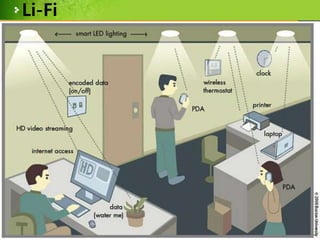
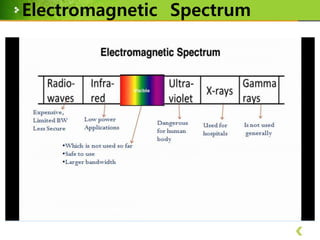
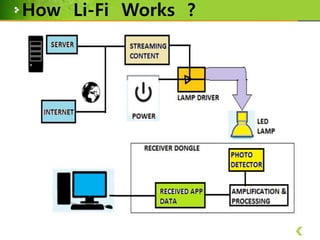
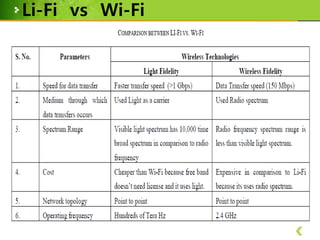
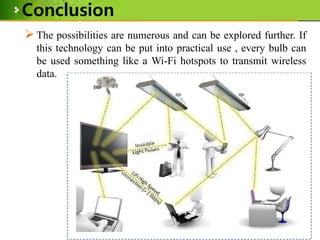
This document provides an overview of Li-Fi technology through a presentation on the topic. It discusses the history of Li-Fi, how it works by transmitting data through LED light, its advantages over Wi-Fi such as higher bandwidth and more secure communication through visible light. Example applications are given such as using traffic lights and street lamps to transmit data. Challenges for Li-Fi are also noted, such as the need for line of sight transmission and potential interference from other light sources.