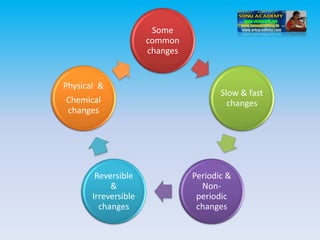
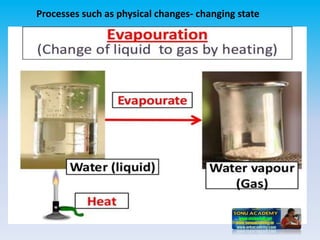
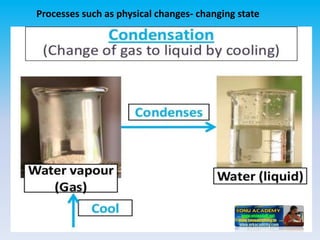
The document defines change in a scientific context, illustrating it as an act that alters the state of a substance, with examples such as ice melting into water. It categorizes changes into types: slow vs. fast, periodic vs. non-periodic, and reversible vs. irreversible, highlighting features and examples for each category. Additionally, it distinguishes between physical changes, which can be reversed, and chemical changes, which result in new substances and are permanent.