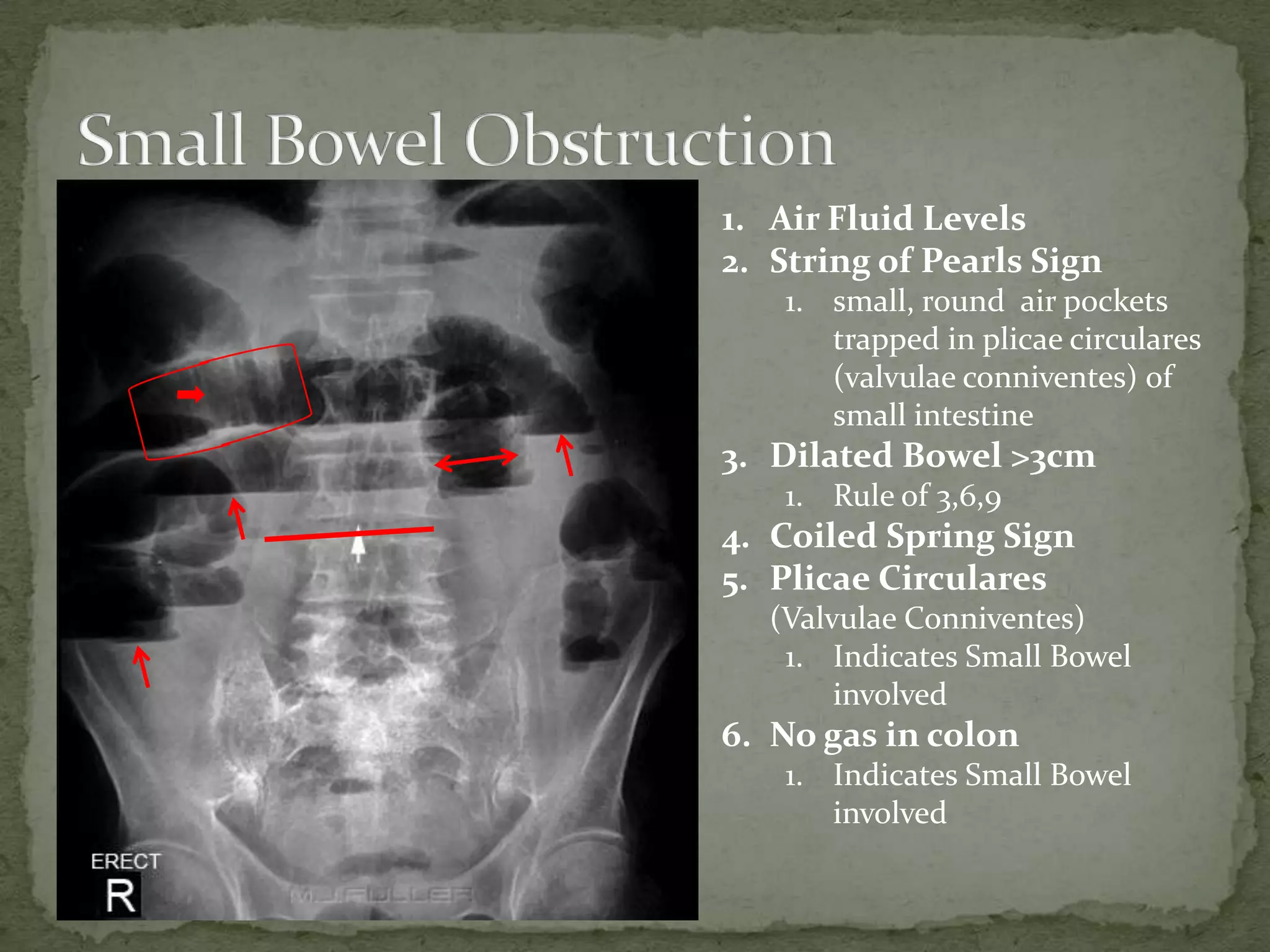
A 65-year-old man presented with diffuse abdominal pain and vomiting for a few hours. He has a history of cholecystectomy and appendectomy. On exam, his abdomen was actively tender with mild distention and high-pitched bowel sounds. Imaging showed small bowel dilation and the "string of pearls" sign, indicating a small bowel obstruction. Non-surgical management was recommended given his stable condition, with surgery as an option if his condition deteriorates.