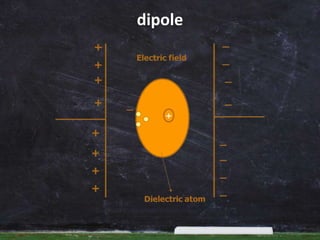
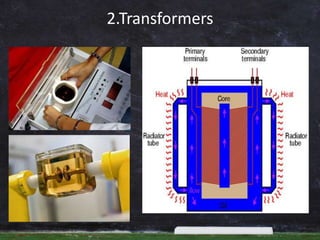
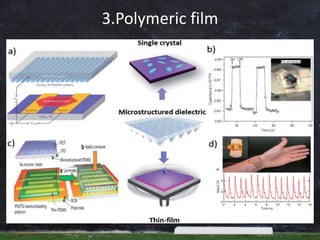
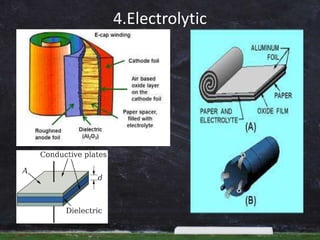
Dielectric materials are insulators that can be polarized by an applied electric field. They have electric dipole moments that result from separated positive and negative charges. Common dielectric materials include mica, glass, ceramics, rubber, oils, and gases. Dielectrics are characterized by their dielectric constant and used widely in capacitors, transformers, films, and other applications to store electric energy.