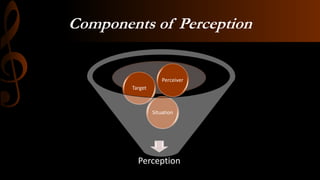
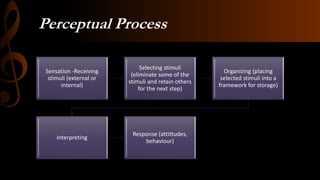
Perception refers to how humans interpret sensory information from their environment. It involves both sensation, which is the initial processing of sensory inputs, and perception, which is the interpretation and organization of those sensations. Perception allows humans to make sense of their surroundings. The process of perception can be influenced by factors related to the perceiver themselves, such as attitudes and experiences, as well as factors related to the external situation and stimuli being perceived. Accurate perception is important for humans to appropriately respond to their environment, while errors in perception like illusions and hallucinations can lead to mistaken interpretations.