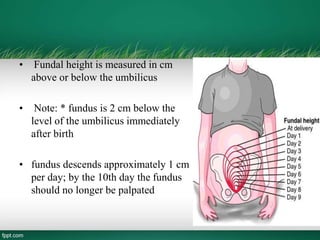
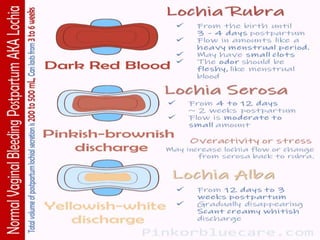
This document outlines the phases of puerperium a new mother goes through, including the taking-in phase where she focuses on self-care, the taking-hold phase where she takes responsibility as a mother, and the letting-go phase when she returns home and accepts her new role. It also describes how to conduct a postpartum physical assessment using the acronym BUBBLERS to check the breasts, uterus, bladder, bowel, lochia, episiotomy, Homans' sign, and emotional response. The assessment is meant to identify needs or potential problems and ensure the mother's recovery is progressing normally.