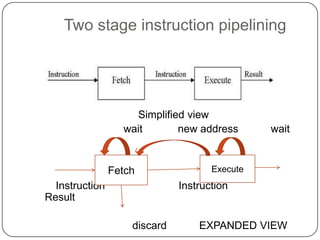
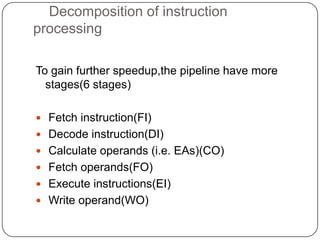
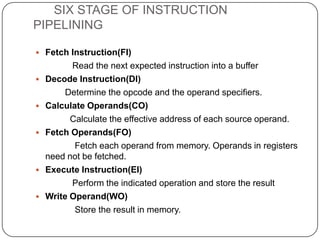
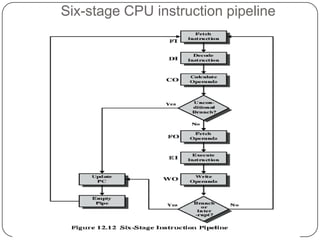
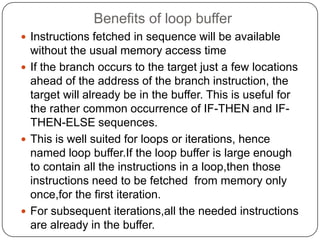
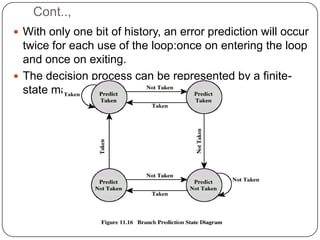
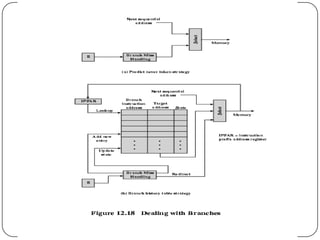
The document discusses instruction pipelining in CPUs. It explains that instruction pipelining achieves greater CPU performance by overlapping the execution of multiple instructions. It describes the different stages in a basic two-stage pipeline as fetch and execute. It then discusses how further dividing the pipeline into more stages, such as six stages for fetch, decode, calculate, fetch operands, execute, and writeback, can provide even higher performance. However, it notes conditional branches can reduce efficiency since the next instruction is unknown until the branch is resolved. Various techniques to handle branches like branch prediction, prefetching the target, and delayed branches are described to improve pipeline performance.