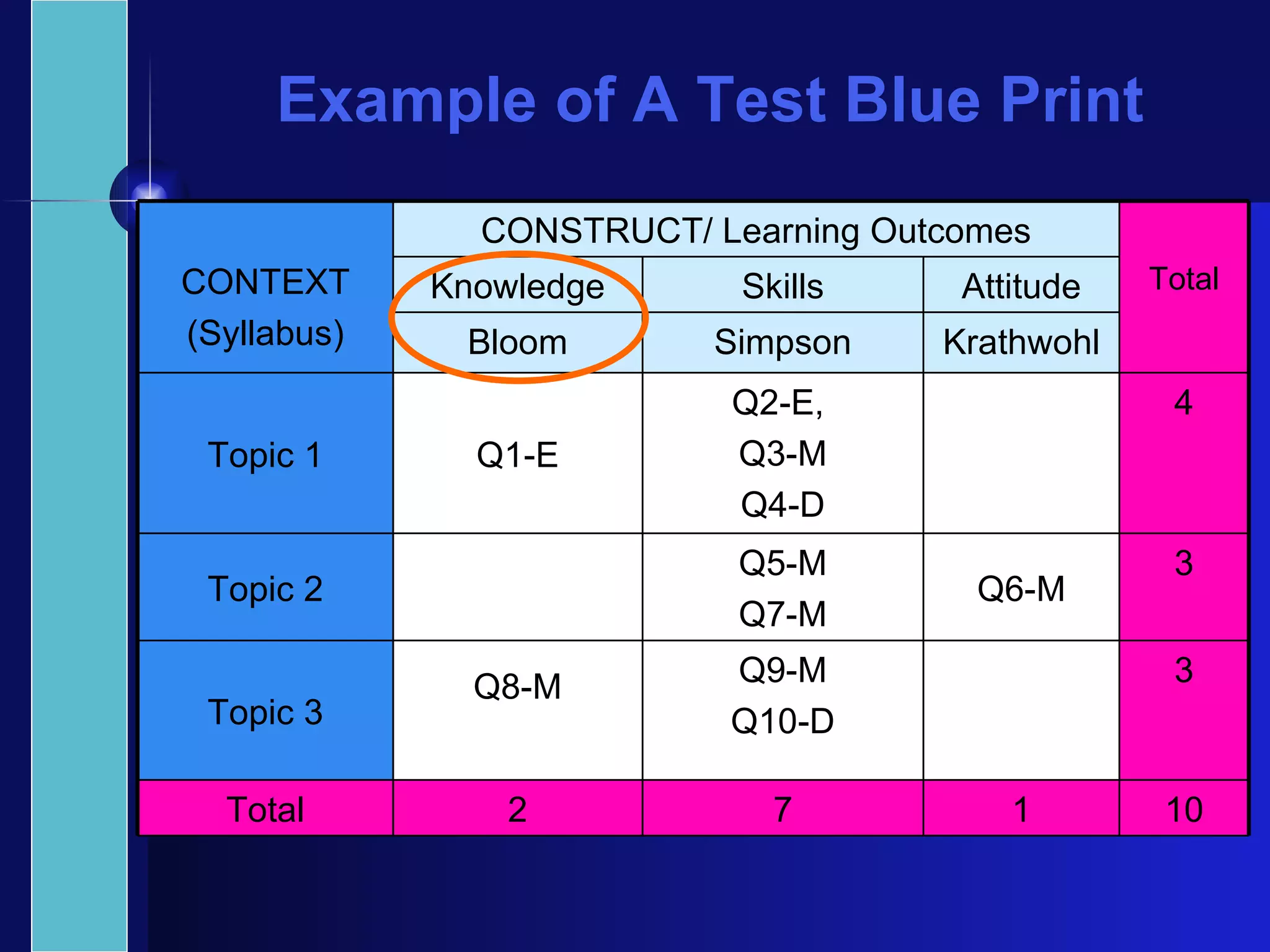
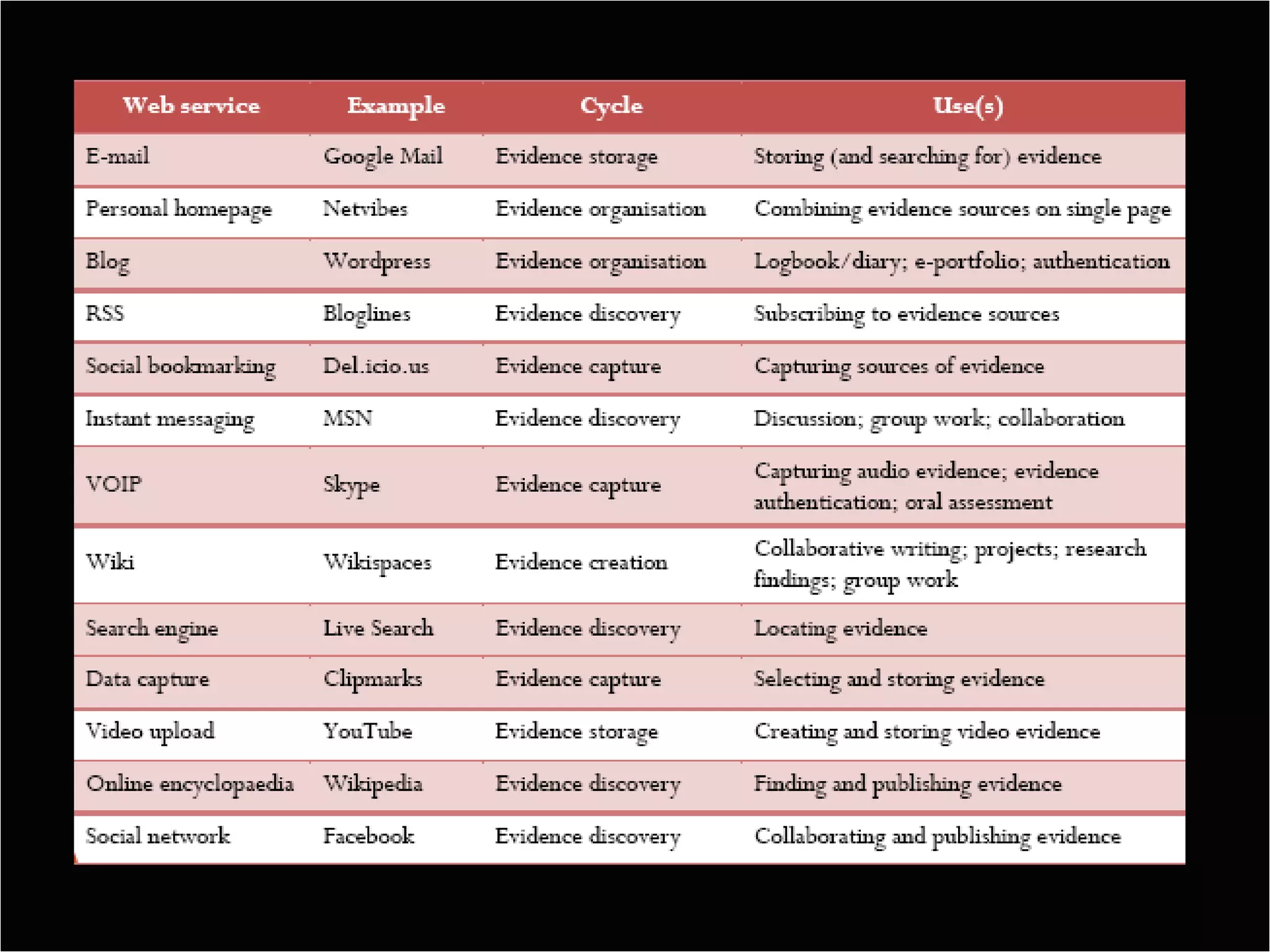
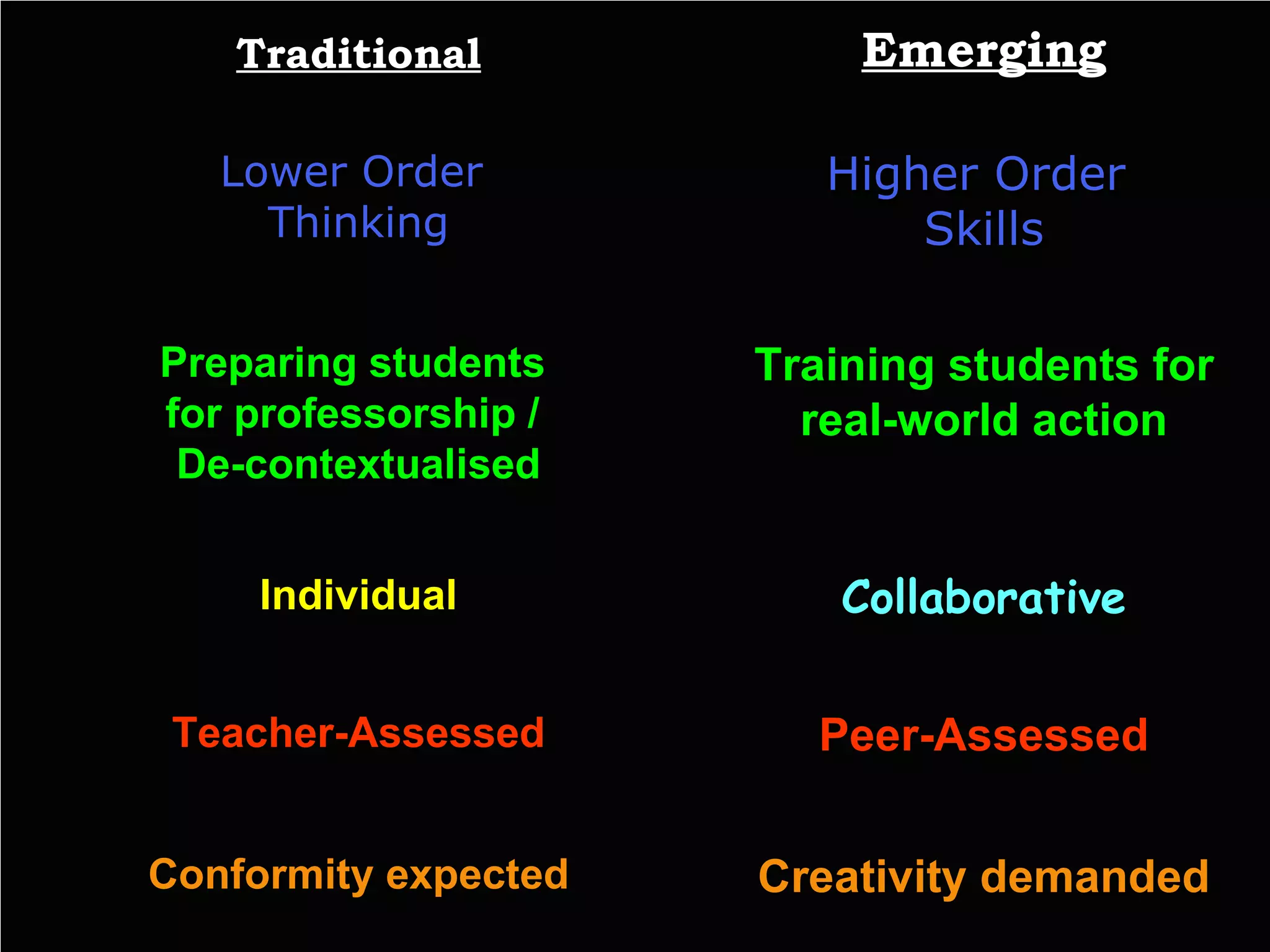
The document discusses principles of effective assessment, including ensuring validity through accurate representation of course content and appropriate difficulty levels, and reliability through consistent question formats, language, and marking schemes. It also covers types of assessments, levels of learning outcomes, and how to develop an assessment plan and test blueprint to align assessments with learning objectives and standards. The goal is to design 21st century assessments that evaluate higher-order skills through real-world, collaborative tasks rather than isolated performances.