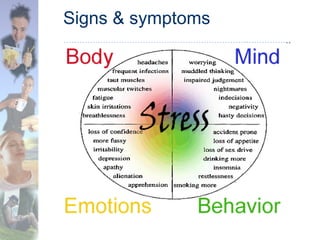
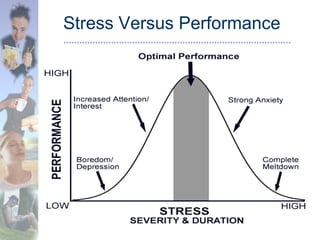
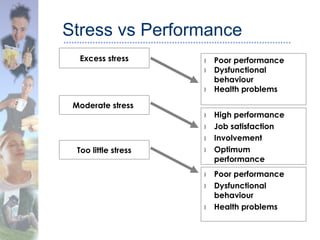
This document discusses the nature and causes of work stress and strategies for managing stress. It defines stress and lists common signs and symptoms. Stress can be caused by factors like unrealistic deadlines, office politics, and not meeting targets. Both psychological factors like limiting beliefs and physiological responses like the fight-or-flight response contribute to stress. The document recommends strategies for managing stress such as recognizing stress triggers, adopting a positive mindset, maintaining health through diet and exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, and effectively managing time.