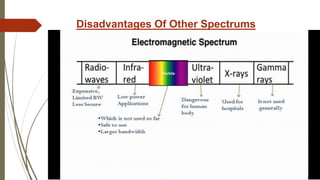
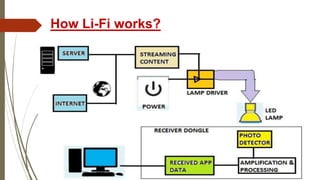
Li-Fi is a wireless optical networking technology that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for data transmission. It was invented by Professor Harald Haas from the University of Edinburgh. Li-Fi transmits data through LED bulbs and receives it with photoreceptors, providing higher speeds than Wi-Fi without interference. Potential applications include use in traffic lights, industrial settings, airplanes, and underwater where radio frequencies do not work well. While Li-Fi provides more security and bandwidth than Wi-Fi, it requires line of sight and lights to remain on for operation.