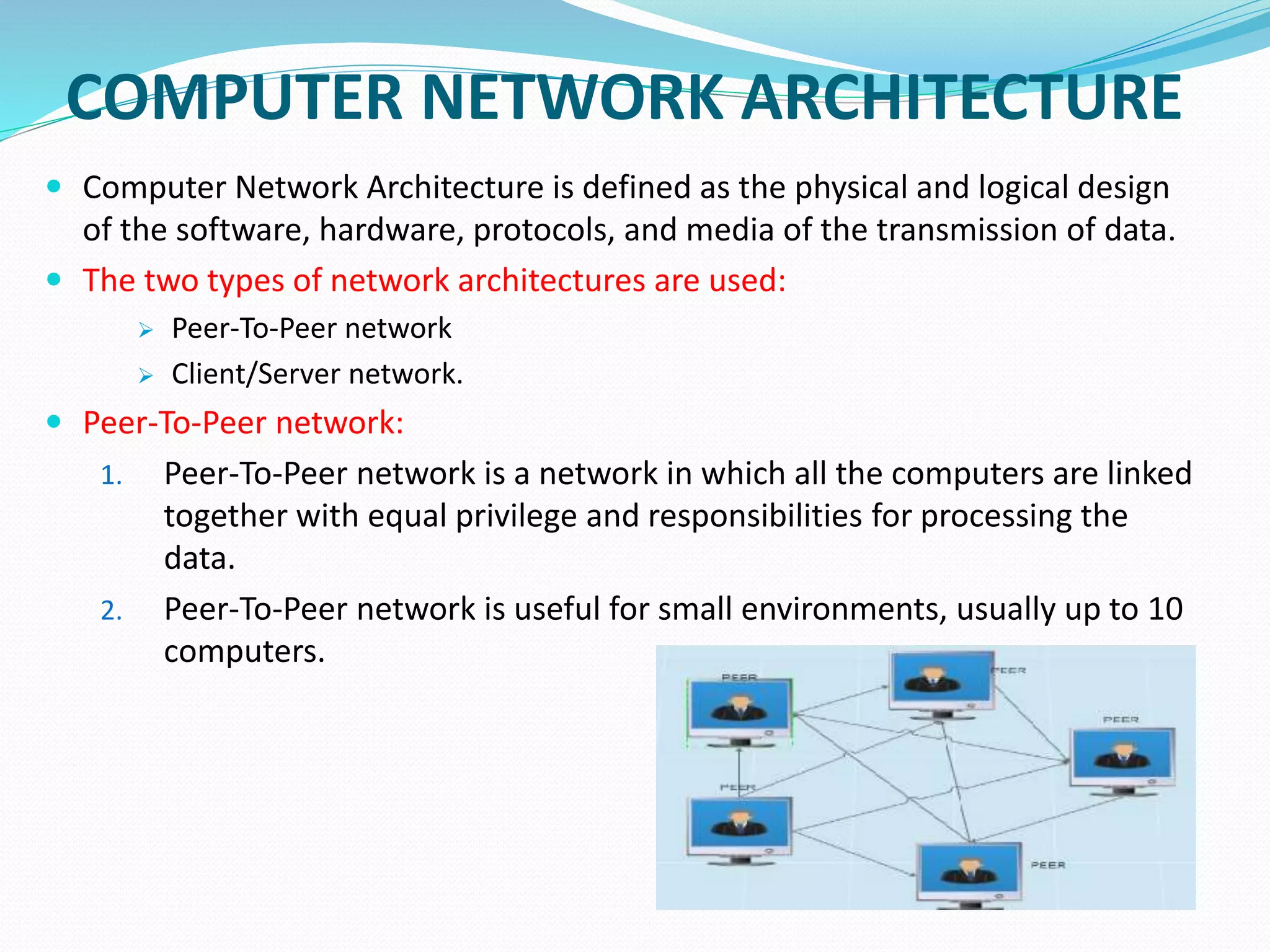
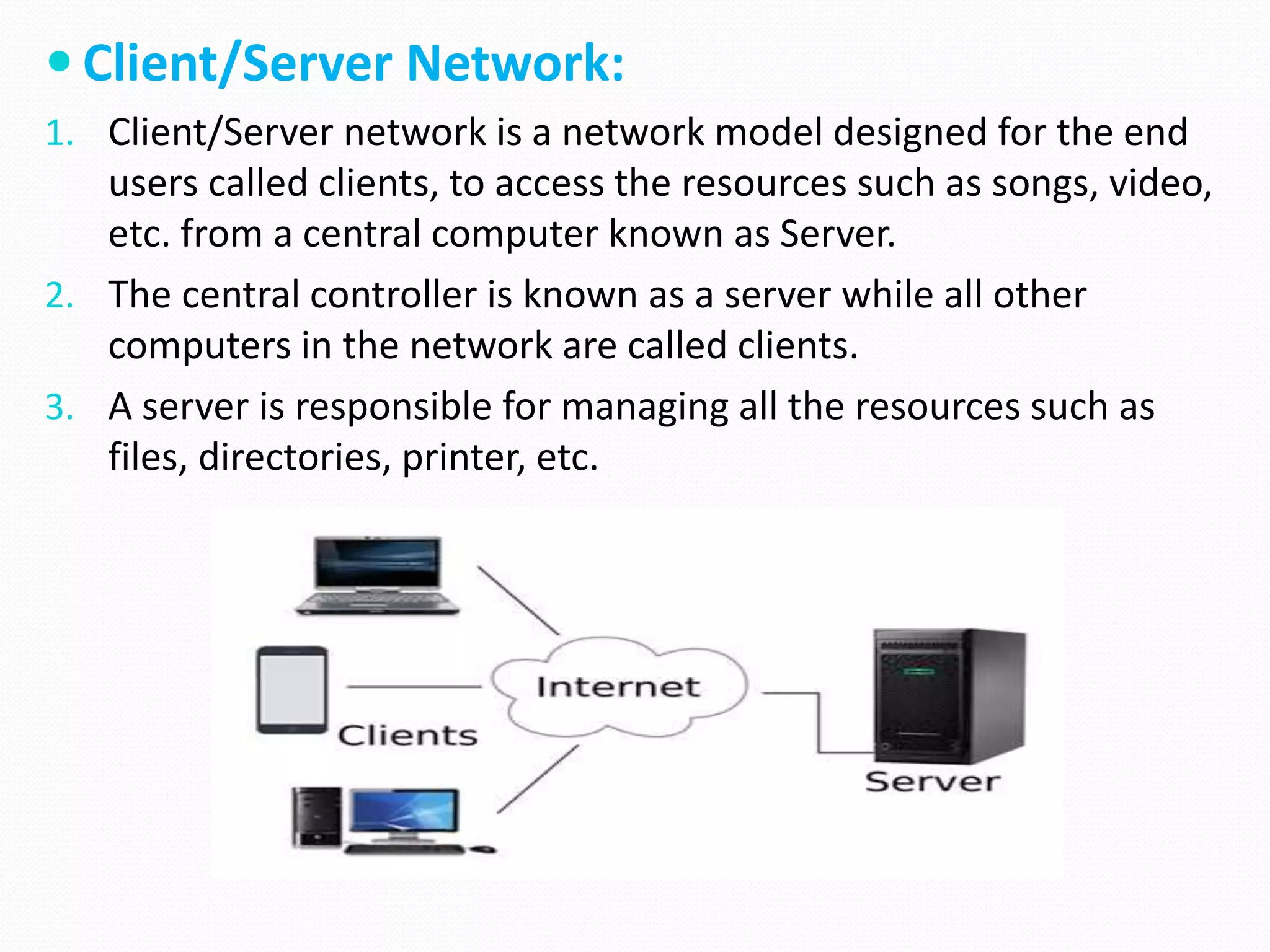
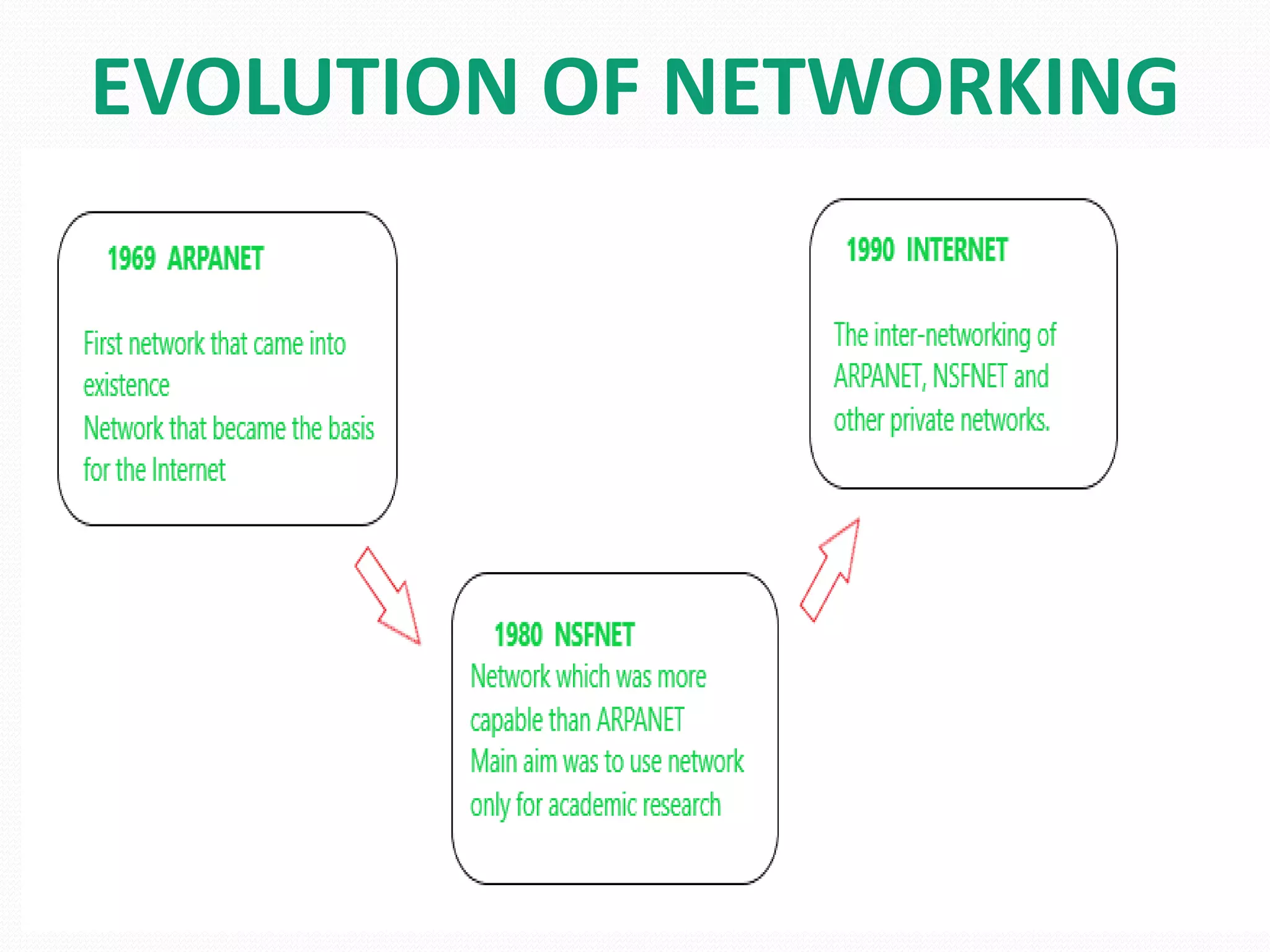
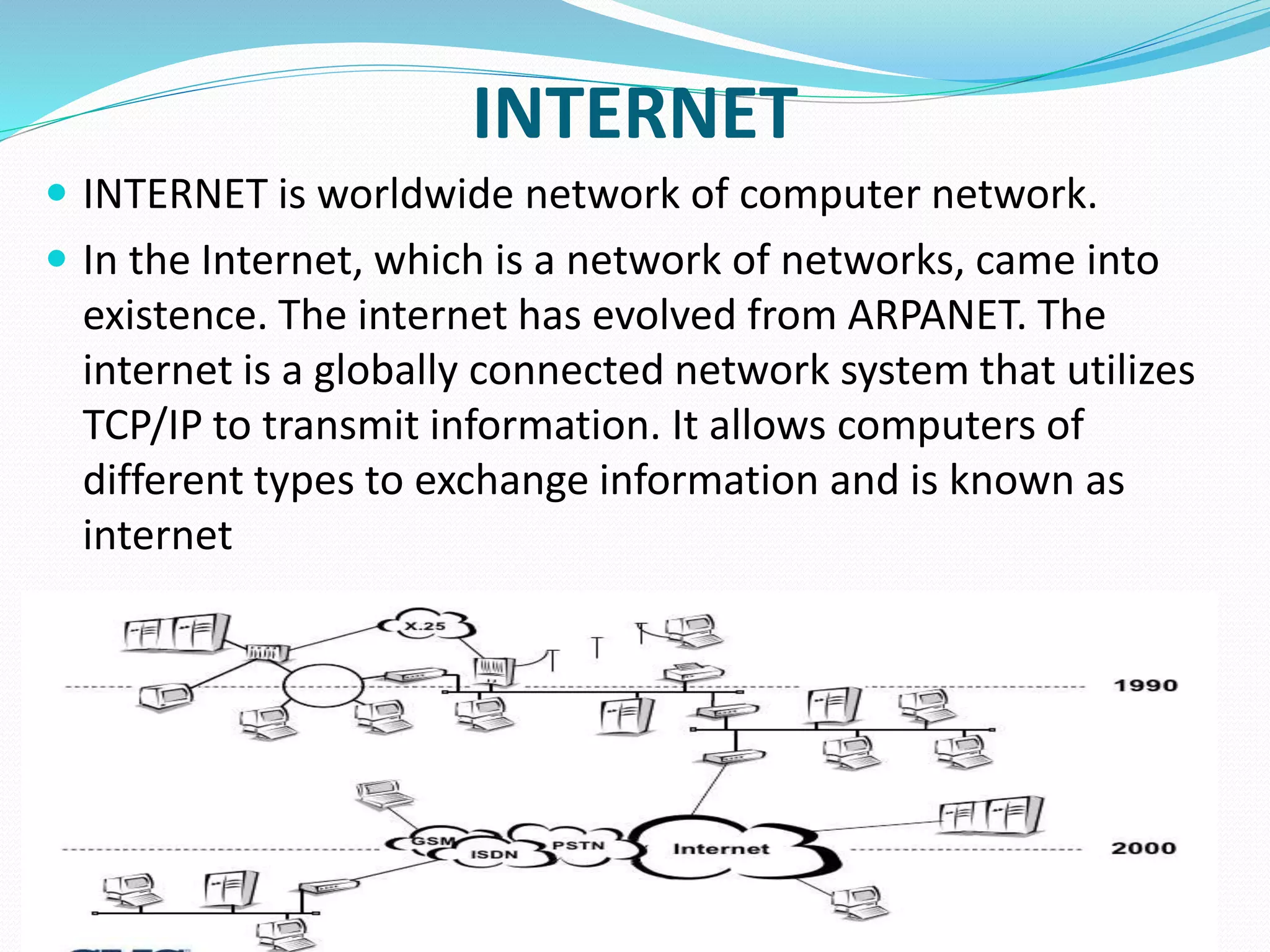
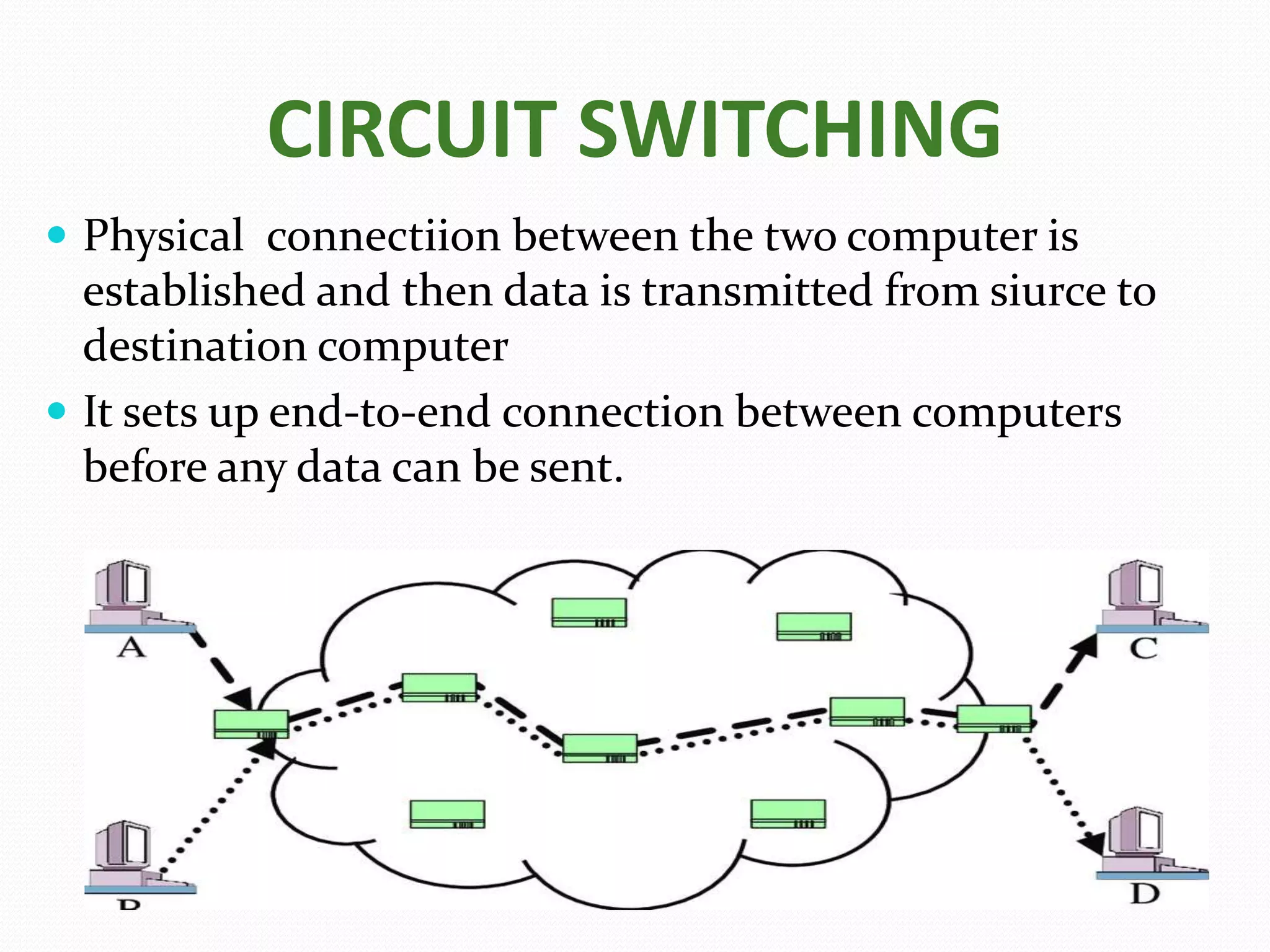
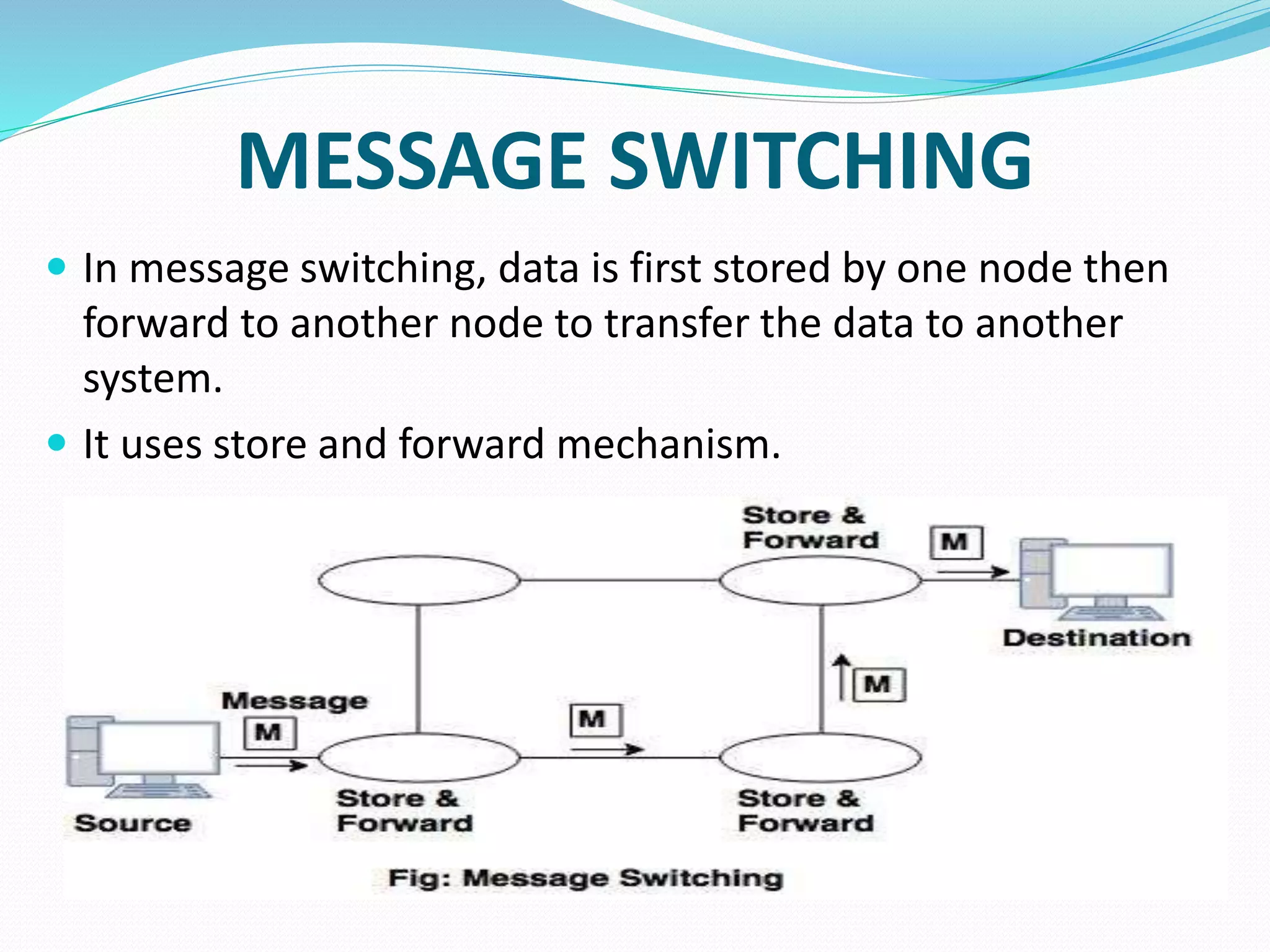
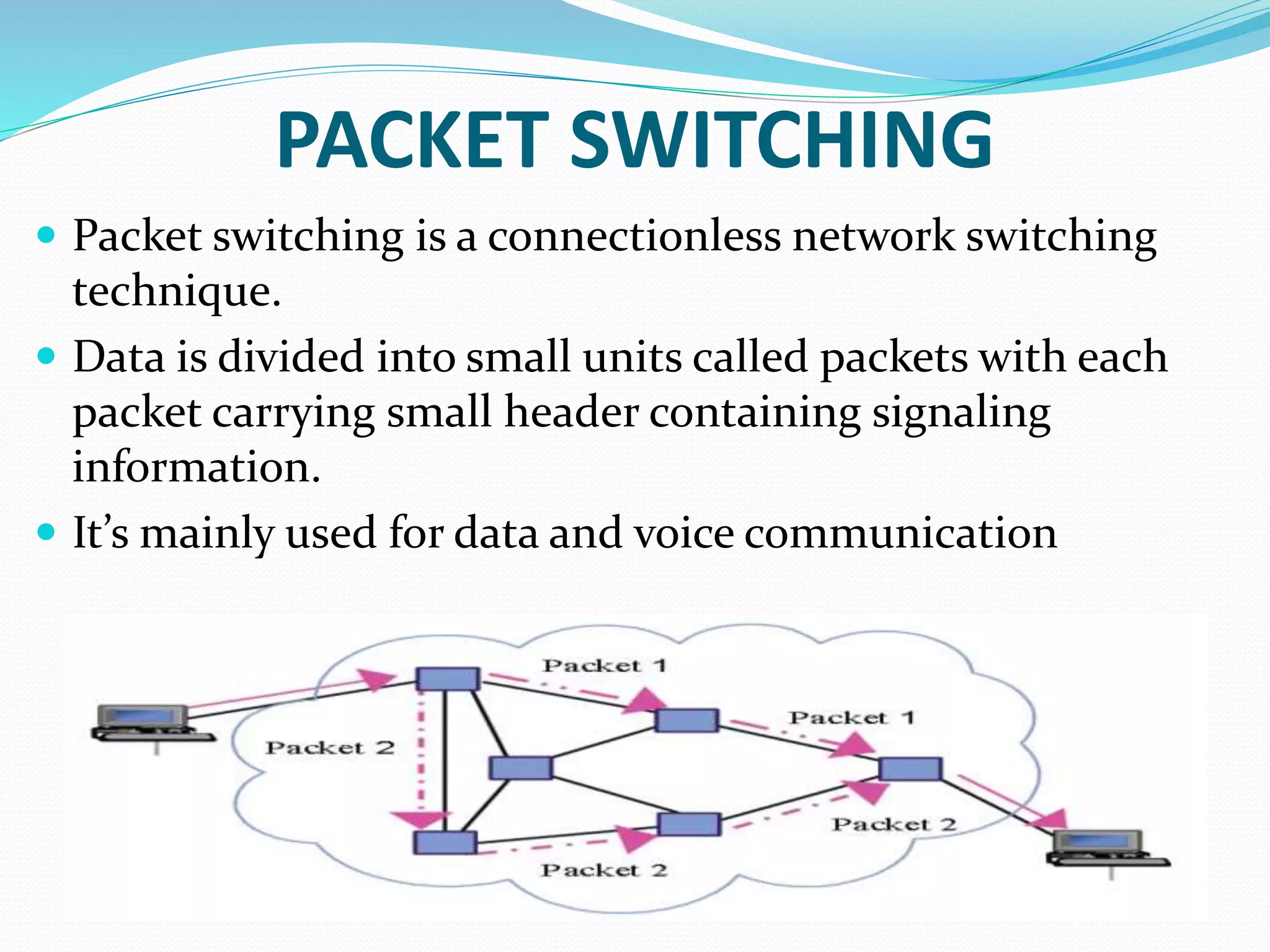
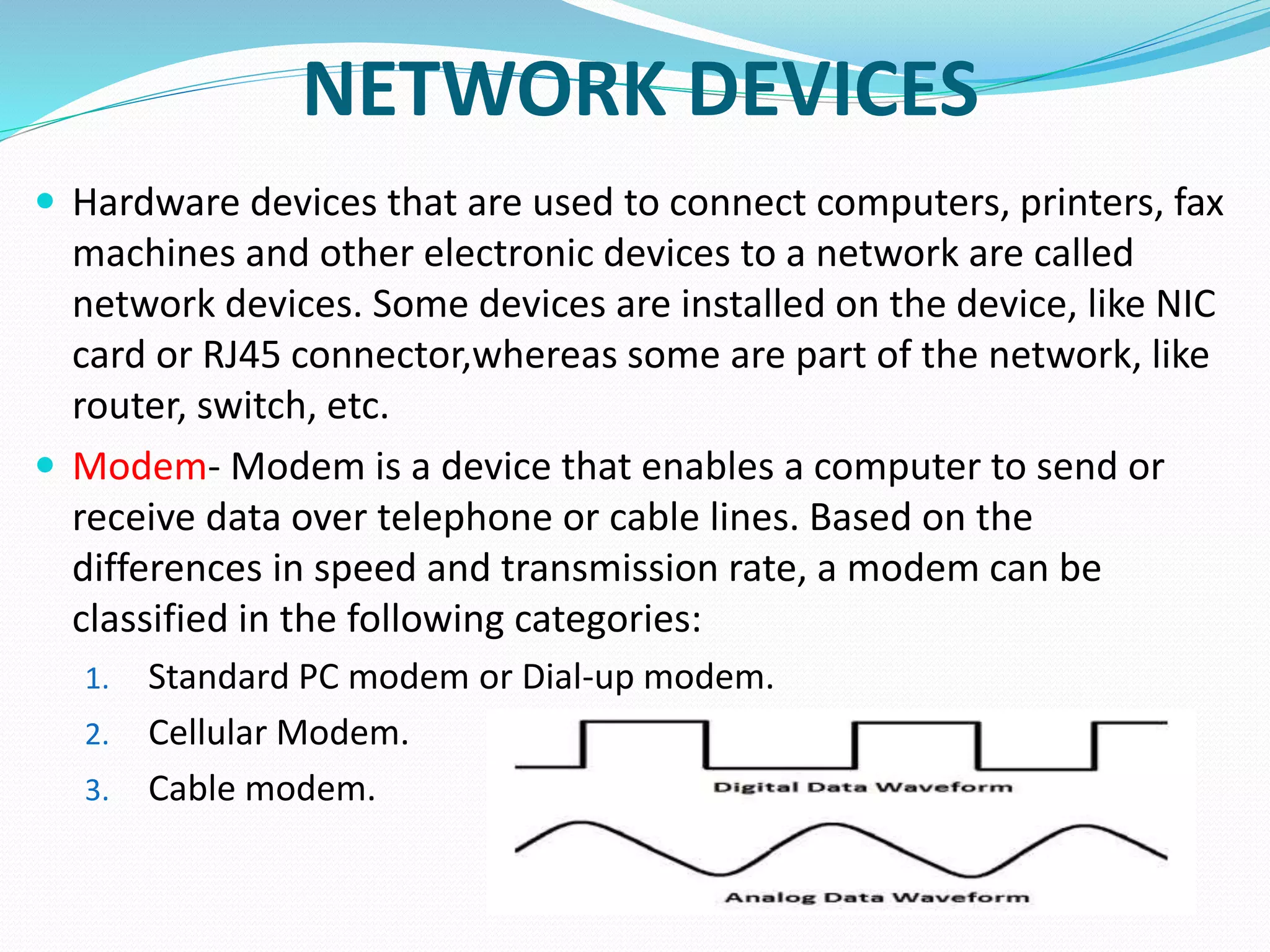
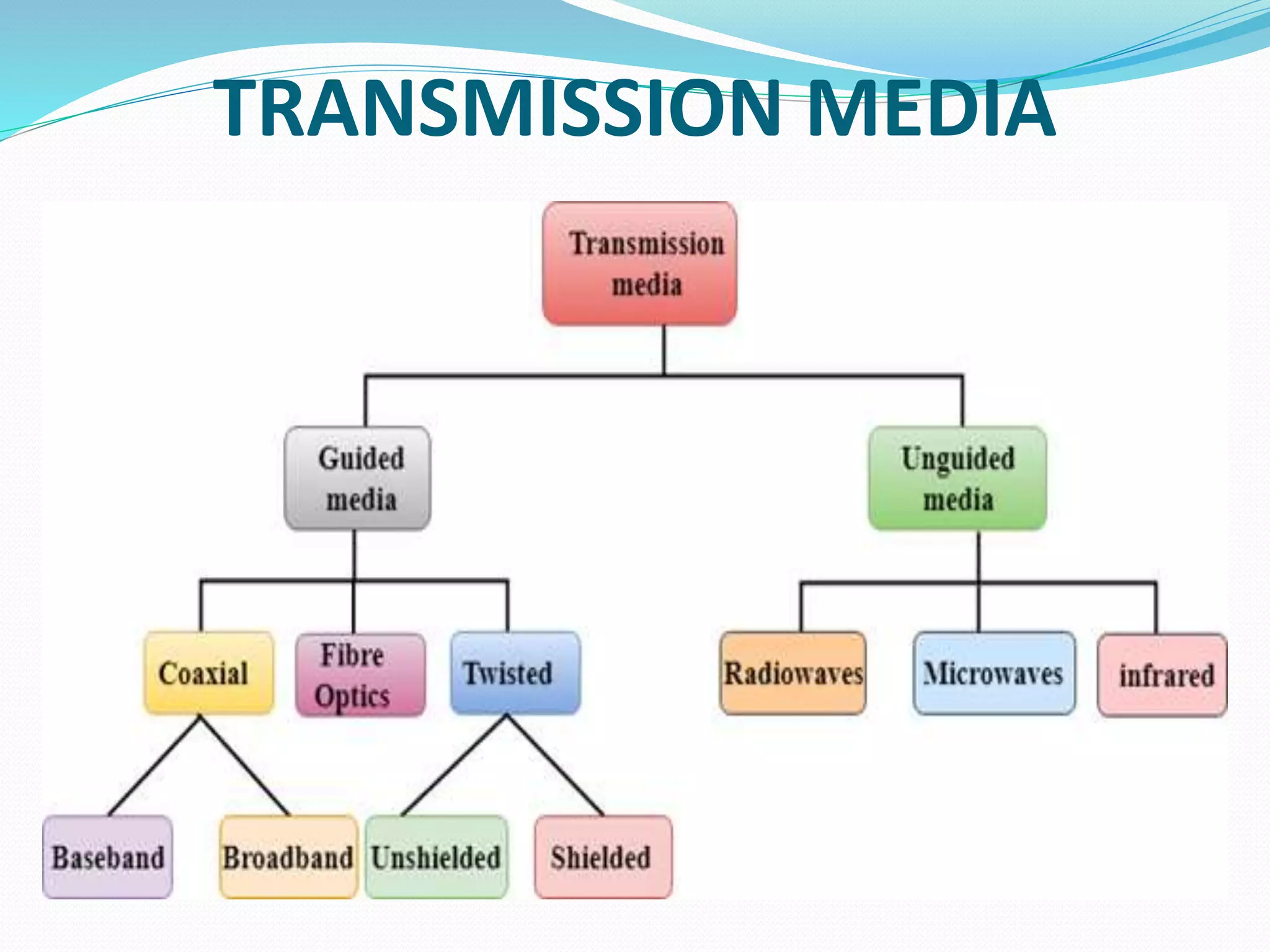
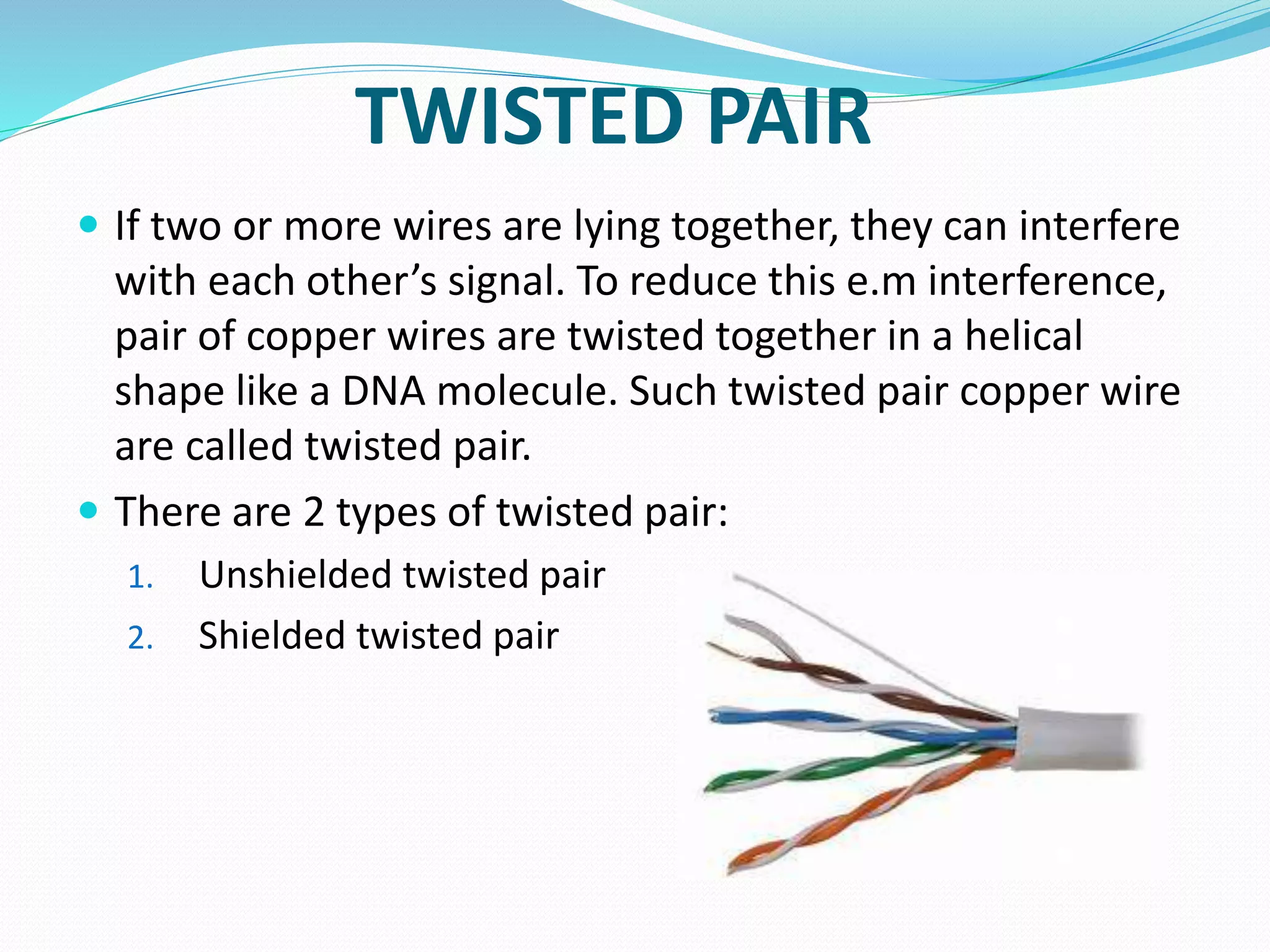
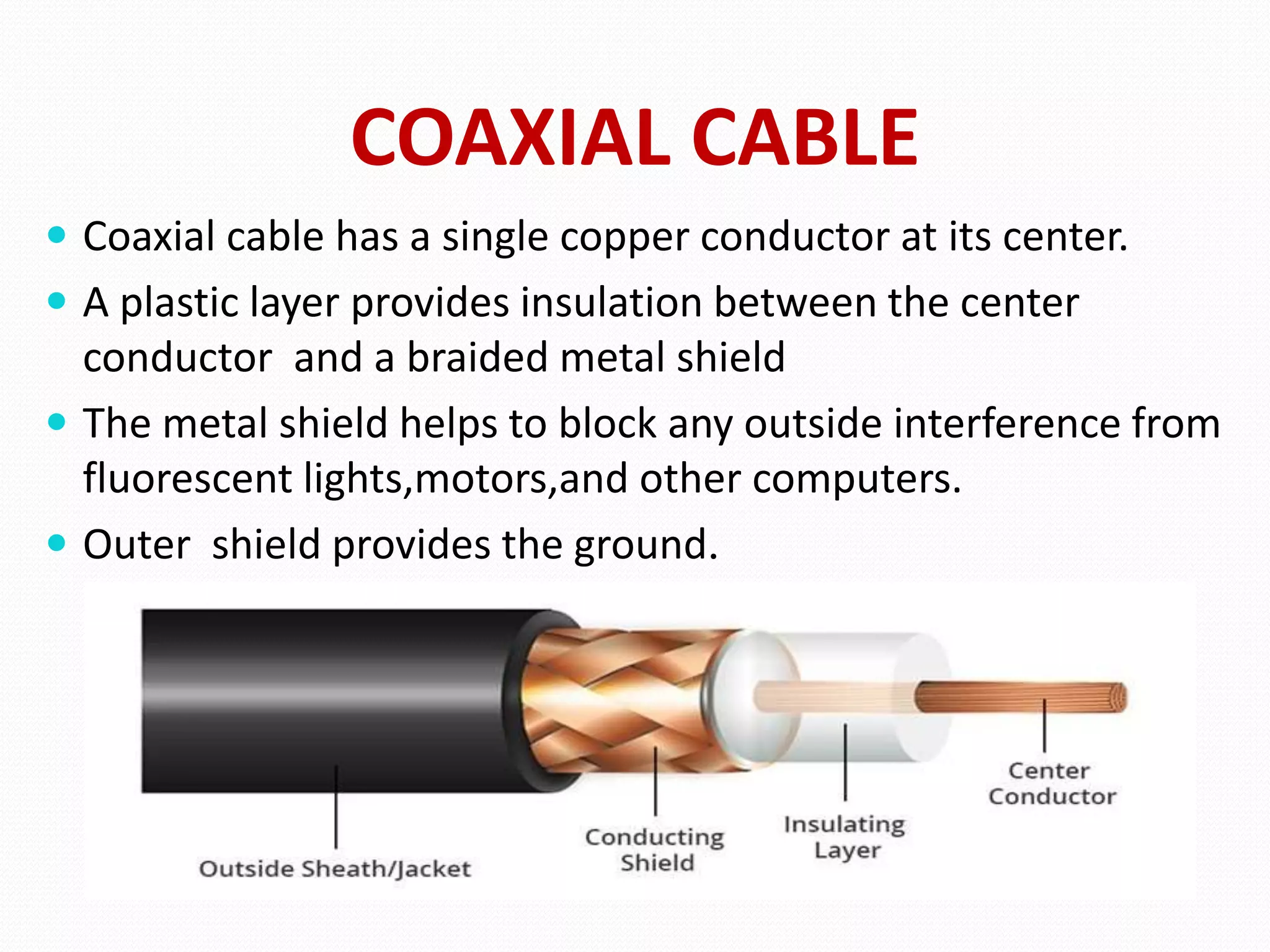
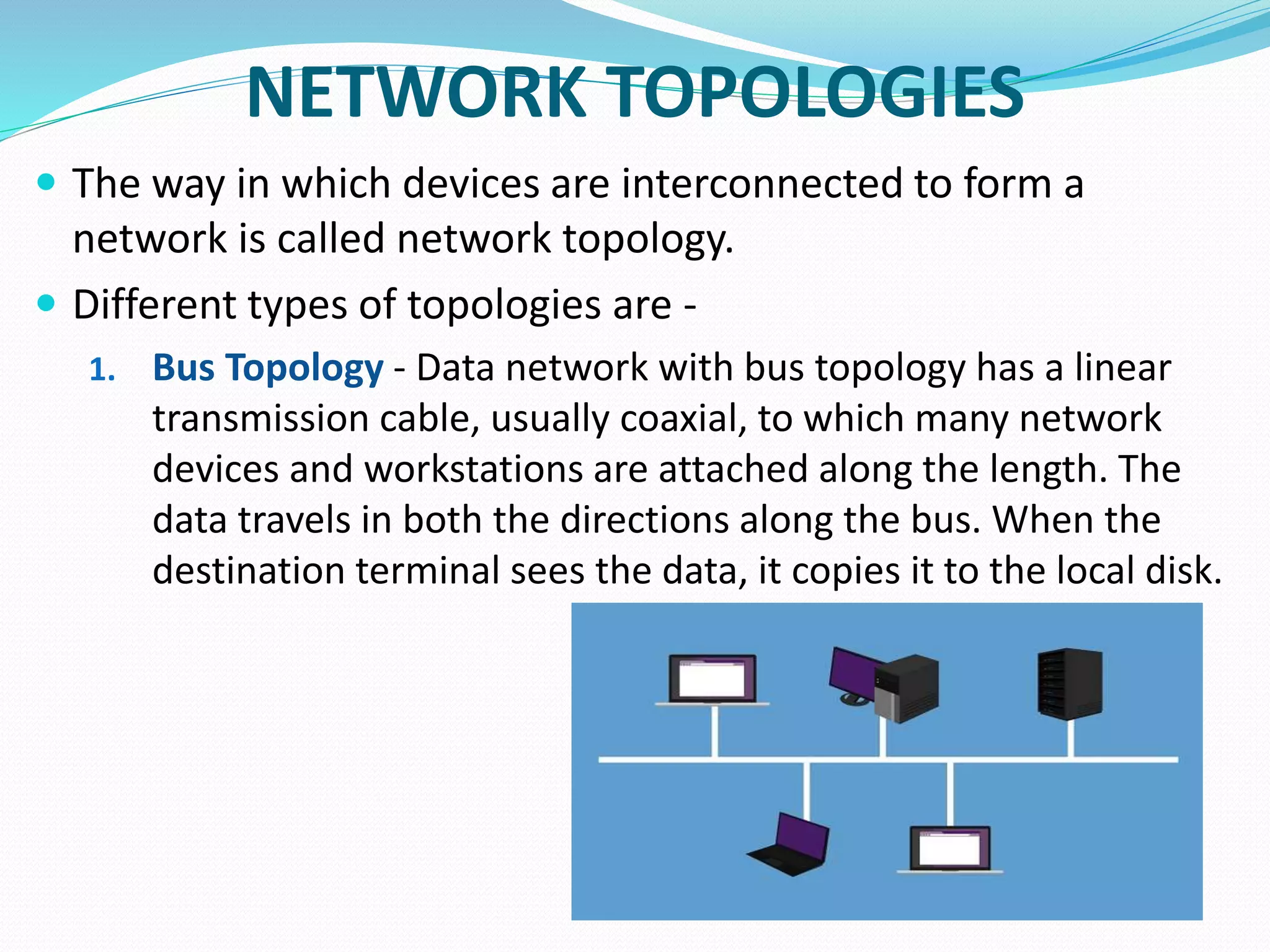
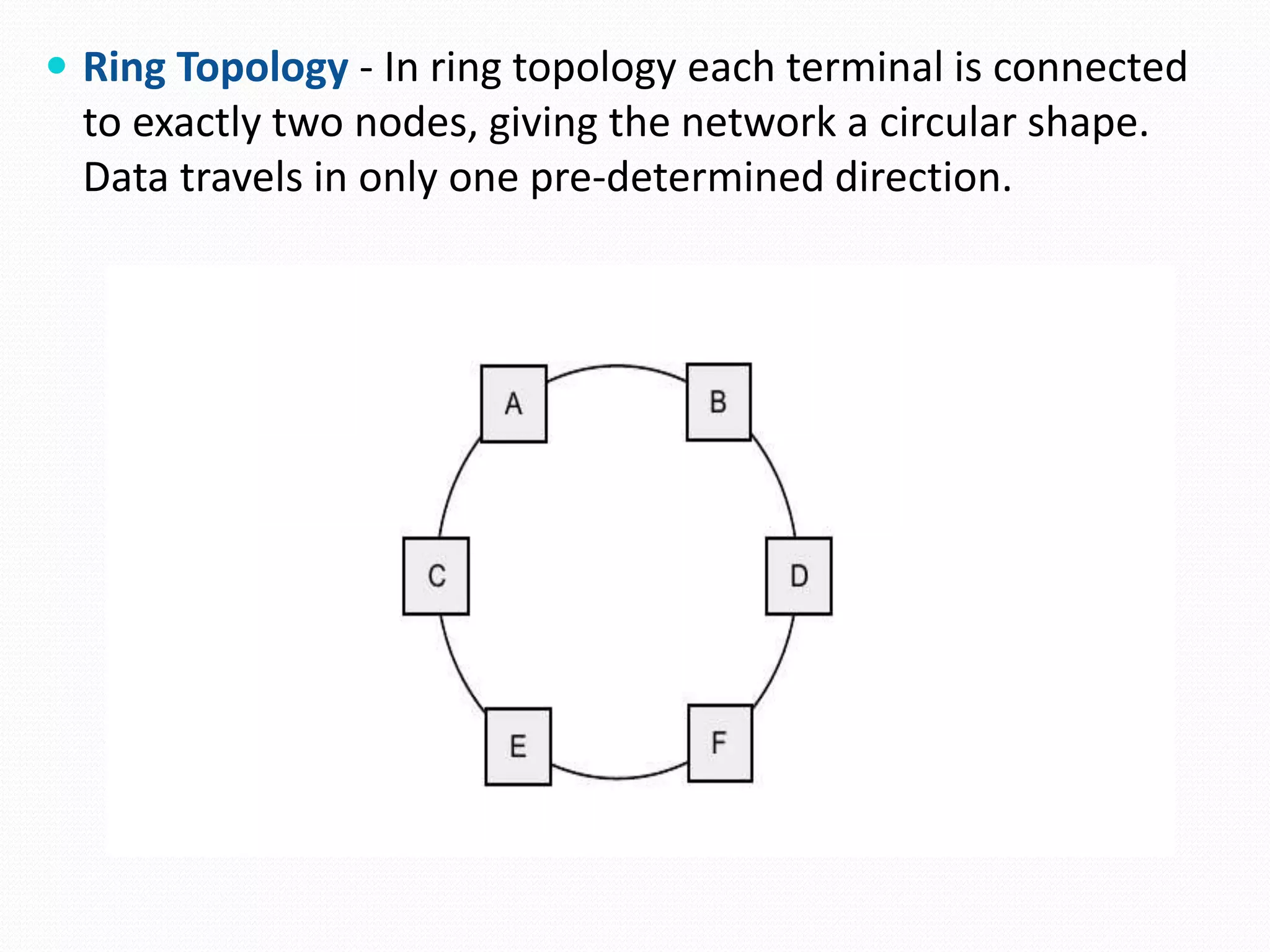
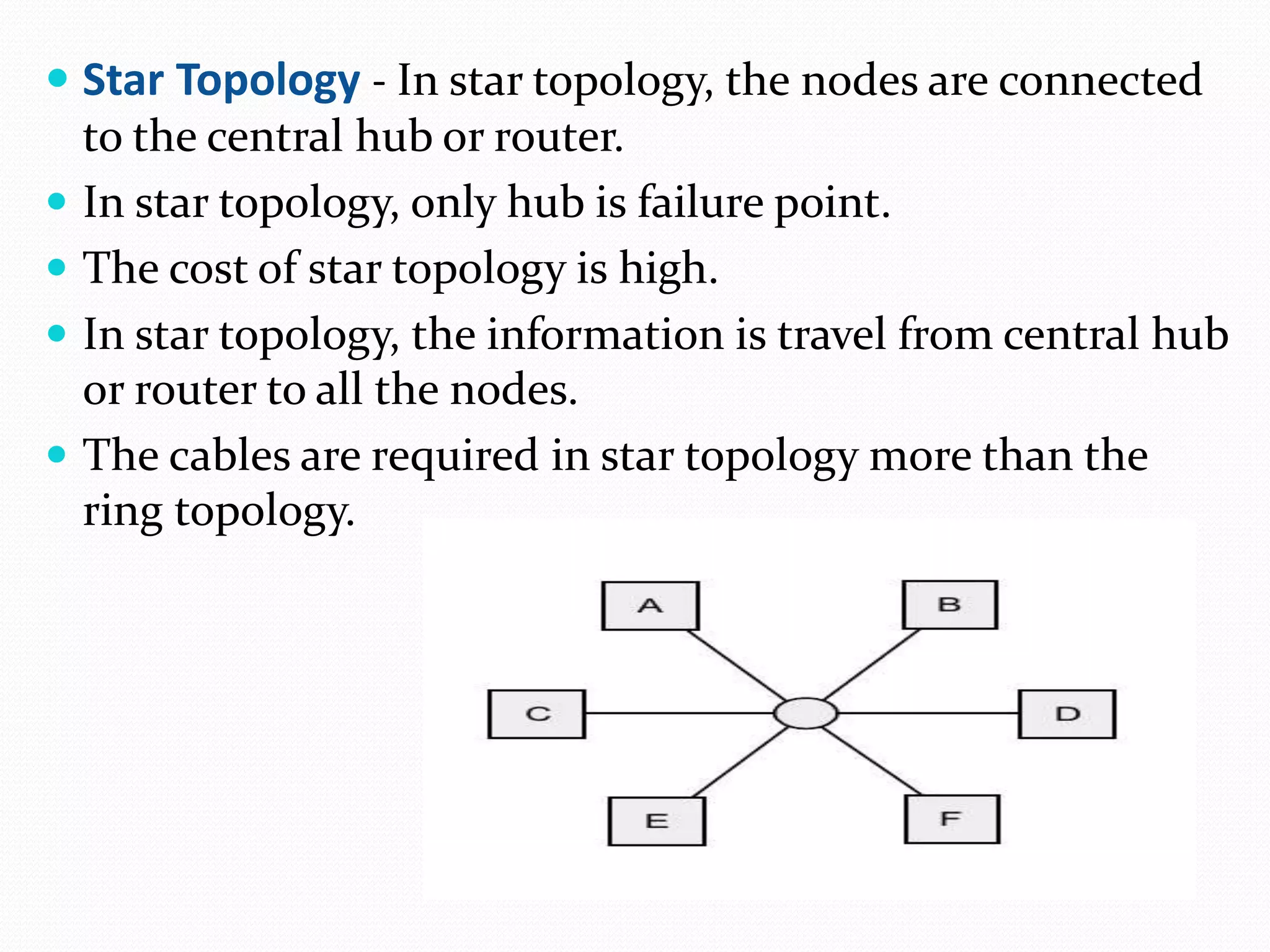
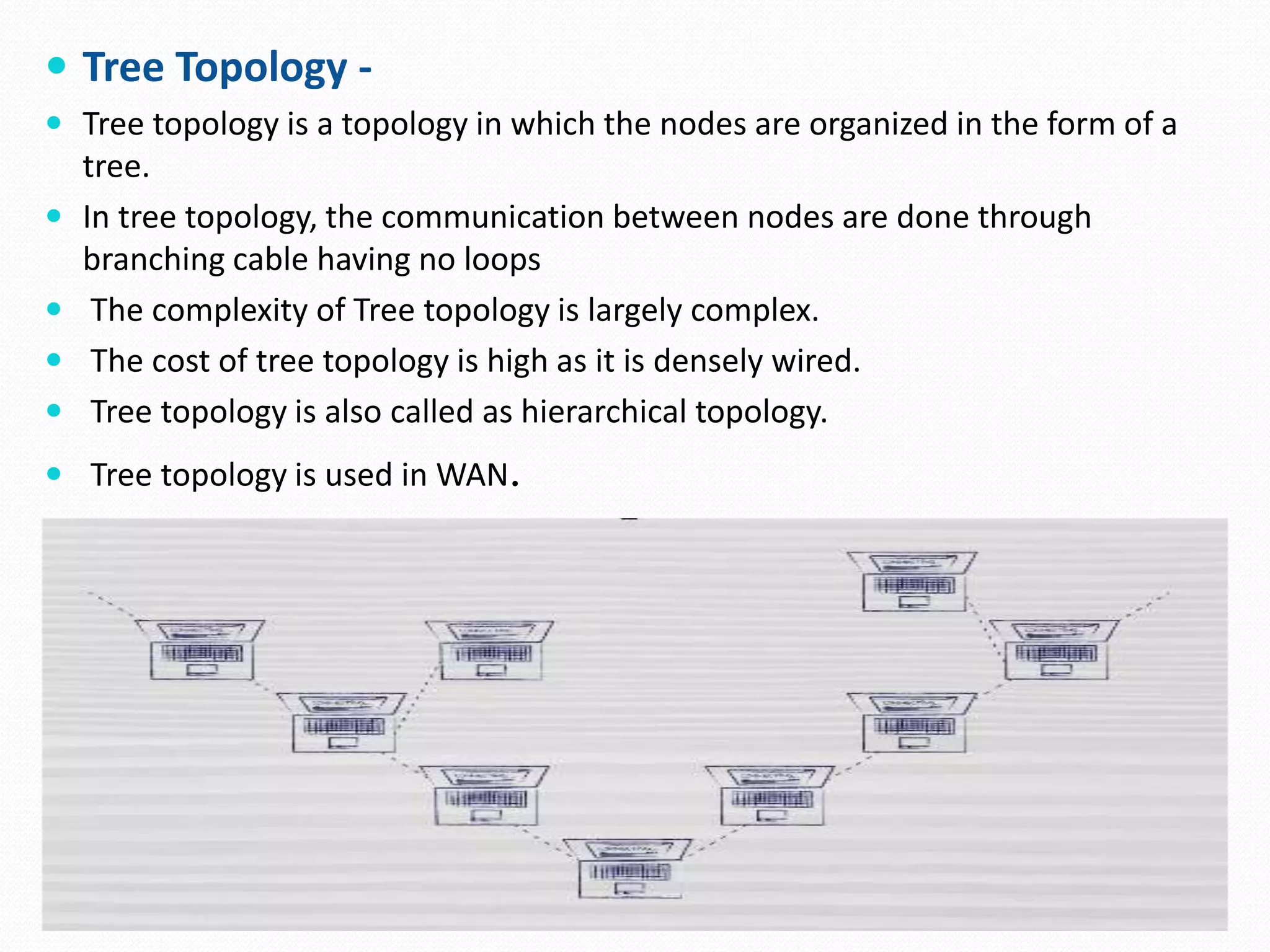
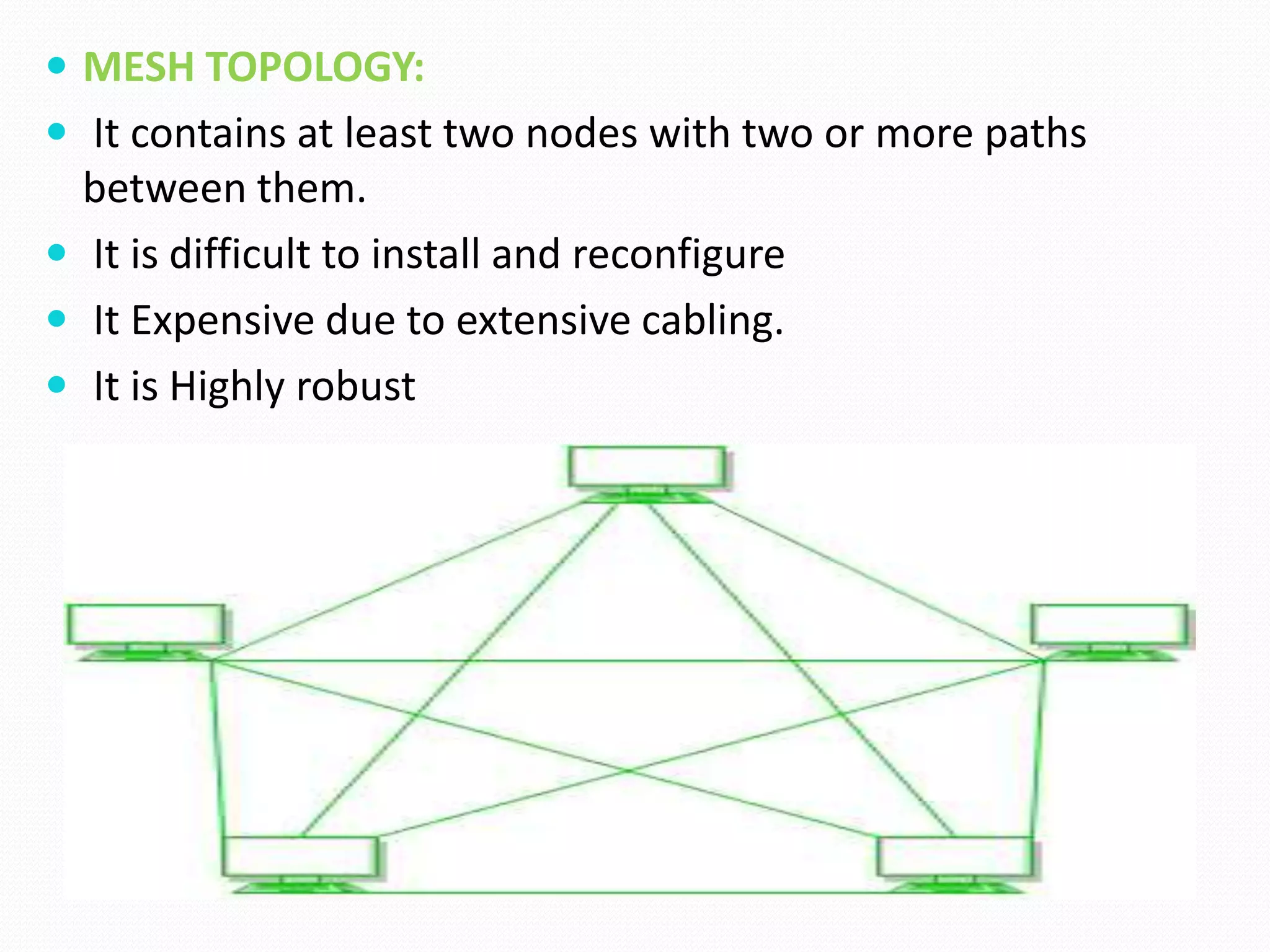
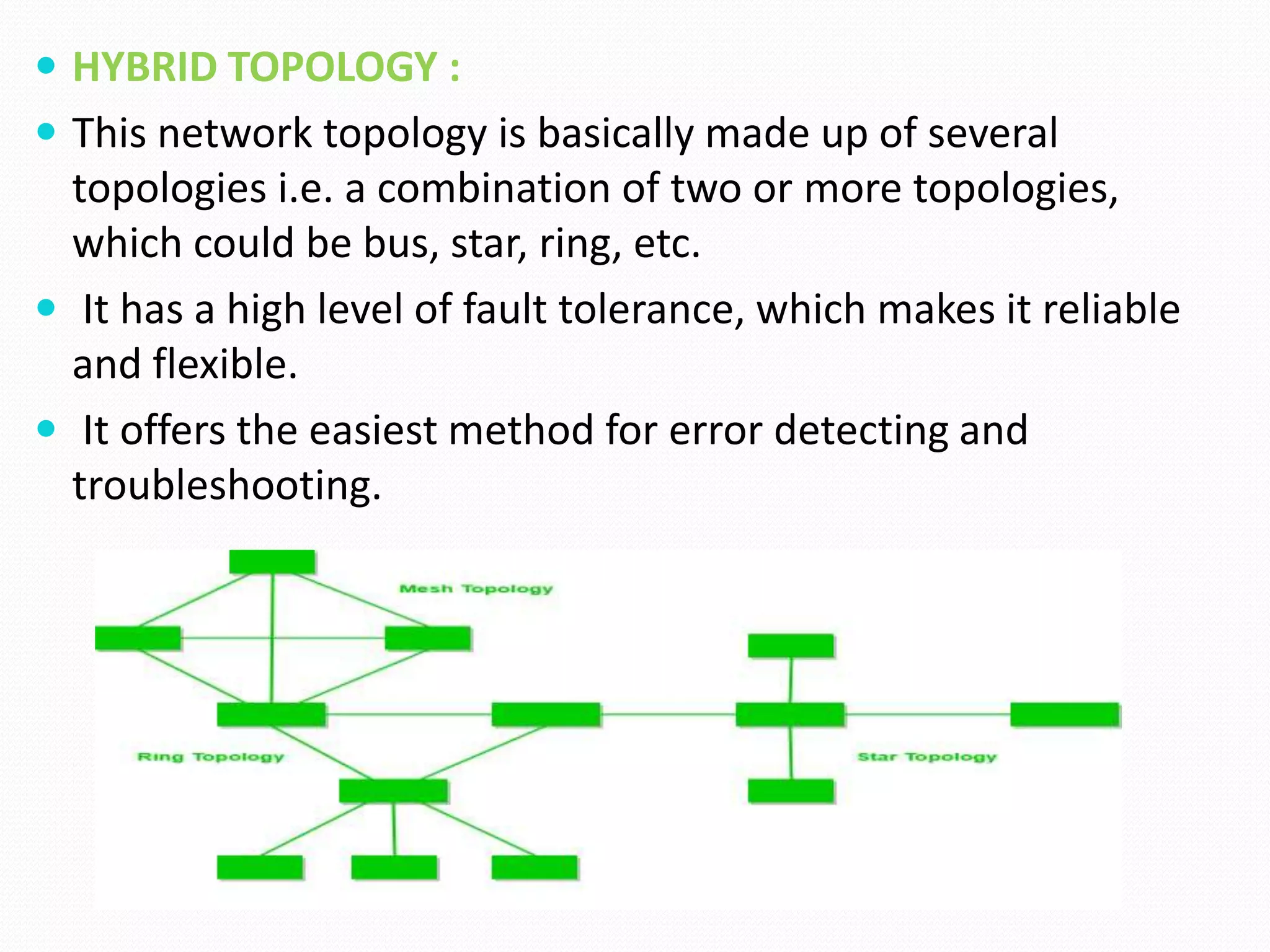
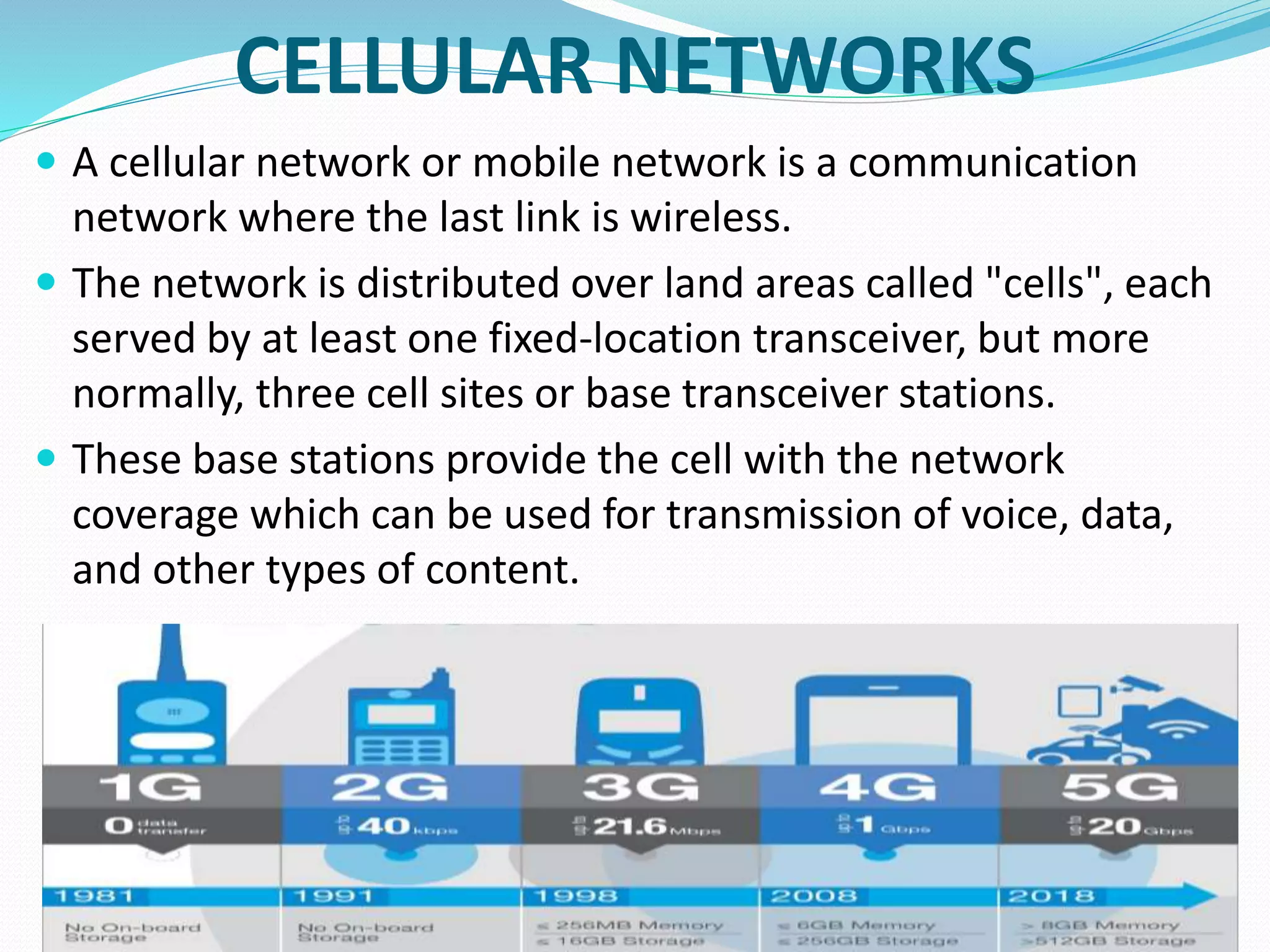
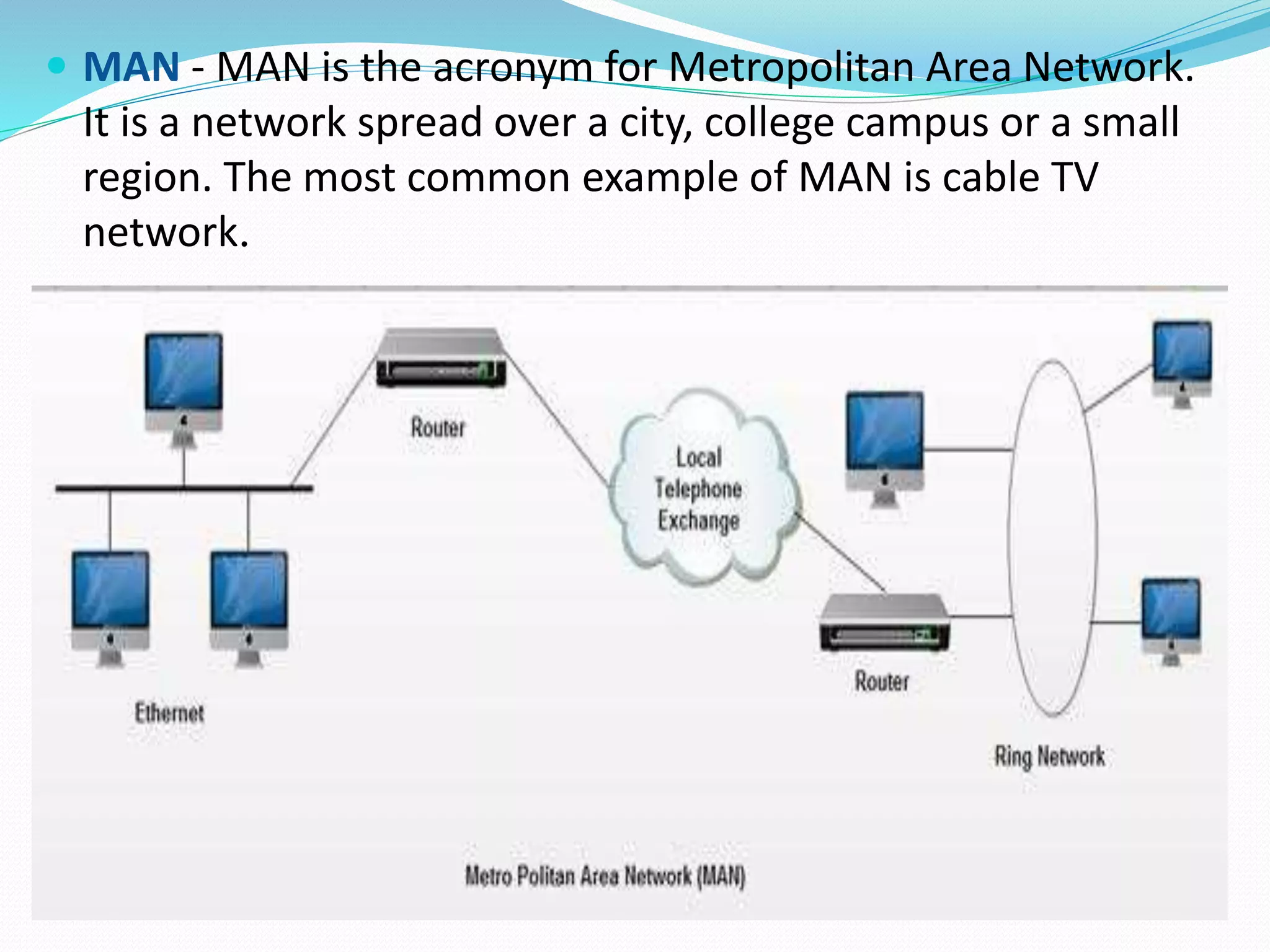
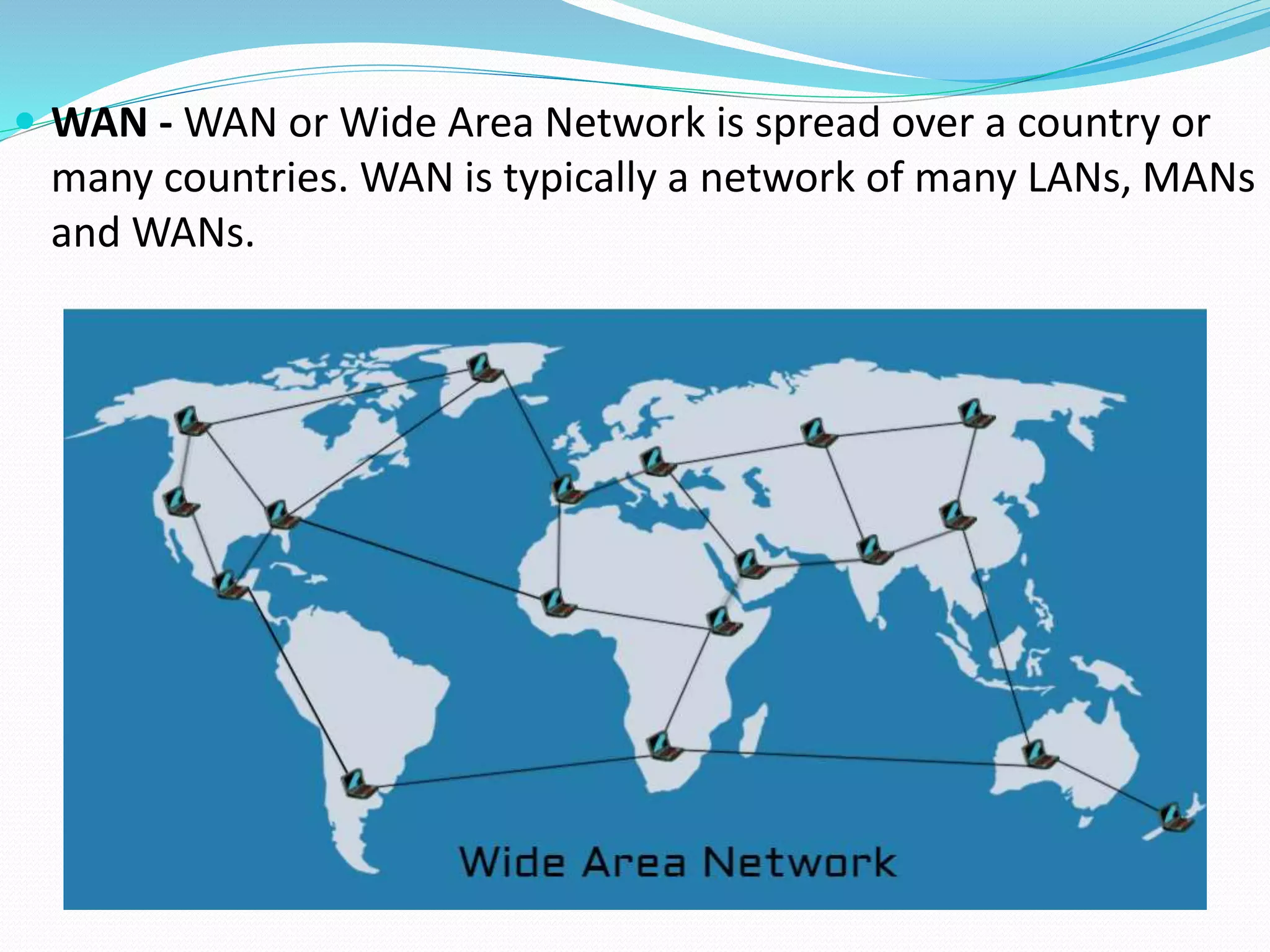
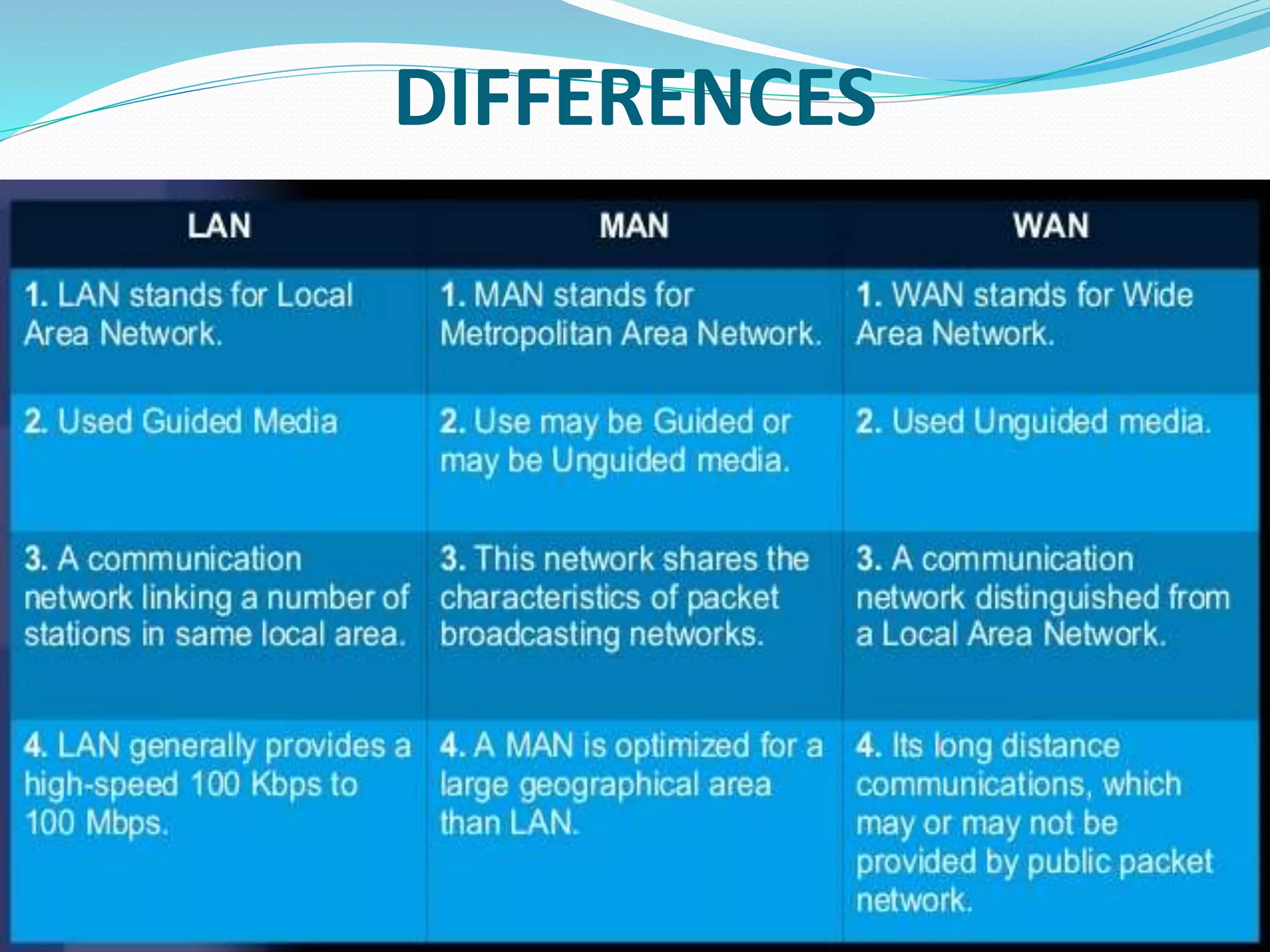
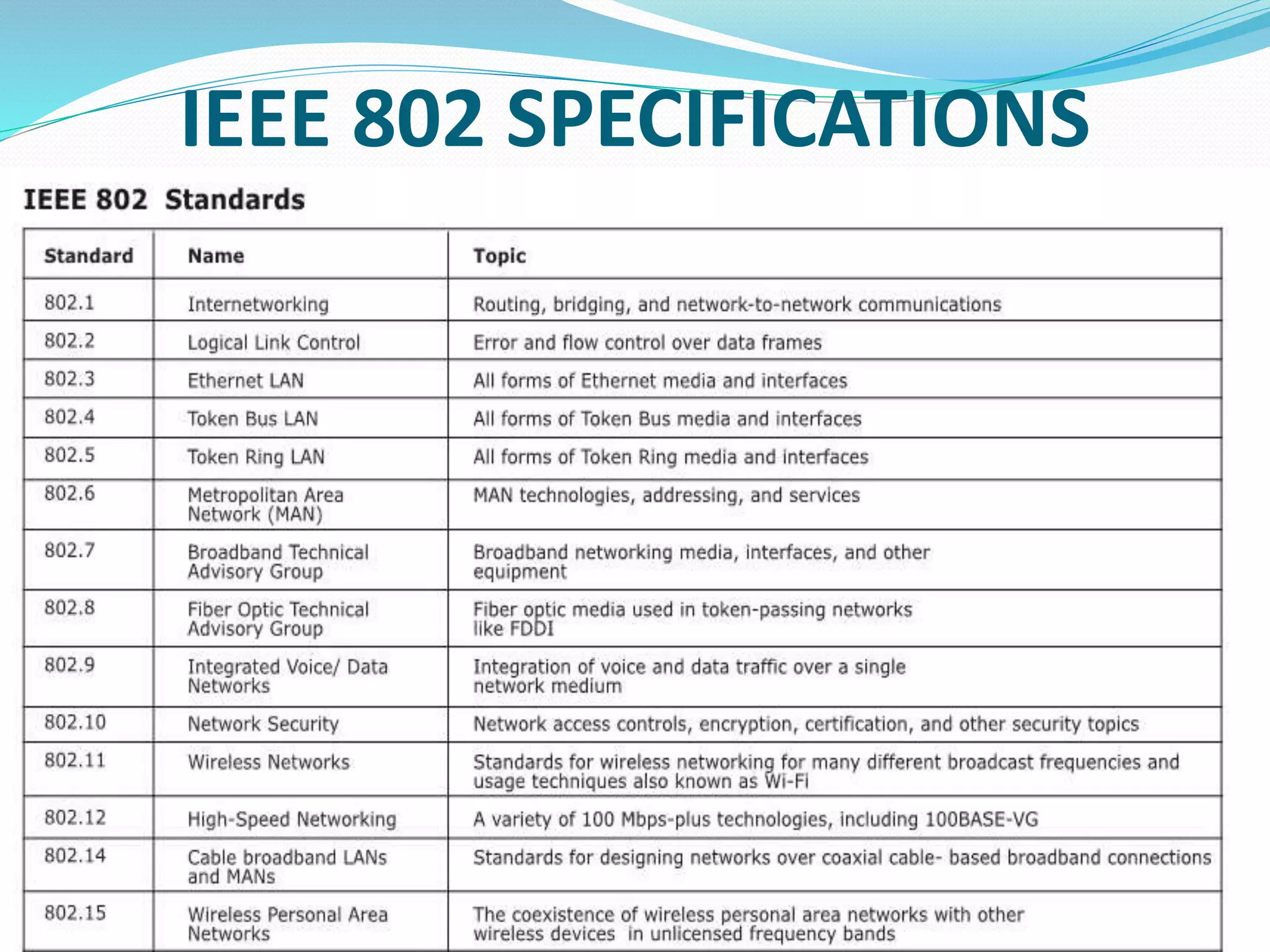
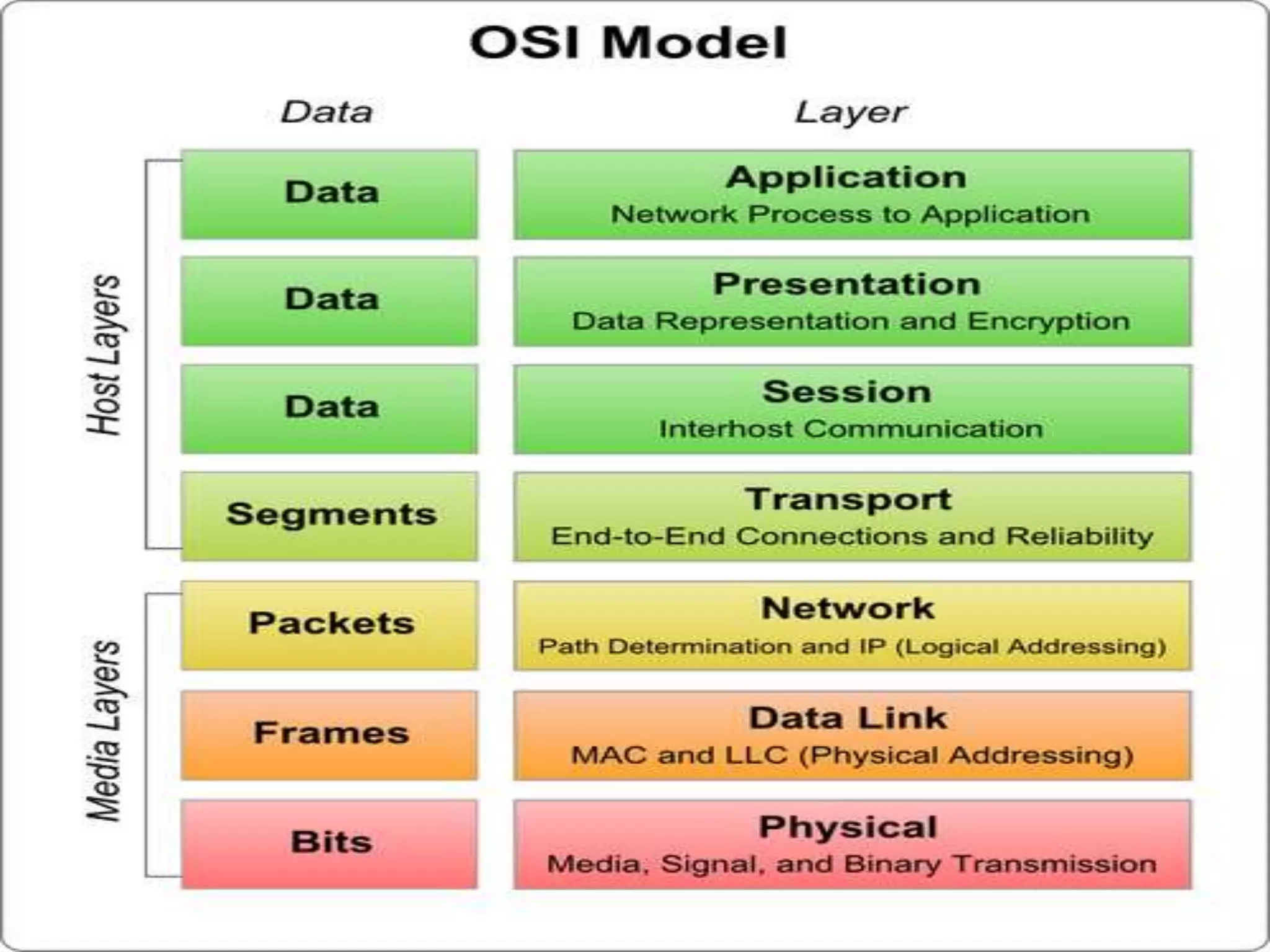
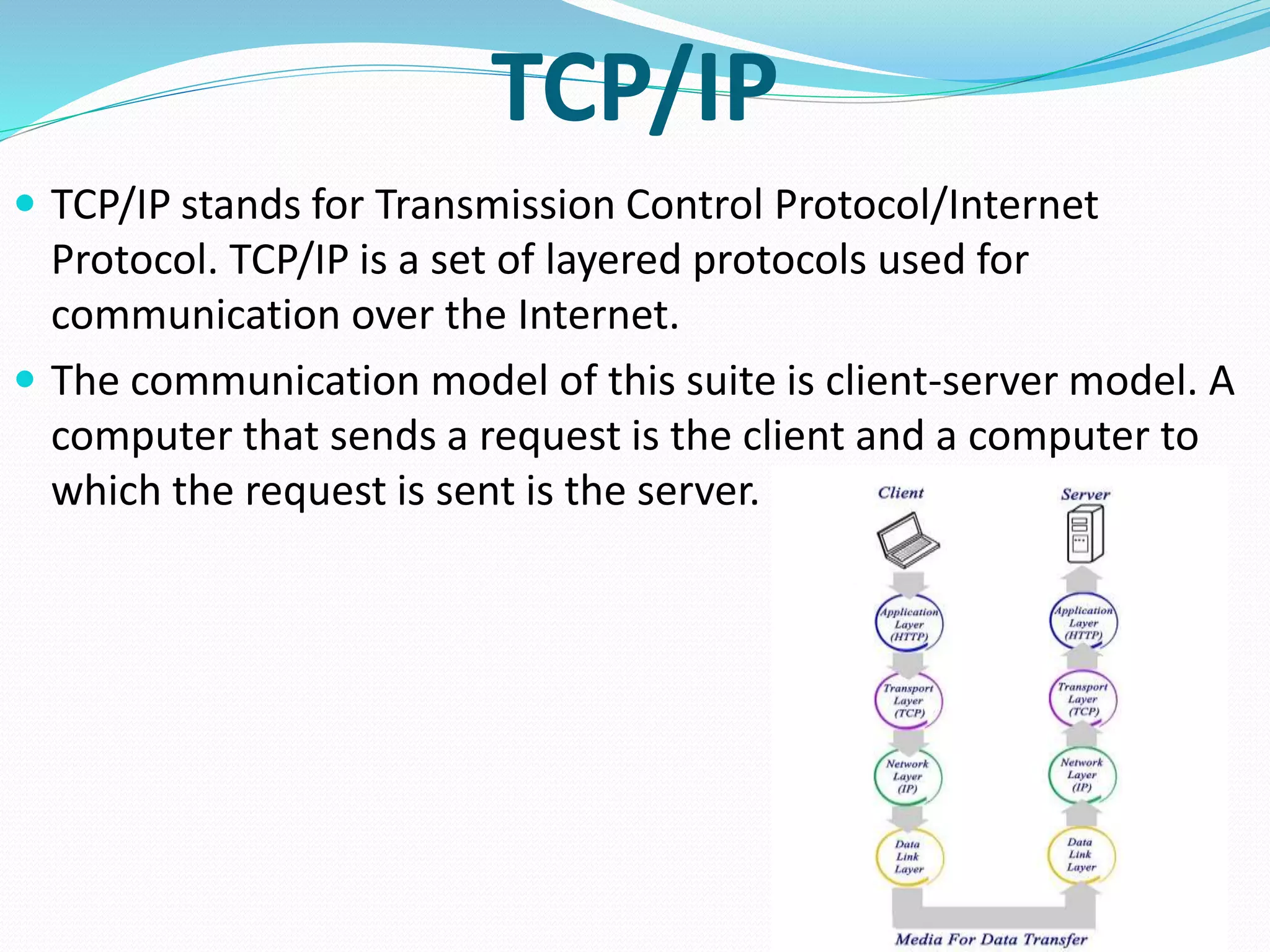
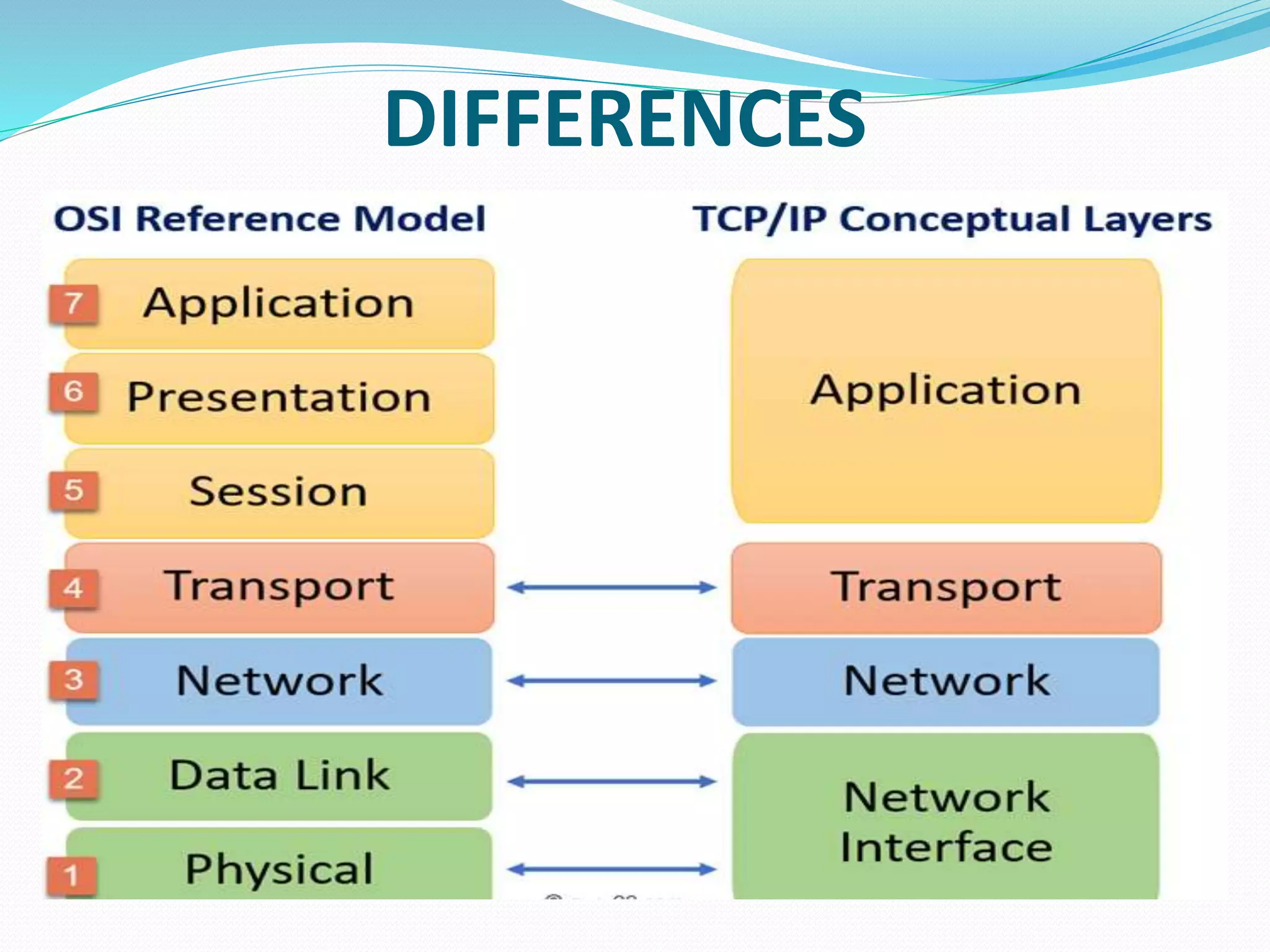
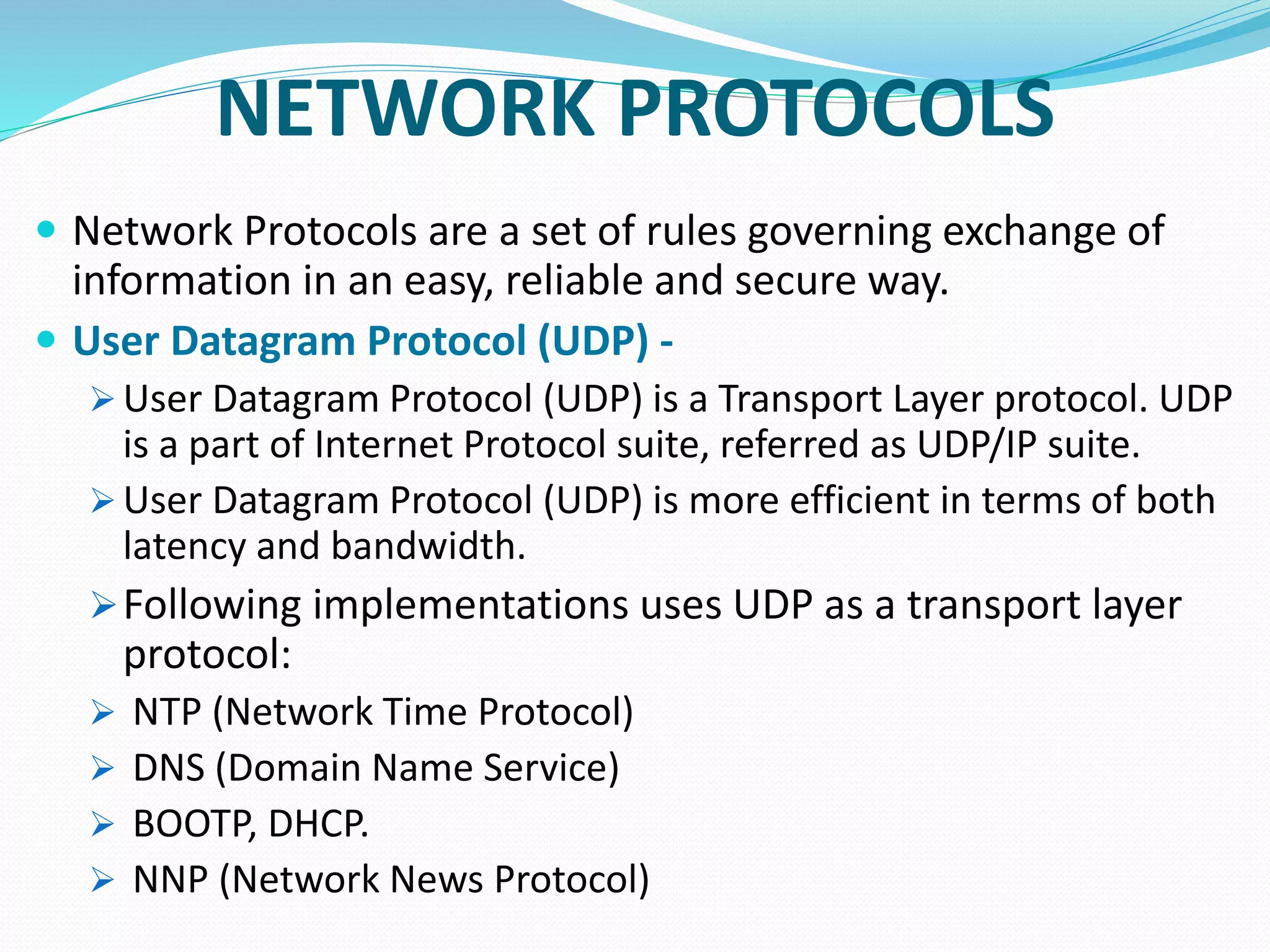
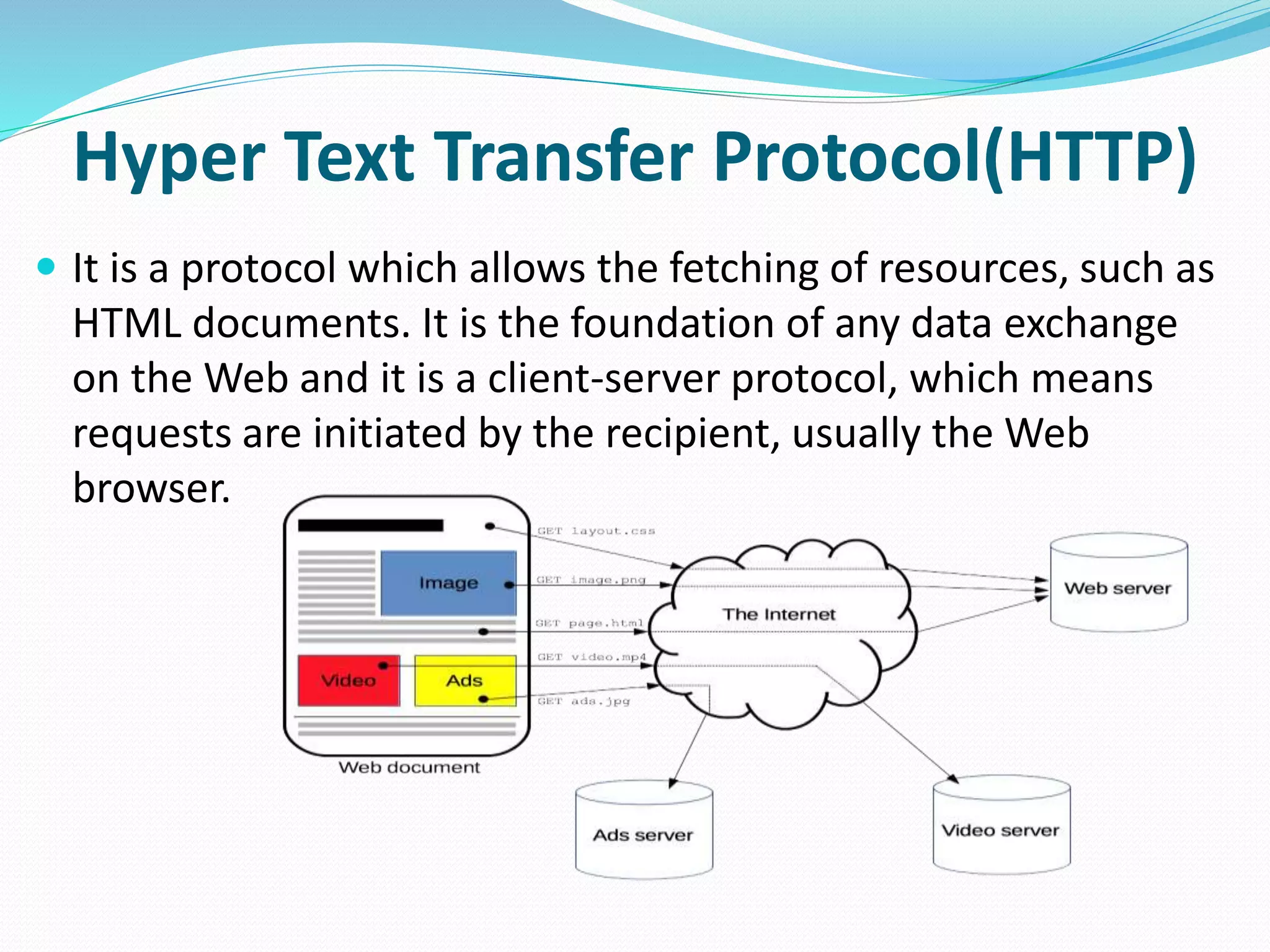
This document provides an overview of computer networking concepts including network architecture, evolution of networking technologies, common network devices, transmission media, network topologies, wireless technologies, types of networks, standards organizations like IEEE, common network models, important network protocols, and types of servers. It covers fundamental topics in a comprehensive manner suitable for an introductory course on computer networks.