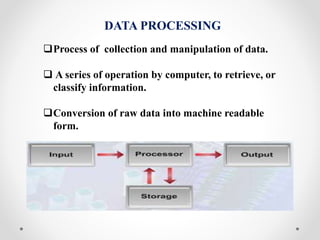
The document discusses the concepts of data and information, defining data as raw facts and information as processed data that is meaningful and organized. It outlines the data processing system, which converts raw data into machine-readable forms and emphasizes the importance of effective information systems in management decision-making. Key characteristics of effective information systems include accuracy, timeliness, completeness, cost-effectiveness, and understandability.