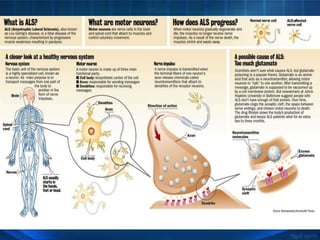
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a fatal neurological disease that causes progressive muscle weakness and paralysis. The exact causes are unknown but may include genetic and environmental factors. Symptoms start with muscle weakness and progress to include slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, and eventually paralysis of the diaphragm leading to respiratory failure. While there is no cure, treatments can help manage symptoms and some medications may slow disease progression. The average life expectancy is 2-5 years from diagnosis but can vary significantly.