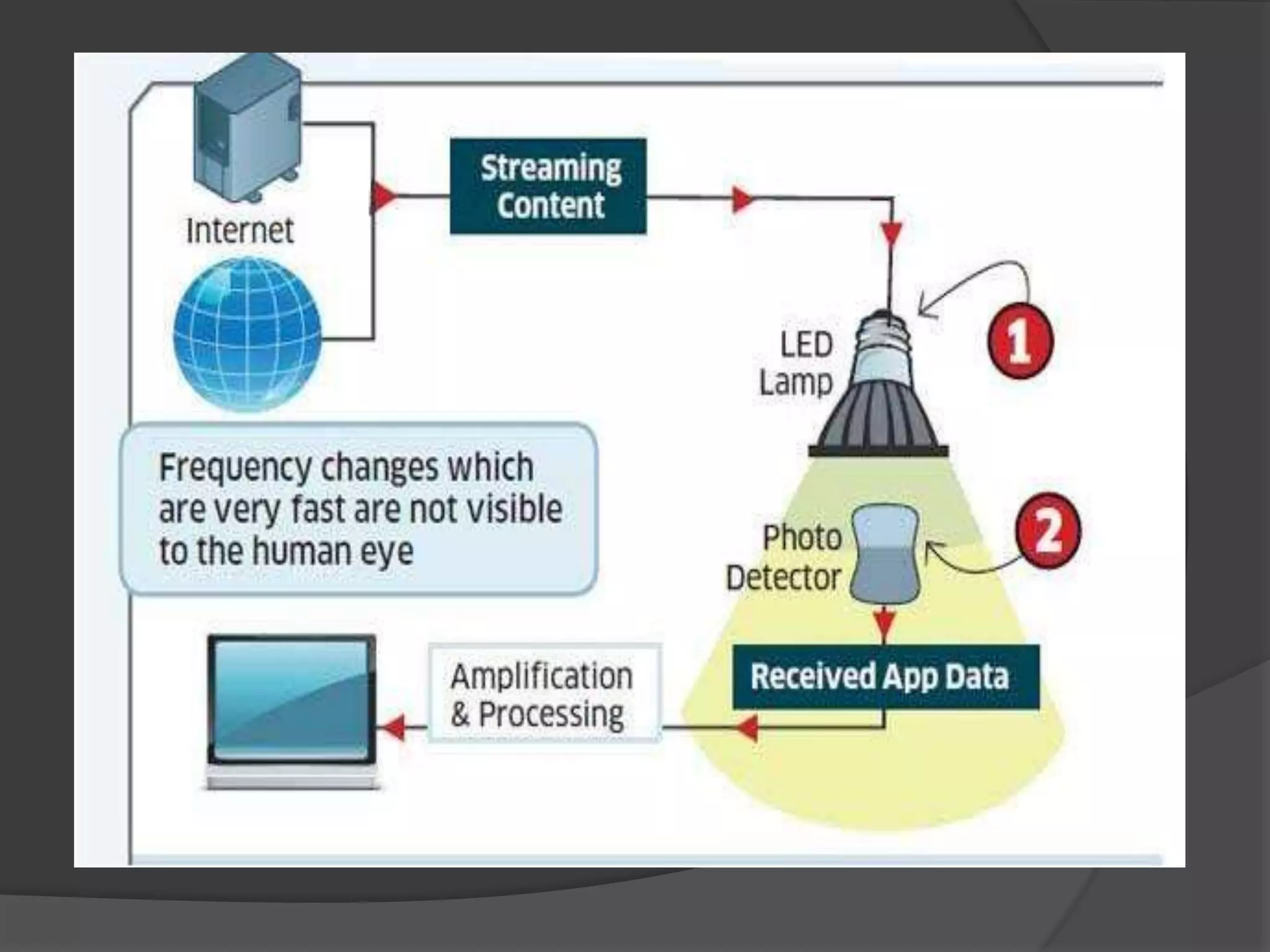
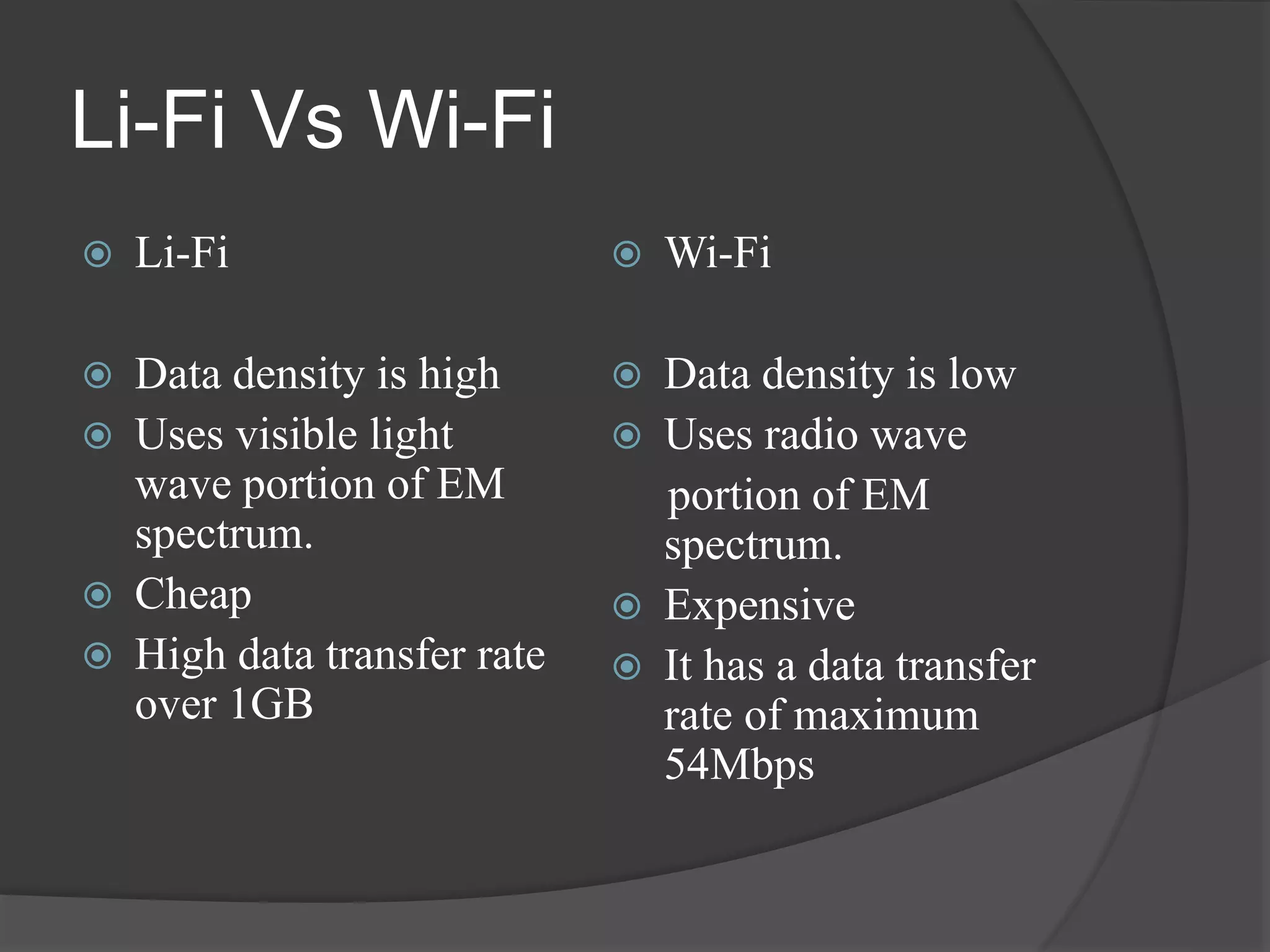
This document provides an overview of LiFi technology. It discusses the history of wireless networks and how they currently rely on radio waves. It then introduces LiFi as a new technology that transmits data through light instead of radio waves. It describes the components and working of LiFi, including how LED lights can be flickered at high speeds to transmit digital data. It compares LiFi to WiFi, discussing LiFi's advantages like higher speeds, more security, and greater available bandwidth. Potential applications and conclusions about LiFi solving bandwidth issues are also presented.