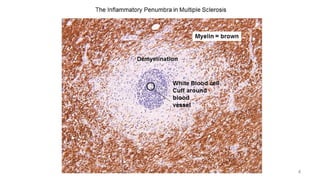
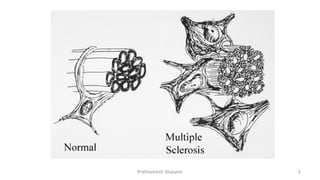
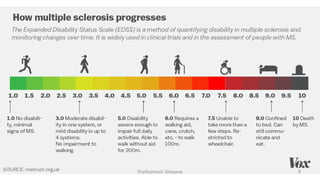
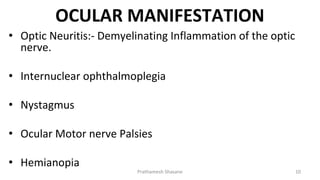
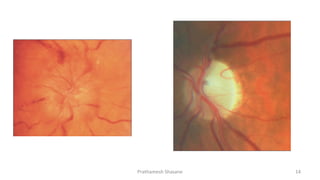
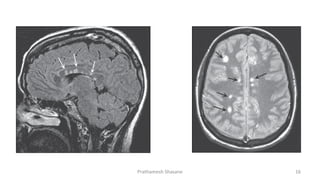
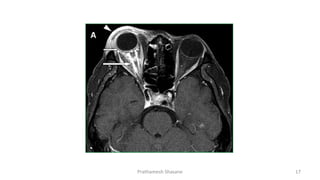
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease characterized by inflammation, demyelination, gliosis, and neuronal loss that typically affects different areas of the central nervous system. The document discusses the pathogenesis of MS including perivascular cuffing, blood brain barrier disruption, astrocytic proliferation, and shadow plaques. It also covers the ocular manifestations of MS such as optic neuritis, internuclear ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus, and ocular motor nerve palsies. Risk of developing MS is about 50% after an acute episode of optic neuritis and 70% for patients with lesions on MRI. Treatment involves steroid therapy and immunomodulatory drugs.