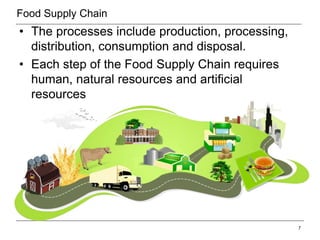
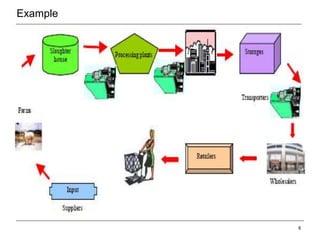
This document provides an overview of the global food supply chain. It discusses key aspects of food logistics including supply chain management, food categories, warehousing, processing and packaging, transportation, cold chain management, and the use of technology. Maintaining proper temperatures is essential throughout the supply chain to preserve food freshness. Transportation requires an unbroken cold chain using refrigeration and temperature monitoring. Technology helps manage operations and track food from farm to table.