Embed presentation
Downloaded 87 times


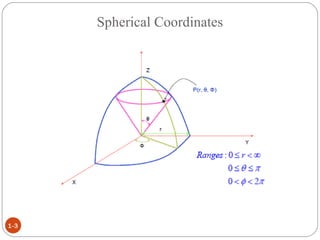
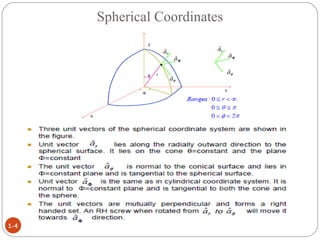
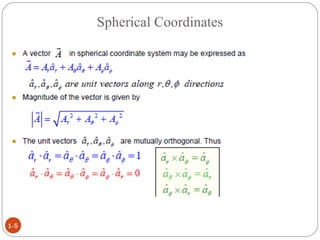
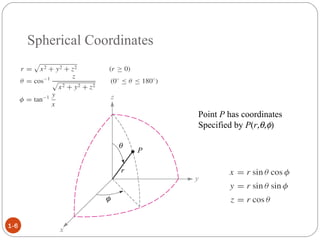
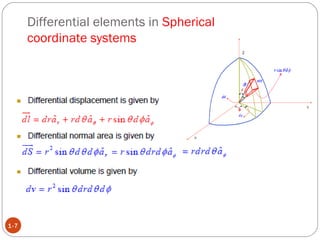
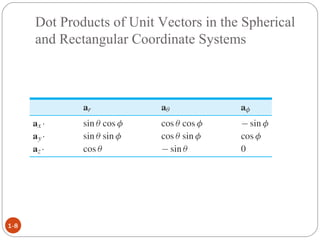
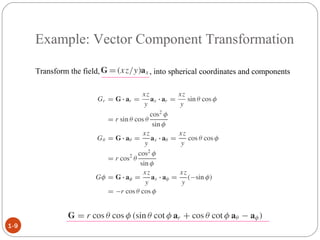

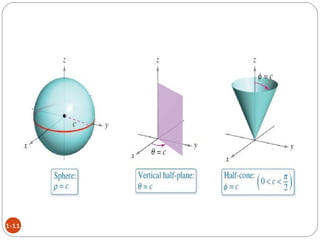

In spherical coordinates, each point is represented by an ordered triple of a distance and two angles, similar to the latitude-longitude system used on Earth. A point P is specified by its coordinates P(r,θ,φ), where r is the distance from the origin and θ and φ are the angular coordinates. Orthogonal surfaces in the spherical coordinate system are generated by keeping r, θ, or φ constant, resulting in a sphere, circular cone, or semi-infinite plane, respectively.











