(1) The document discusses client factors, which are specific capacities, characteristics, or beliefs that reside within a person and influence their performance in occupations.
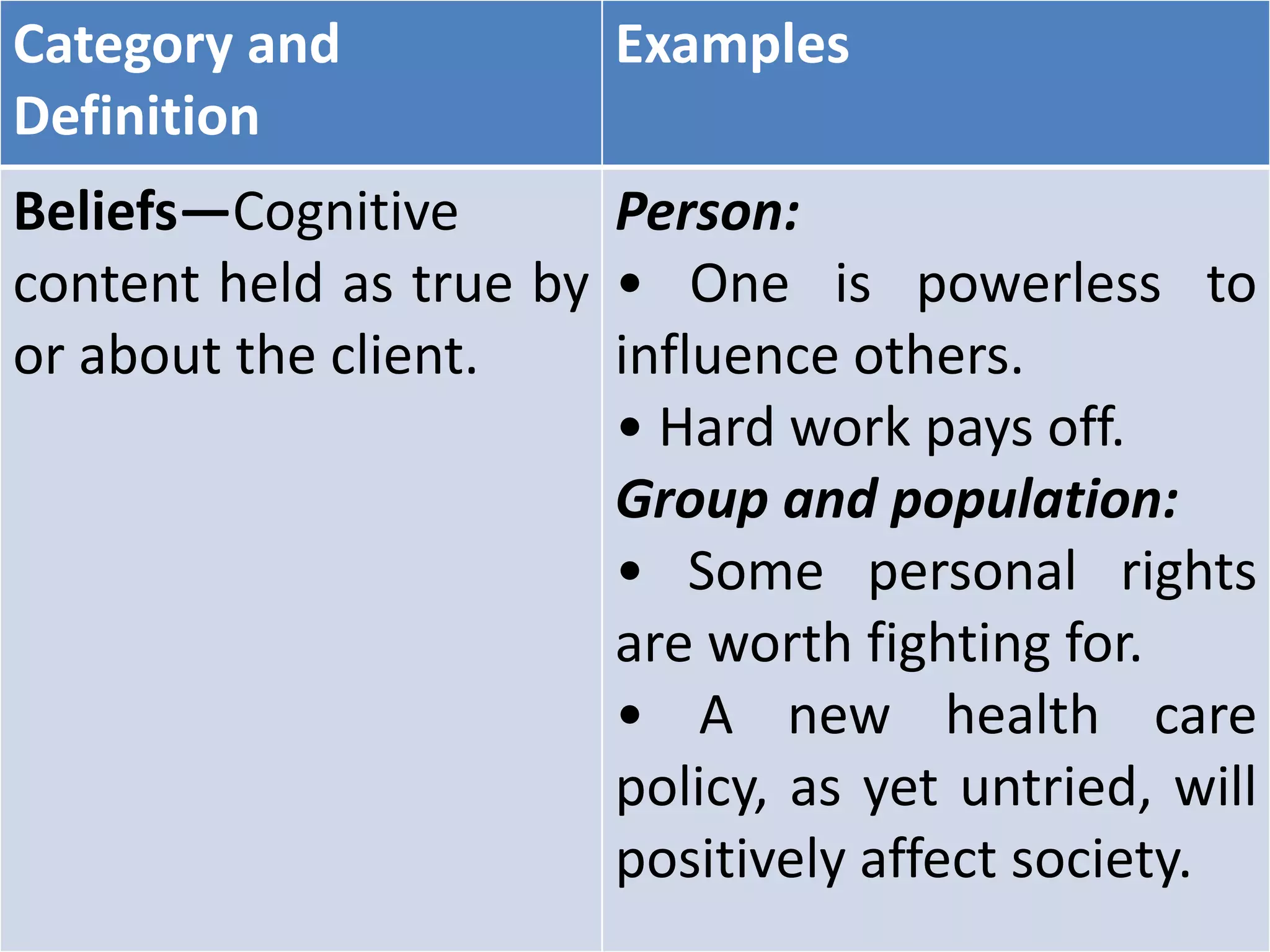
(2) Client factors include values, beliefs, spirituality, body functions, and body structures. Values are acquired beliefs about what is good or important, beliefs are cognitive content held as true, and spirituality refers to how people find meaning and purpose.
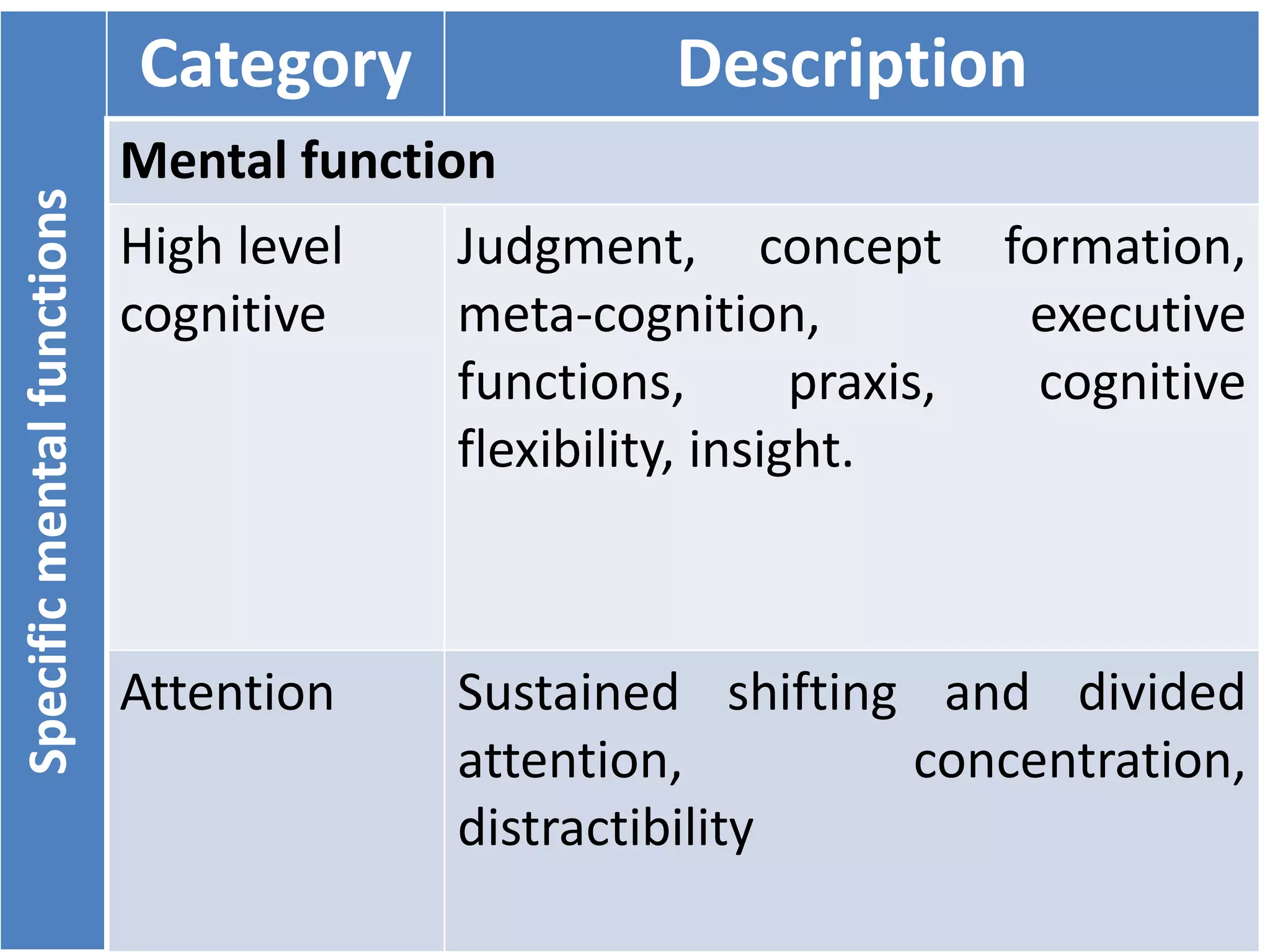
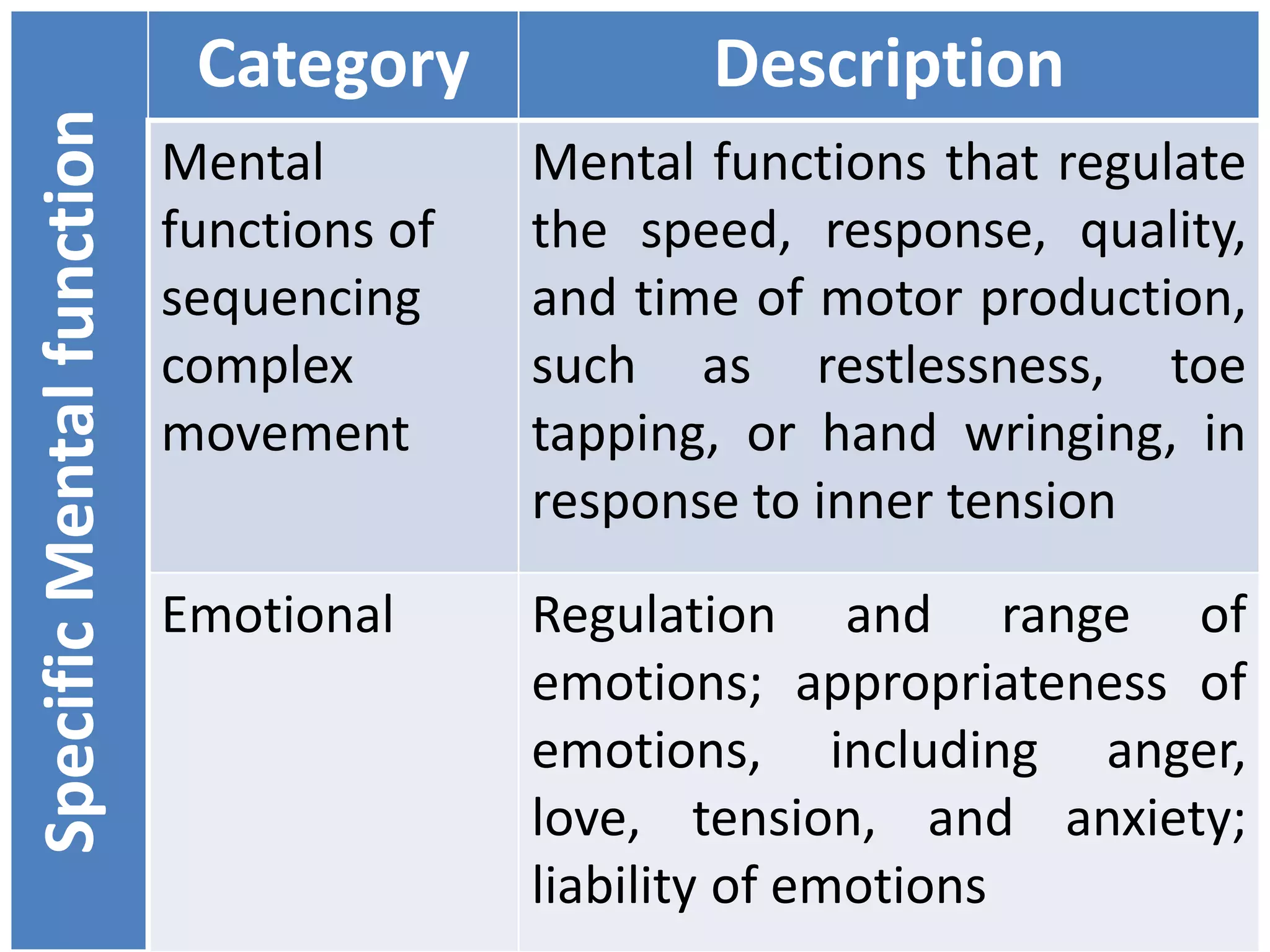
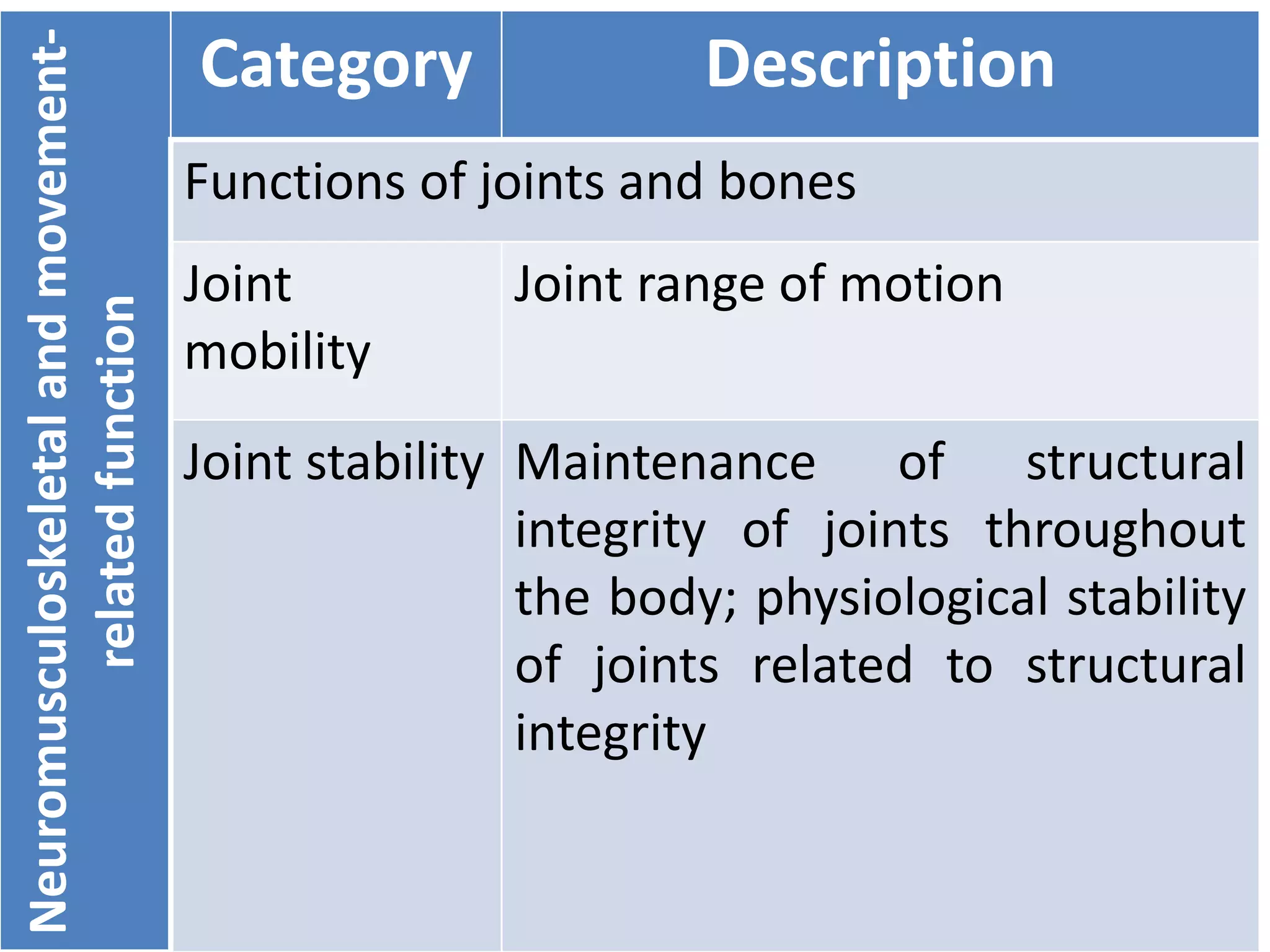
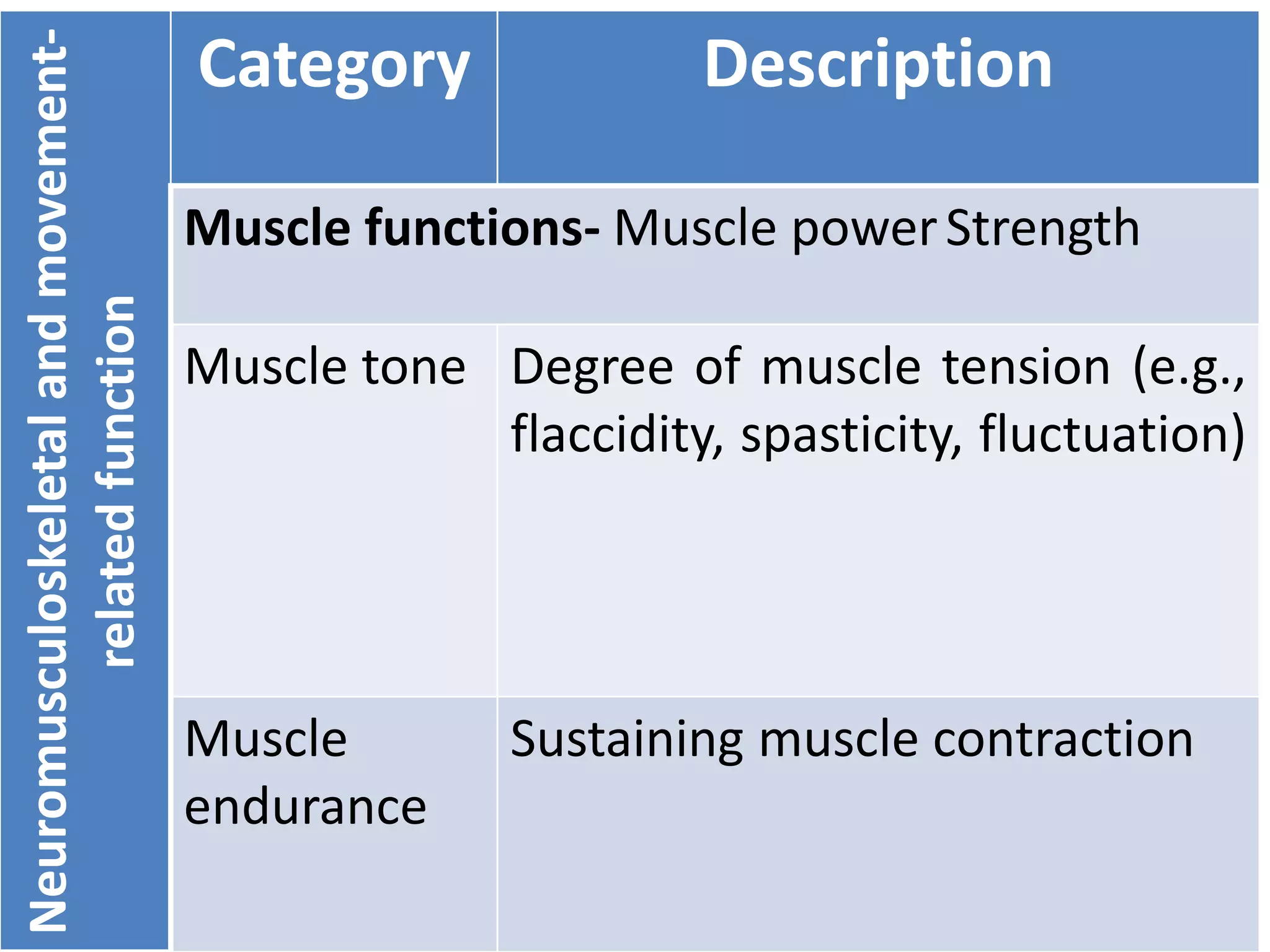
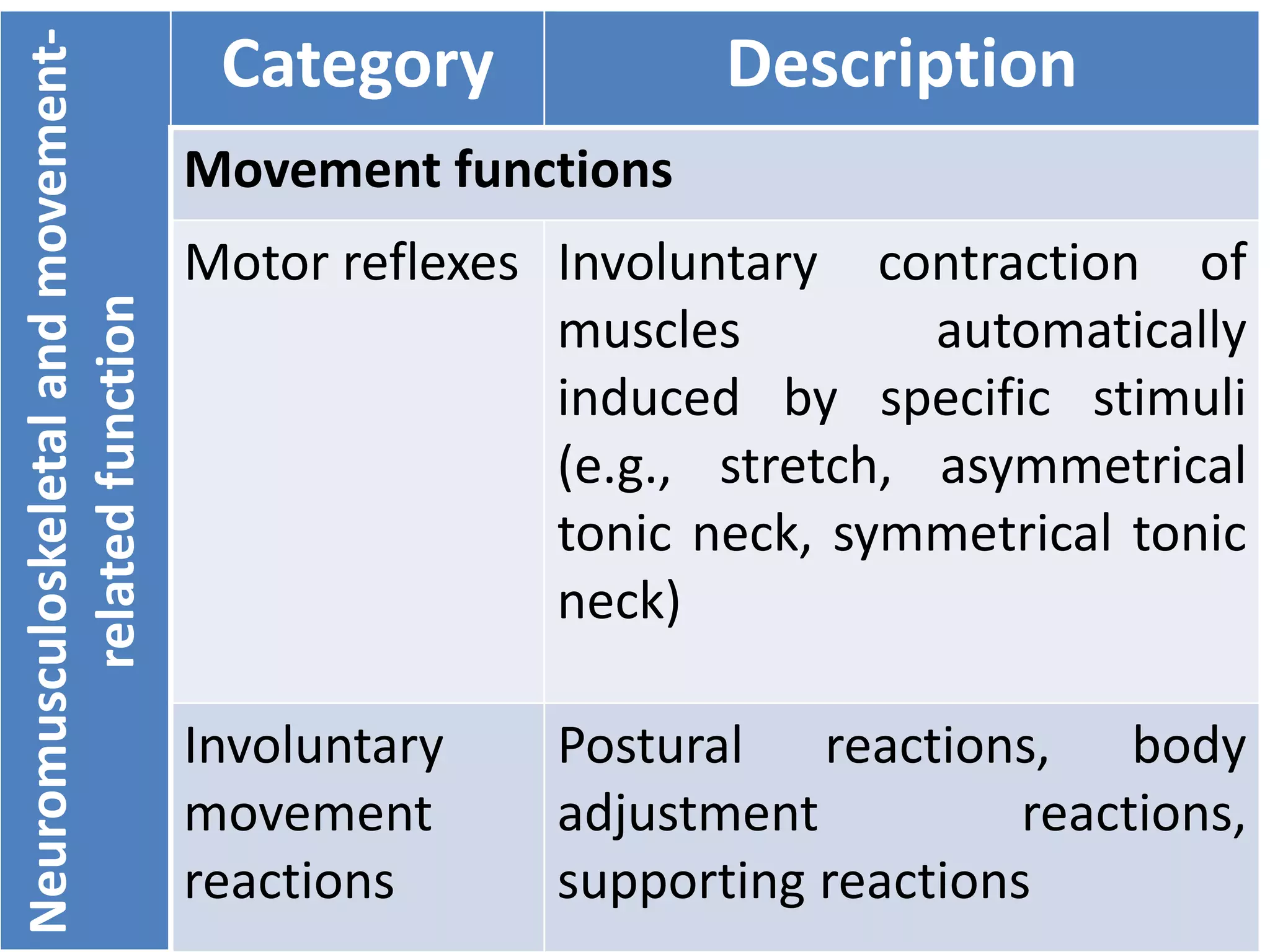
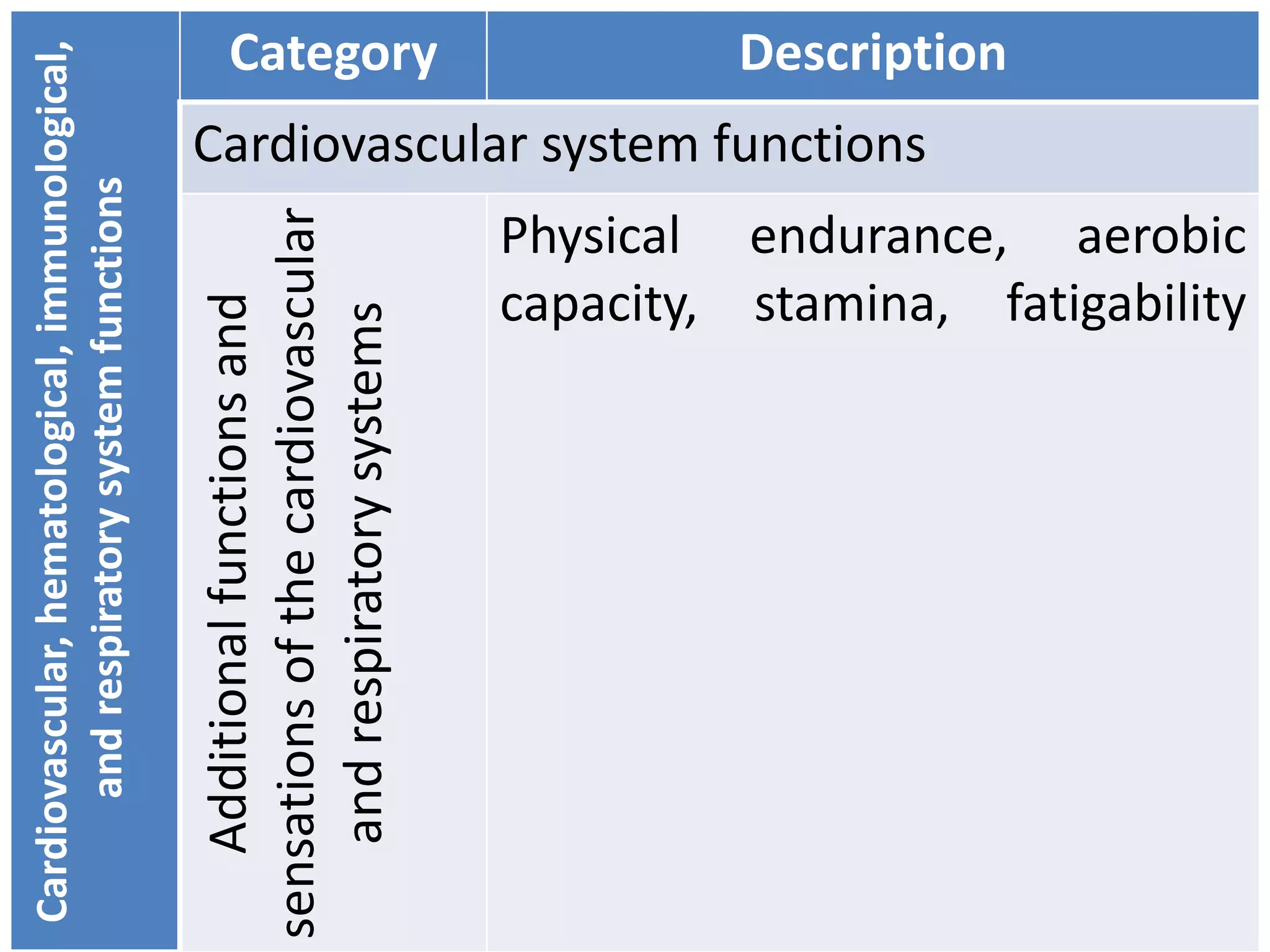
(3) Body functions include mental functions like memory and attention, sensory functions like vision and hearing, and neuromusculoskeletal functions like muscle tone and movement. Body structures are anatomical parts like organs and limbs.