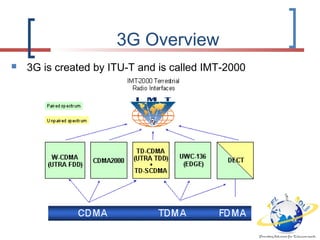
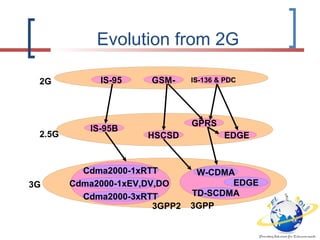
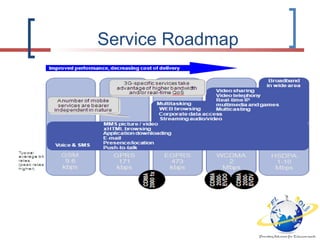
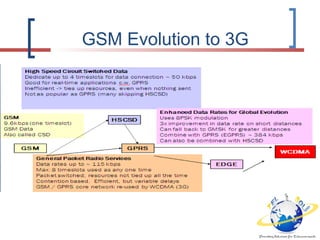
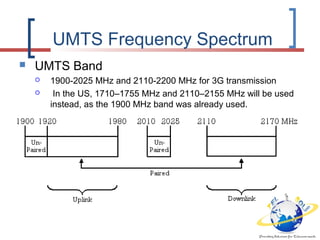
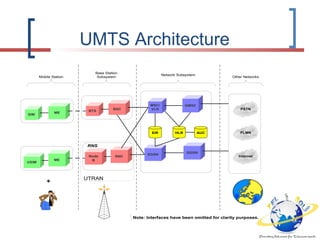
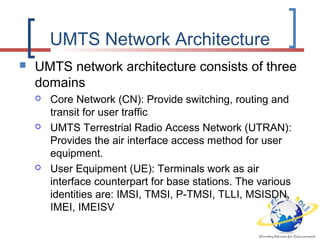
3G is defined by the ITU and called IMT-2000. It evolved from 2G technologies through intermediary 2.5G and 3.5G standards. UMTS is the 3G standard developed by 3GPP as an upgrade from GSM, using W-CDMA technology. UMTS network architecture consists of the core network, UTRAN radio access network, and user equipment. The UTRAN air interface uses W-CDMA technology with Node-B base stations controlled by RNCs. 3.5G technologies like HSPA extend UMTS with features like adaptive modulation and fast scheduling to enhance performance.