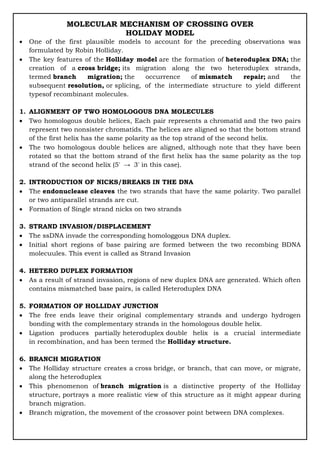
Holliday model of crossing over
- 1. MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF CROSSING OVER HOLIDAY MODEL One of the first plausible models to account for the preceding observations was formulated by Robin Holliday. The key features of the Holliday model are the formation of heteroduplex DNA; the creation of a cross bridge; its migration along the two heteroduplex strands, termed branch migration; the occurrence of mismatch repair; and the subsequent resolution, or splicing, of the intermediate structure to yield different typesof recombinant molecules. 1. ALIGNMENT OF TWO HOMOLOGOUS DNA MOLECULES Two homologous double helices, Each pair represents a chromatid and the two pairs represent two nonsister chromatids. The helices are aligned so that the bottom strand of the first helix has the same polarity as the top strand of the second helix. The two homologous double helices are aligned, although note that they have been rotated so that the bottom strand of the first helix has the same polarity as the top strand of the second helix (5′ → 3′ in this case). 2. INTRODUCTION OF NICKS/BREAKS IN THE DNA The endonuclease cleaves the two strands that have the same polarity. Two parallel or two antiparallel strands are cut. Formation of Single strand nicks on two strands 3. STRAND INVASION/DISPLACEMENT The ssDNA invade the corresponding homologgous DNA duplex. Initial short regions of base pairing are formed between the two recombing BDNA molecuules. This event is called as Strand Invasion 4. HETERO DUPLEX FORMATION As a result of strand invasion, regions of new duplex DNA are generated. Which often contains mismatched base pairs, is called Heteroduplex DNA 5. FORMATION OF HOLLIDAY JUNCTION The free ends leave their original complementary strands and undergo hydrogen bonding with the complementary strands in the homologous double helix. Ligation produces partially heteroduplex double helix is a crucial intermediate in recombination, and has been termed the Holliday structure. 6. BRANCH MIGRATION The Holliday structure creates a cross bridge, or branch, that can move, or migrate, along the heteroduplex This phenomenon of branch migration is a distinctive property of the Holliday structure, portrays a more realistic view of this structure as it might appear during branch migration. Branch migration, the movement of the crossover point between DNA complexes.
- 2. 7. RESOLUTION OF HOLLIDAY JUNCTION The Holliday structure can be resolved by cutting and ligating either the two originally exchanged strands or the originally unexchanged strands. Resolution of the structure shown in part c can proceed in two ways, depending on the points of enzymatic cleavage, yielding the structures The former generates a pair of duplexes that are parental, except for a stretch in the middle containing one strand from each parent. If the two parents had different alleles in this stretch, as indicated here, then the DNA will be heteroduplex. The latter resolution step generates two duplexes that are recombinant, with a stretch of heteroduplex DNA. The Holliday model also postulated that the heteroduplex DNA mismatches can be repaired by an enzymatic correction system that recognizes mismatches and excises the mismatched base from one of the two strands, filling in the excised base with the correct complementary base.
