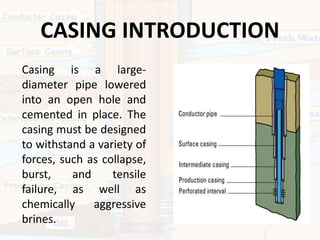
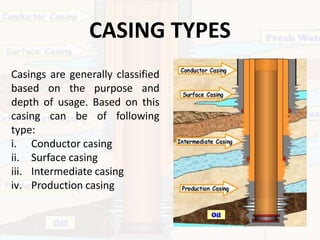
Casing is run in wells to seal off different formation layers and pressure zones, control fluid migration, and provide structural support. There are typically four casing types:
1) Conductor casing is near the surface to protect shallow zones.
2) Surface casing isolates freshwater and provides a foundation for wellhead equipment.
3) Intermediate casing seals between pressure zones or problem formations.
4) Production casing isolates the producing reservoir and allows zone-specific extraction. Properly cementing each casing string is important for isolation and containment of fluids.