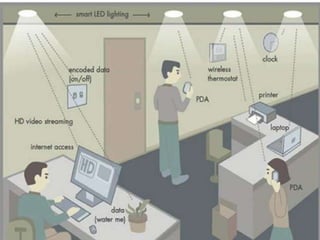
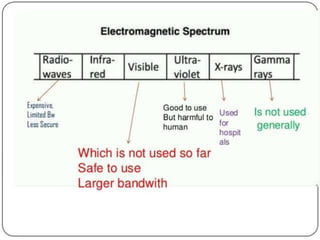
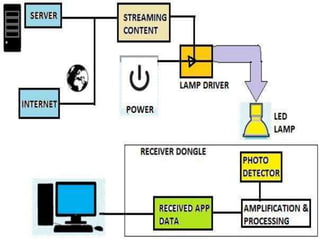
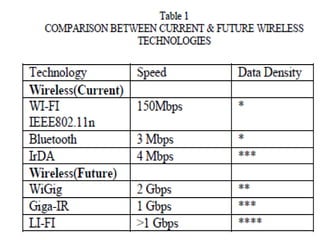
The document discusses Li-Fi, a technology that transmits data through light using LEDs, offering high-speed, bidirectional communication. It highlights advantages like solving radio frequency congestion and providing secure transmission, while also addressing challenges such as light obstruction and high installation costs. Applications of Li-Fi include traffic lights, safe environments, and public internet hotspots, suggesting a future where every light source could serve as a data transmission hub.