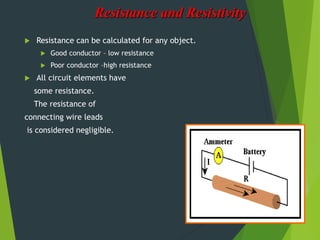
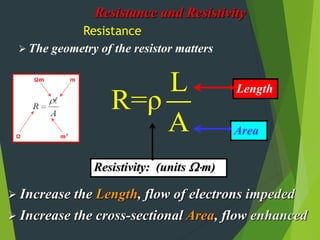
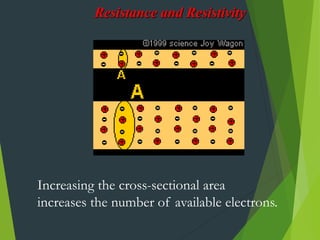
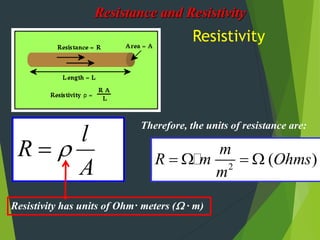
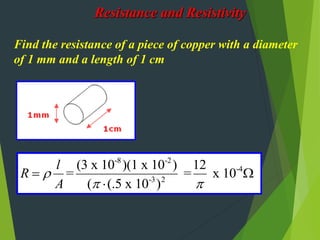
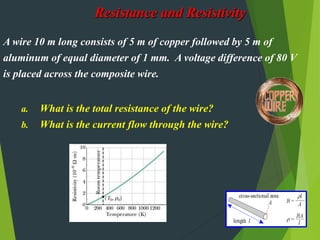
Resistivity is a measure of how effectively a material slows the flow of electricity, with insulators having high resistivity and conductors having low resistivity. Resistance depends on the material's resistivity as well as the length and cross-sectional area of the material. Resistance increases with length and decreases with increasing cross-sectional area. Superconductivity causes resistance to become zero below a critical temperature.

![Resistance and Resistivity
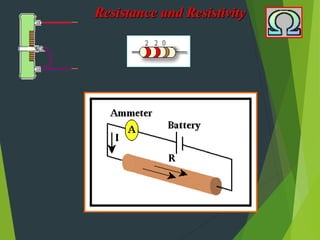
A conductor’s Resistance is defined as the ratio of the Applied Voltage to
the Current produced.
R = V/I
Scalar
Units: Ohm [Ω] = [V/A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/resistivity-230227001118-27aa4b5f/85/Resistivity-ppt-3-320.jpg)