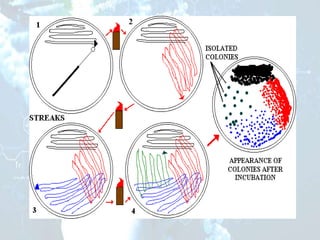
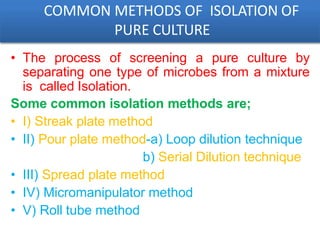
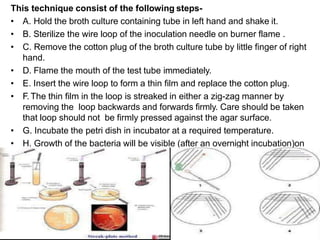
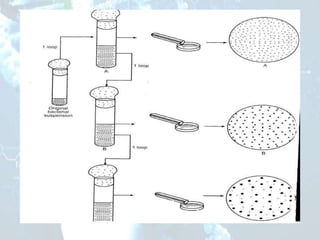
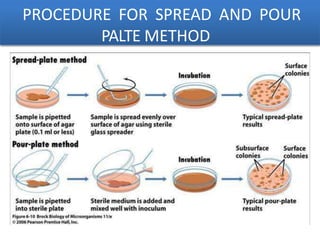
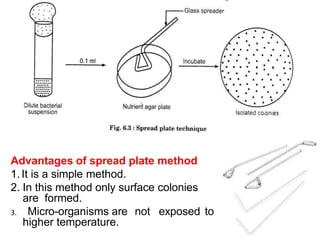
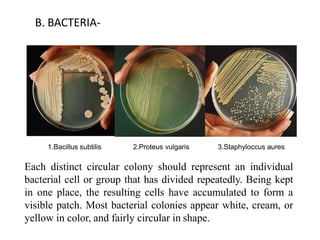
The document discusses methods for isolating microorganisms from mixed cultures to obtain pure cultures. It describes several common isolation techniques including streak plating, pour plating, spread plating, and serial dilution. Streak plating involves streaking a sample on an agar plate to separate individual colonies. Pour and spread plating involve mixing the sample with molten agar and allowing it to solidify. Serial dilution uses successive dilutions to isolate a single microorganism. The document also discusses identifying microorganisms based on characteristics of colonies like shape, color, elevation and margins.