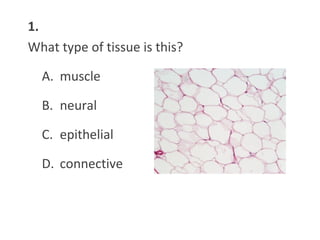
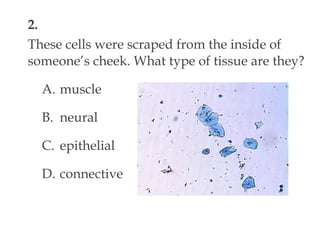
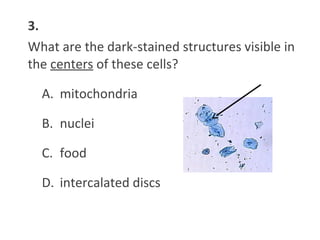
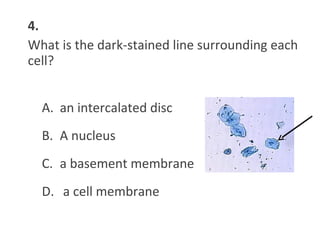
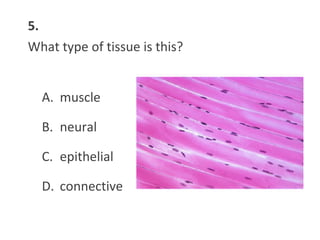
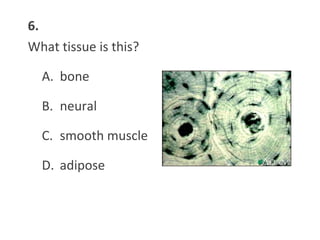
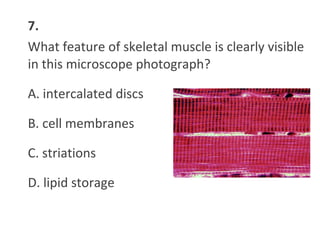
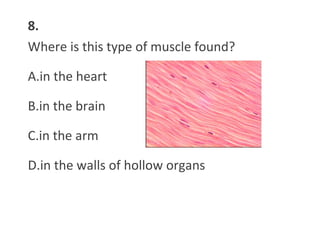
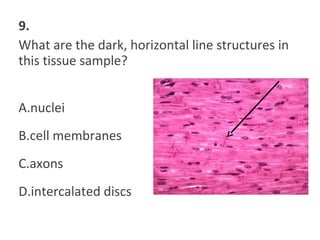
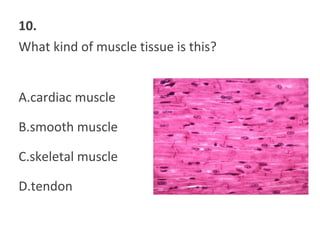
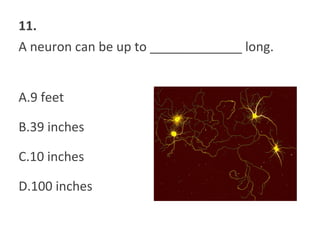
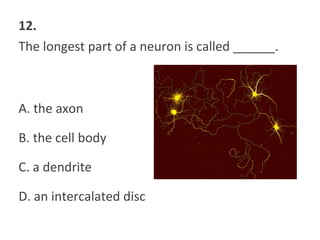
This document contains a self-quiz about identifying different types of tissues under a microscope, including epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, neural tissue, connective tissue, and bone tissue. The questions test identification of tissues from the cheek, heart, brain, arm, and other body locations, as well as cellular structures like nuclei, cell membranes, striations, and intercalated discs. Key tissues identified include skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, neurons, adipose tissue, bone, and cartilage.