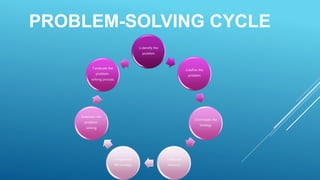
The document discusses creative thinking, problem solving, and various techniques. It defines creativity as having the capacity to consider something new and unique. Developing creativity involves thinking critically, writing down ideas, asking questions, breaking rules, and embracing mistakes. Problem solving is described as investigating issues systematically and finding solutions, while decision making occurs at each problem solving step. Several problem solving techniques are outlined, including force field analysis, the Delphi technique, and SCAMPER which involves substituting, combining, adapting, modifying, putting to other uses, eliminating, and reversing ideas.