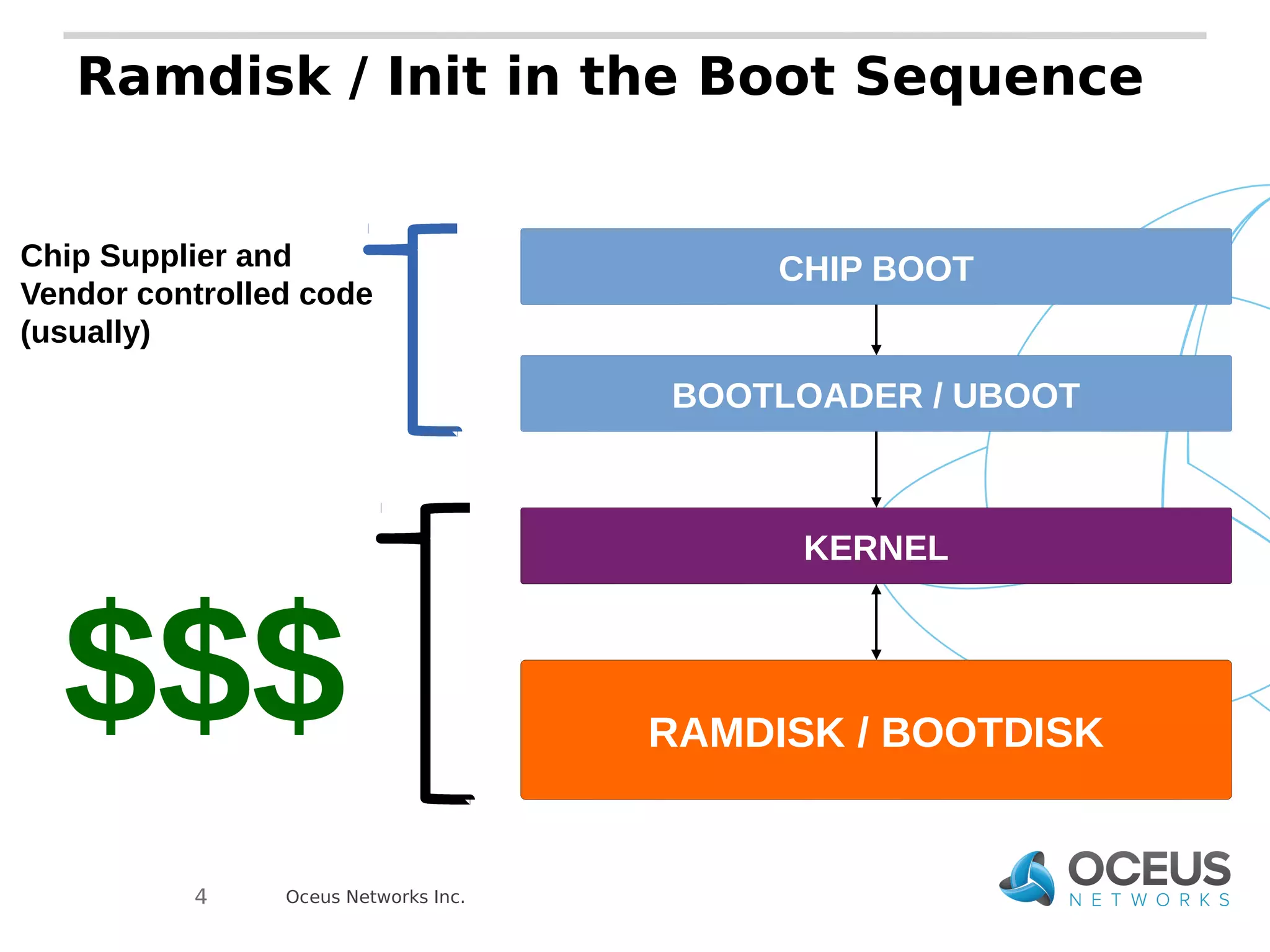
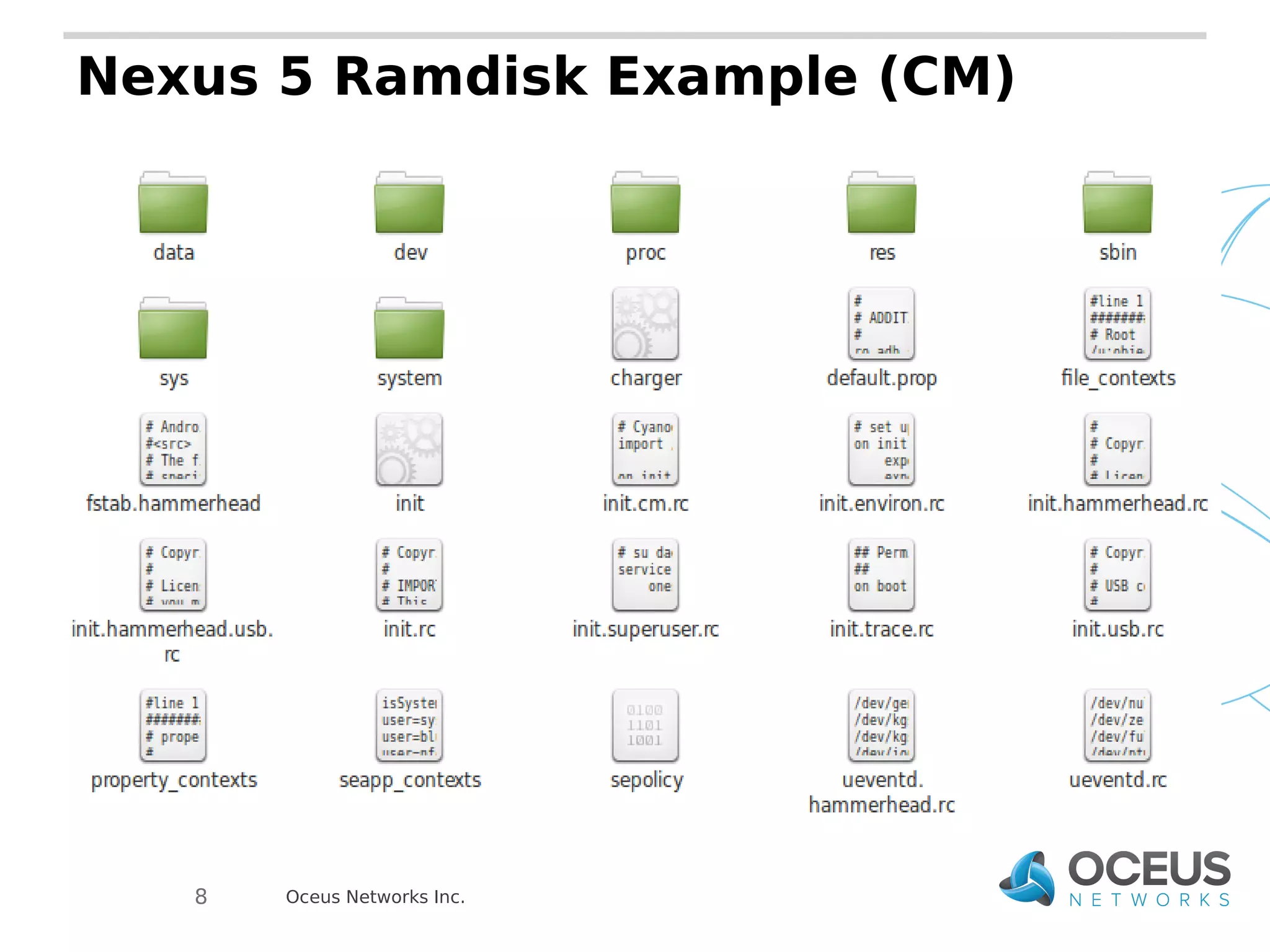
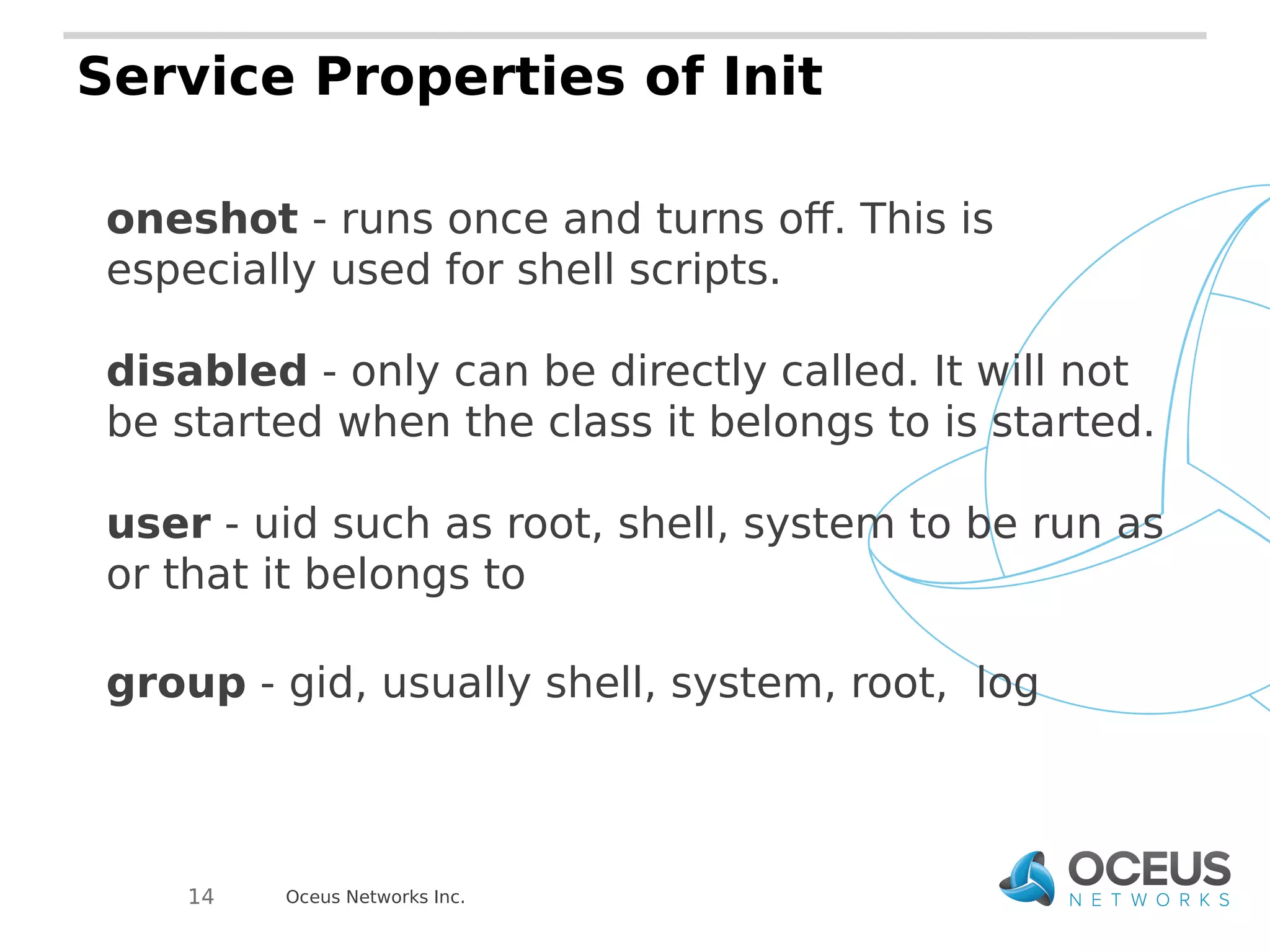
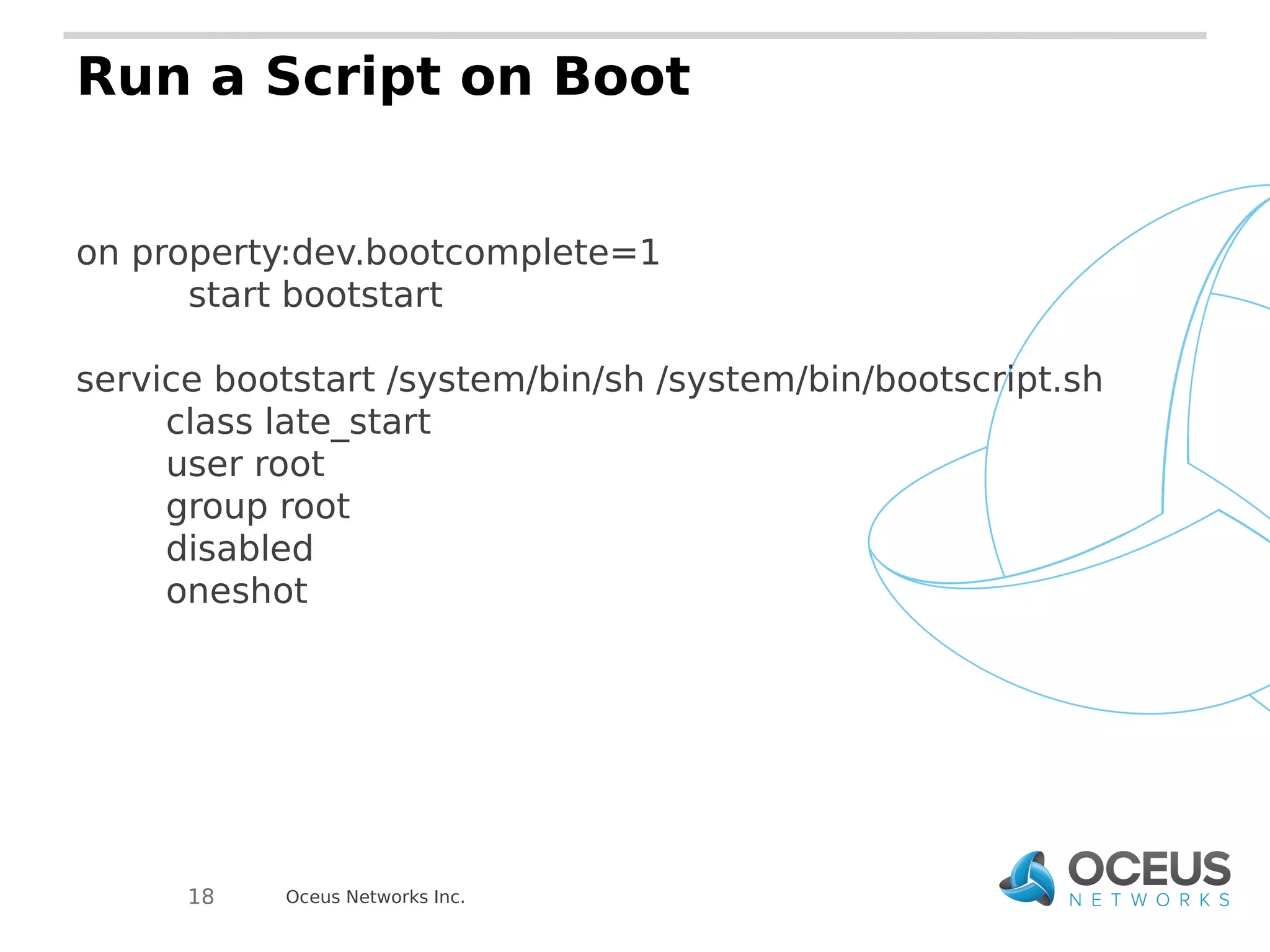
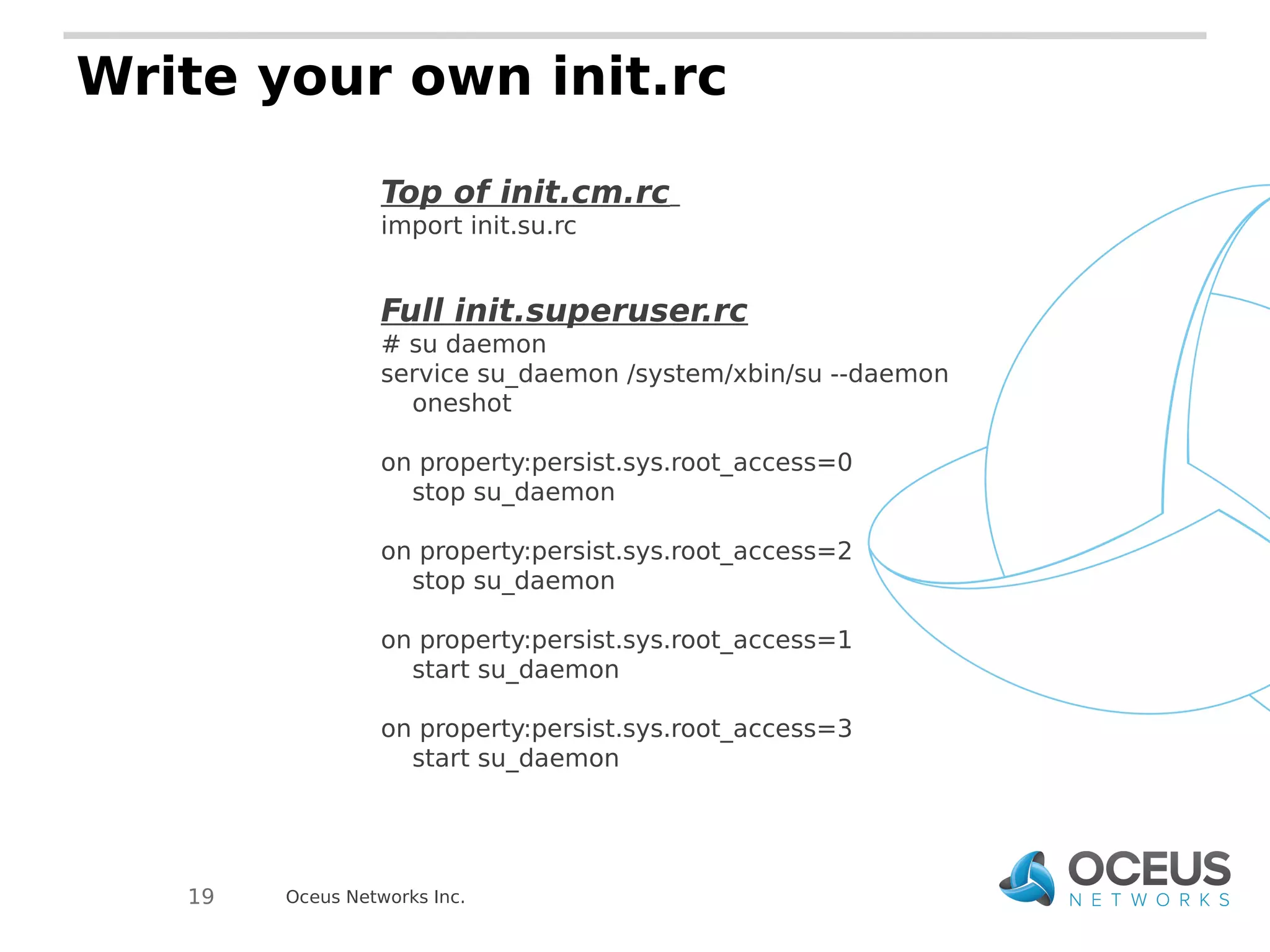
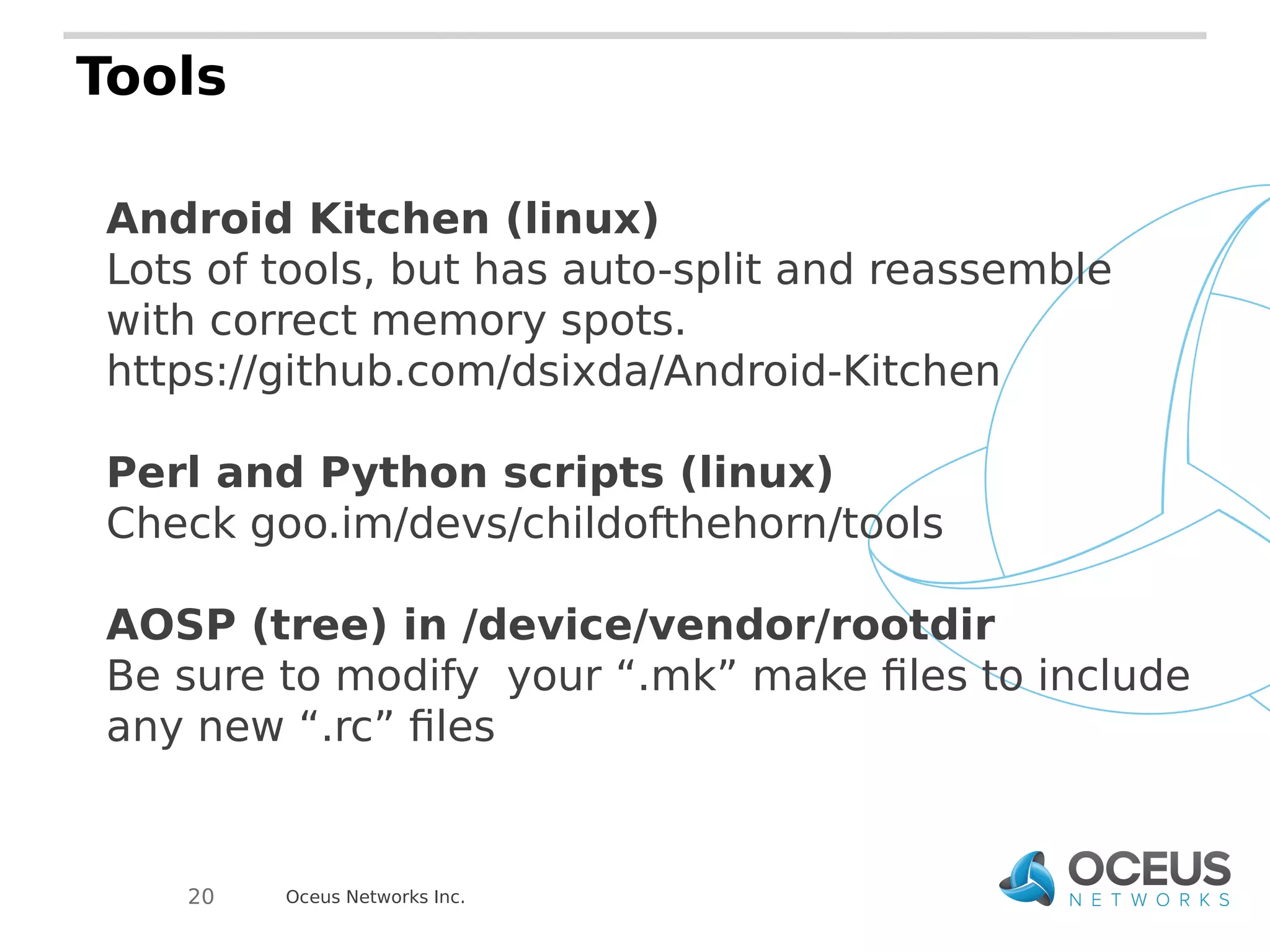
The document discusses the importance of ramdisks in the Android boot process, detailing how init.rc scripts manage system initialization, encryption handling, and directory structure. It highlights issues related to encryption timing, the control of services during boot, and the interaction between init and the vold binary for decryption. Lastly, it provides insights on writing custom init.rc files and utilizing tools for Android development.