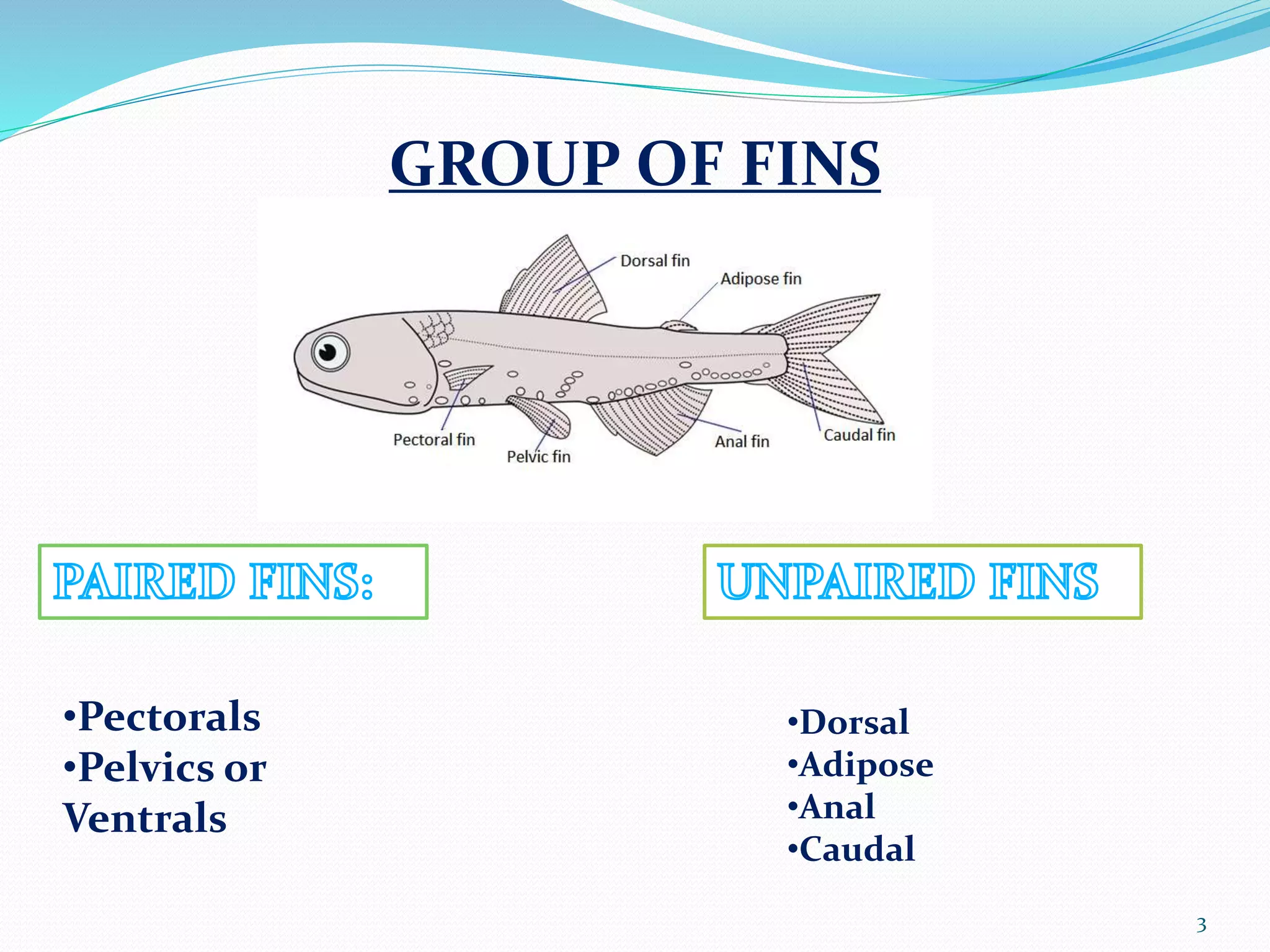
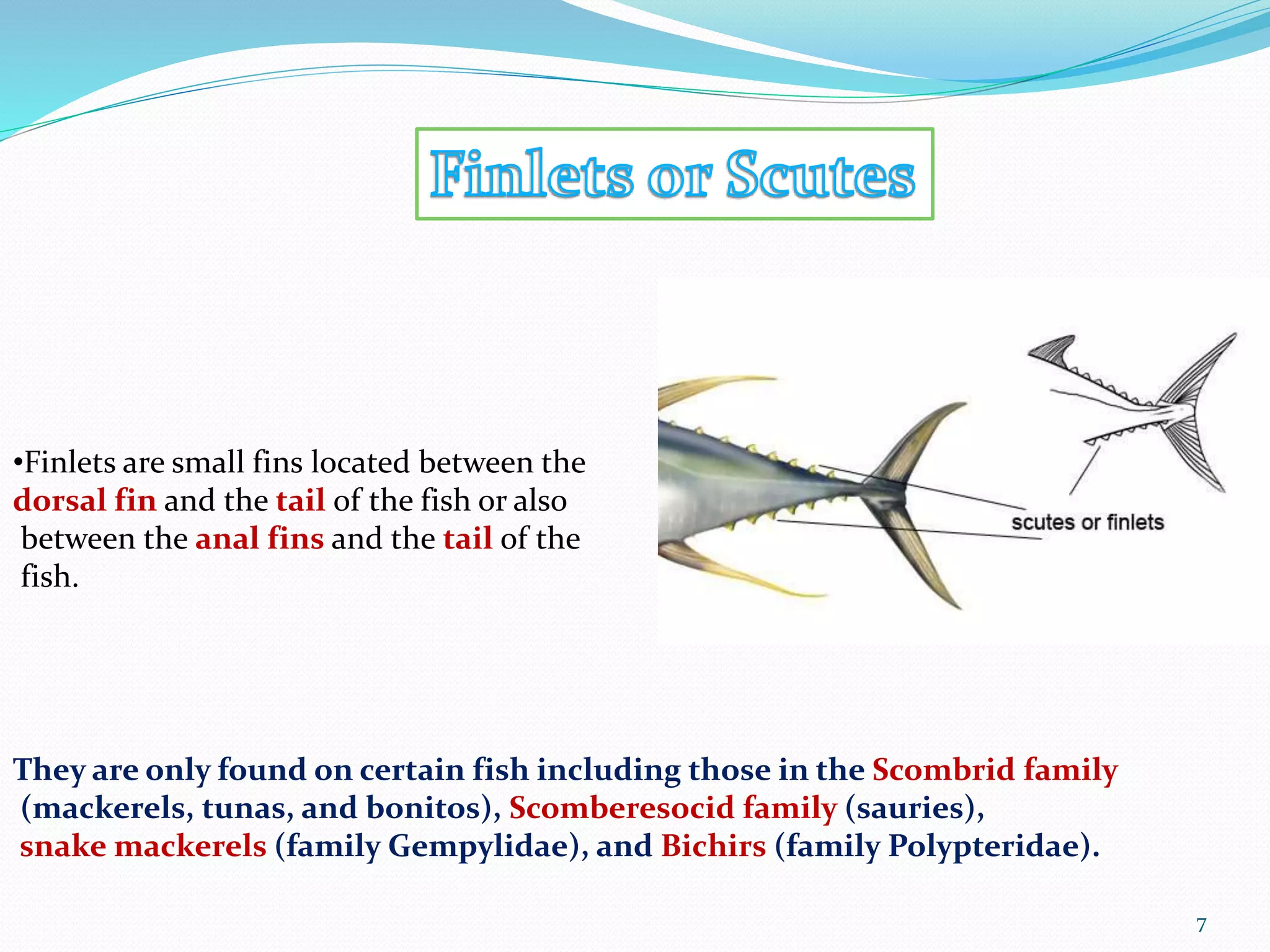
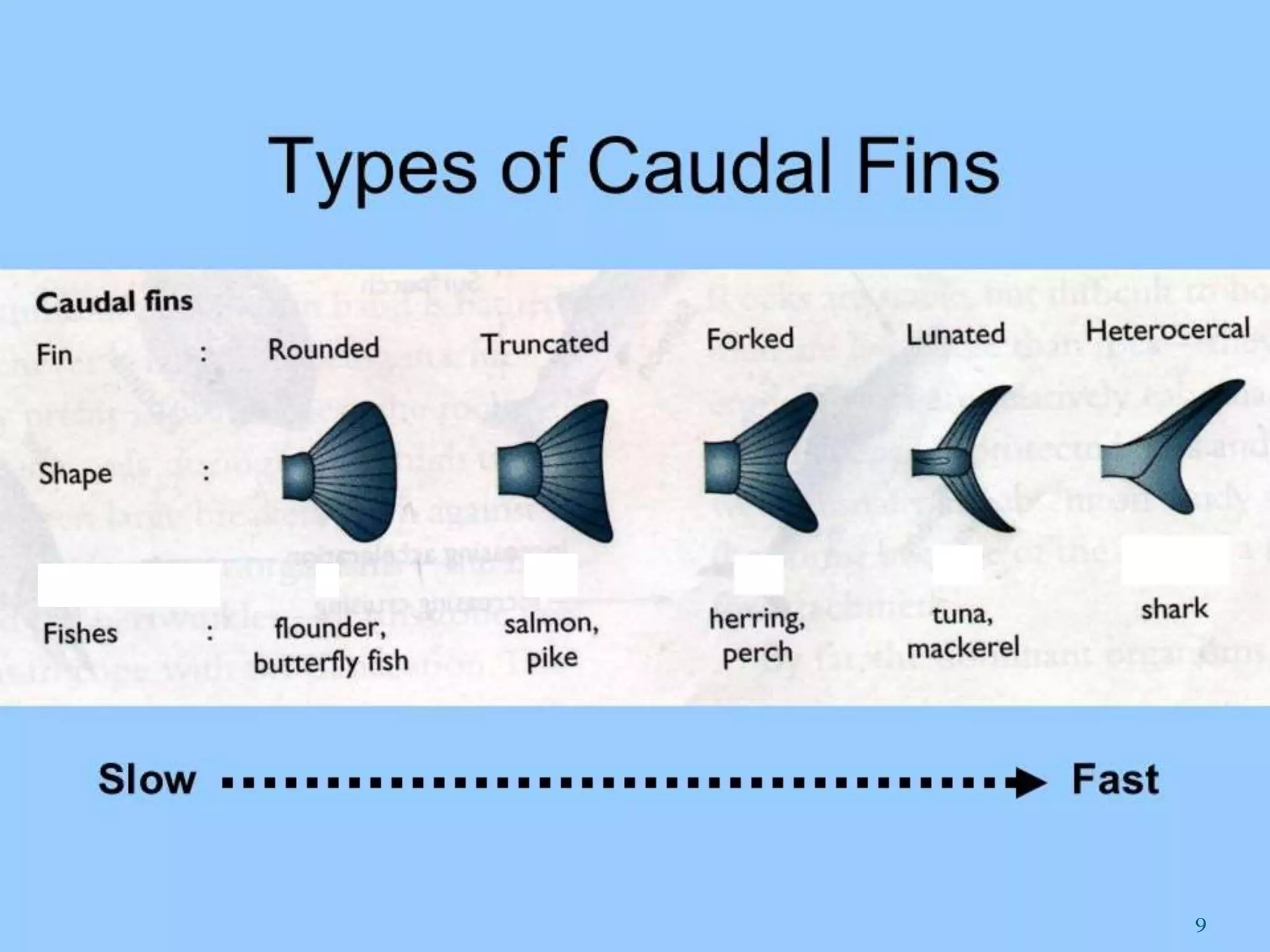
Fish fins are essential organs for locomotion, stability, and maneuverability, allowing fish to move, steer, and stop effectively. They come in various types, including pectoral, pelvic, dorsal, anal, adipose, and caudal fins, each serving specific functions such as propulsion, stability, and protection against predators. Additionally, certain species like flying fish have modified fins that enable them to glide through the air.