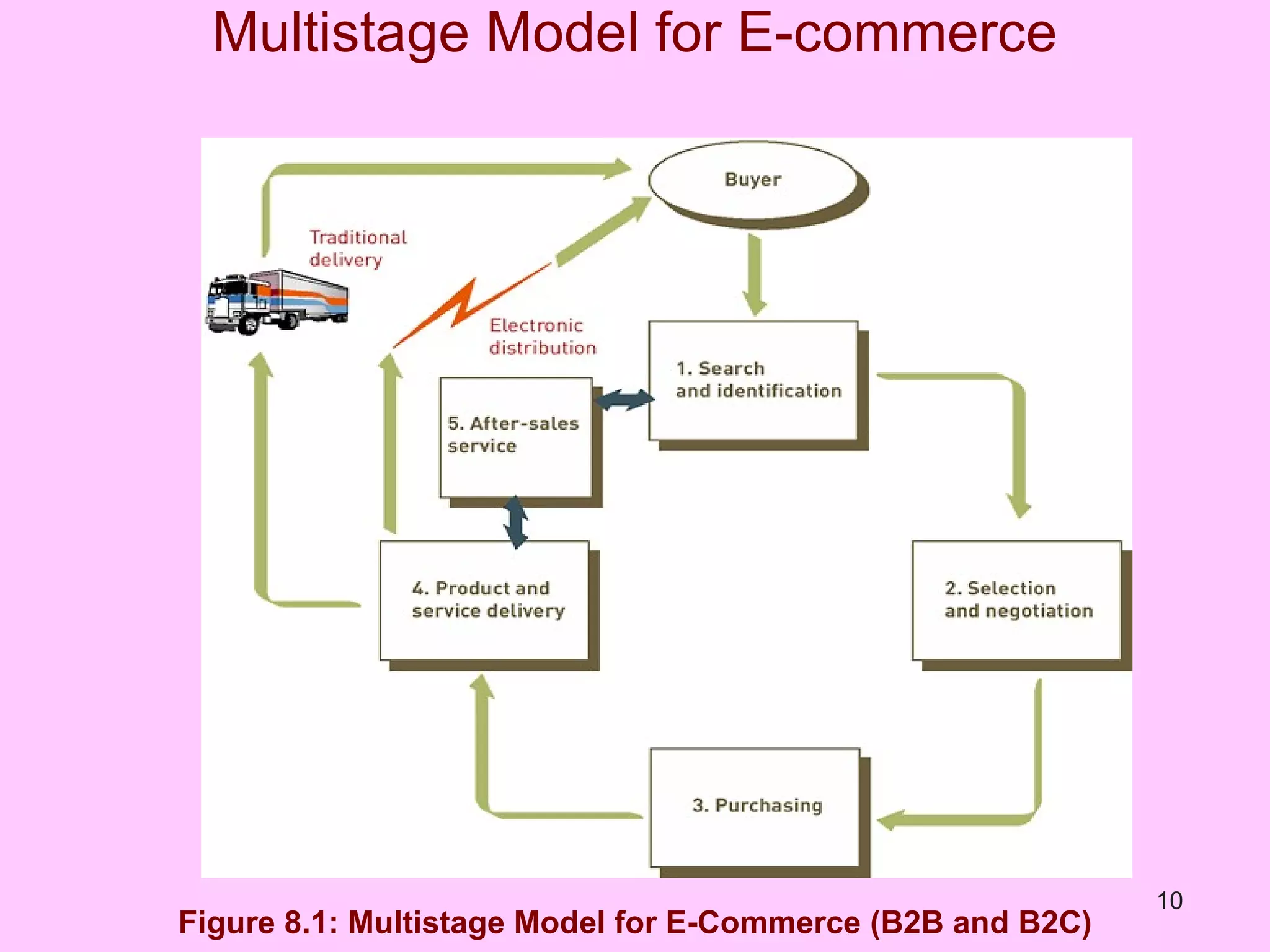
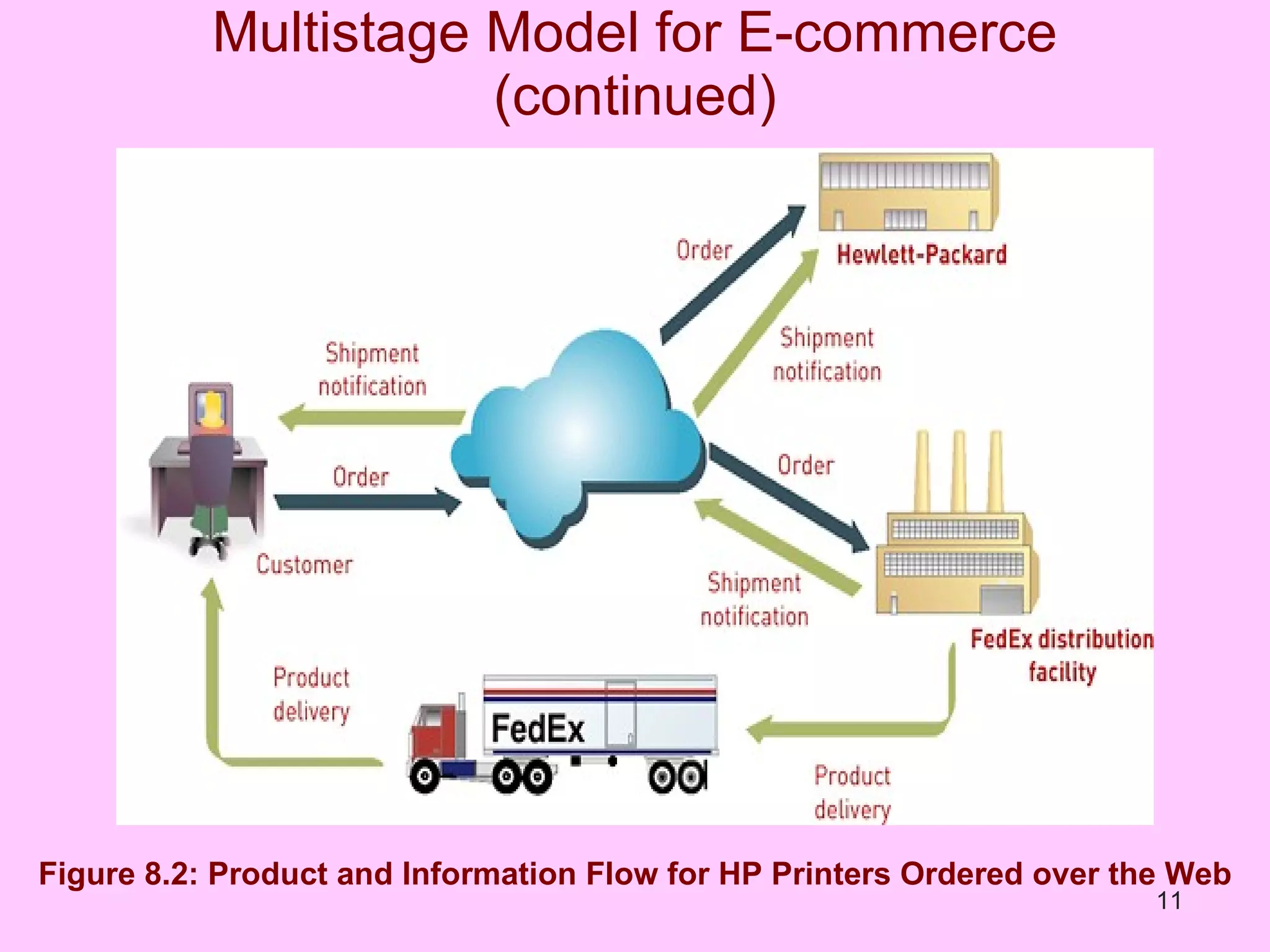
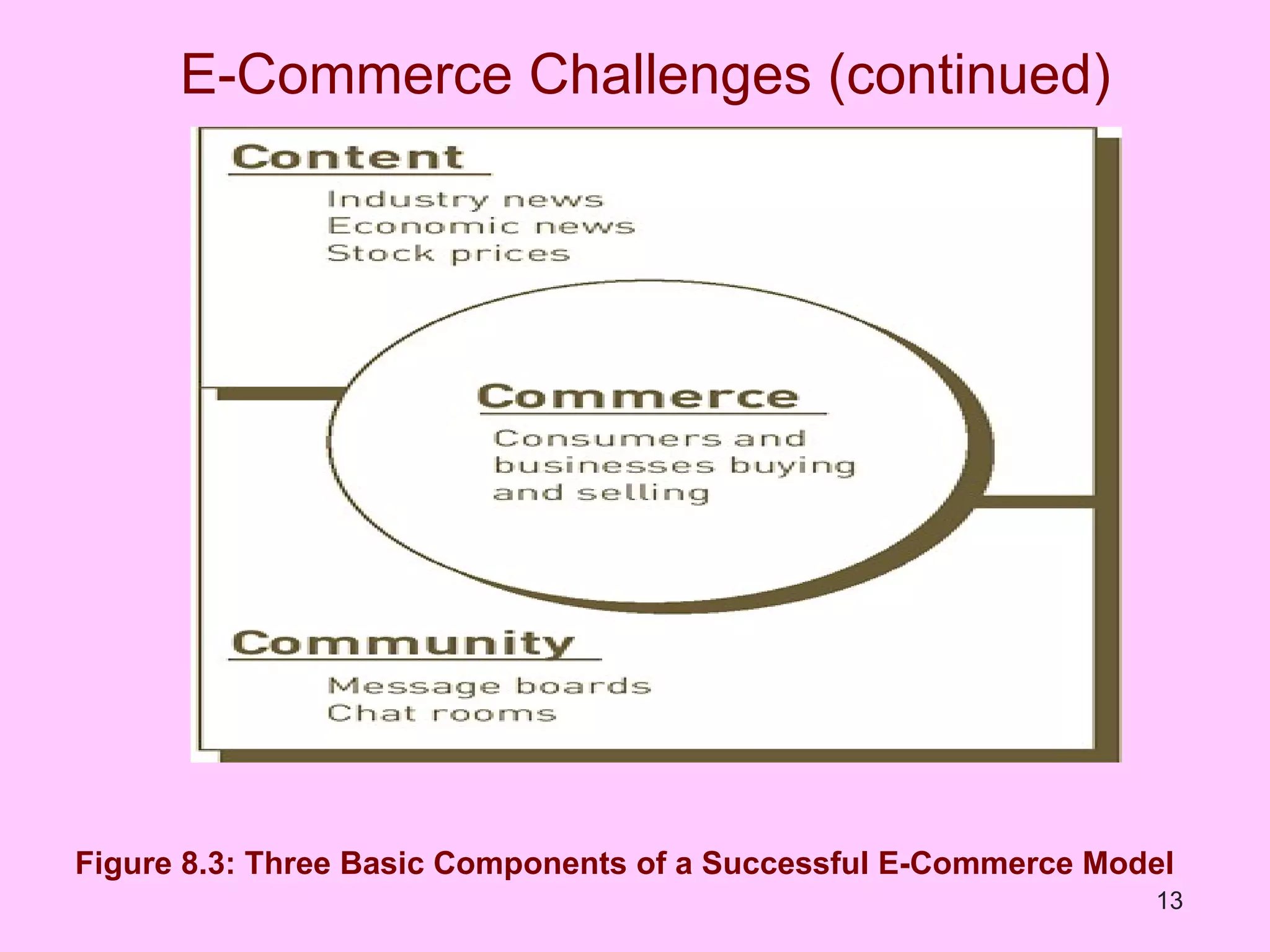
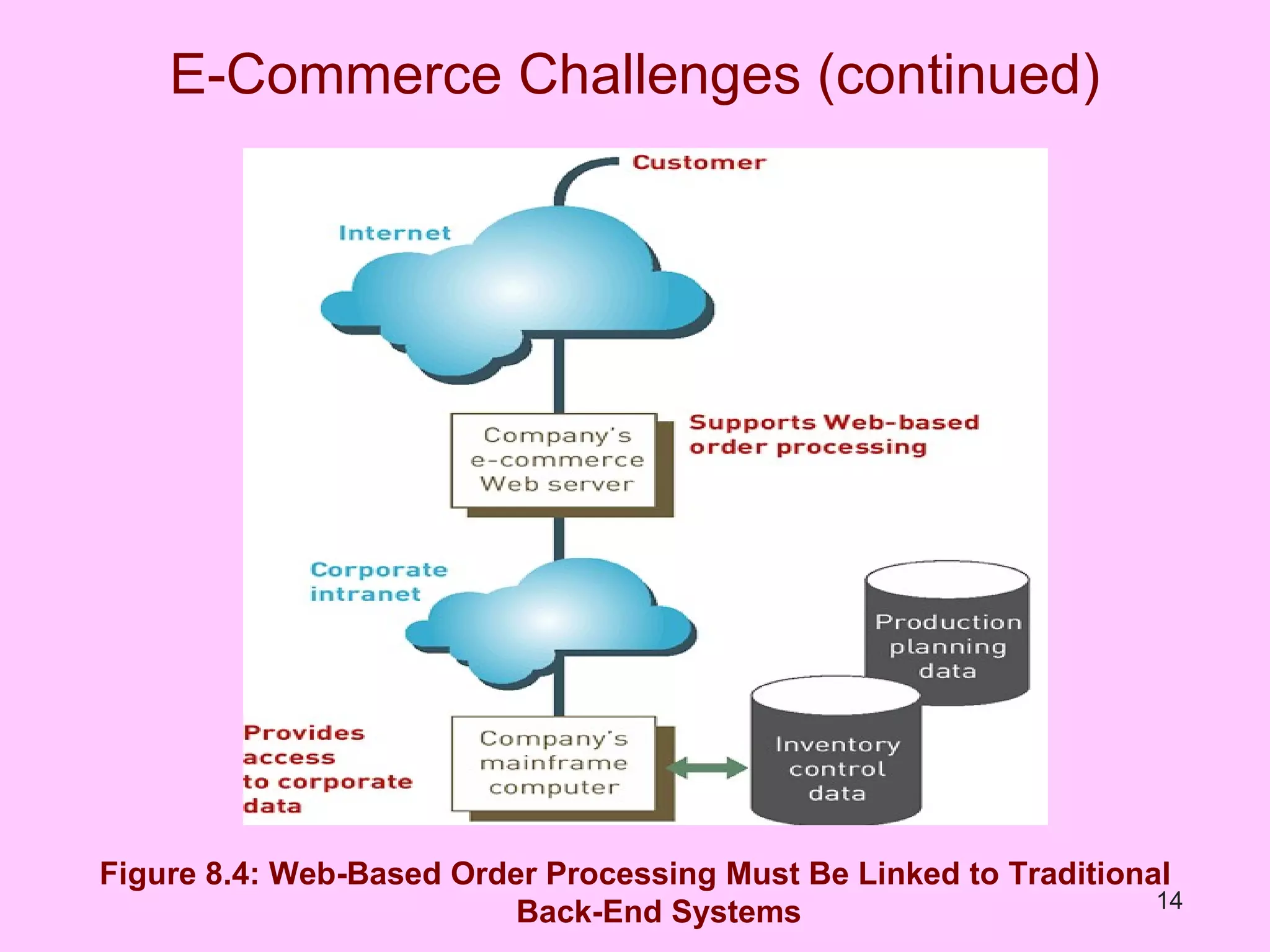
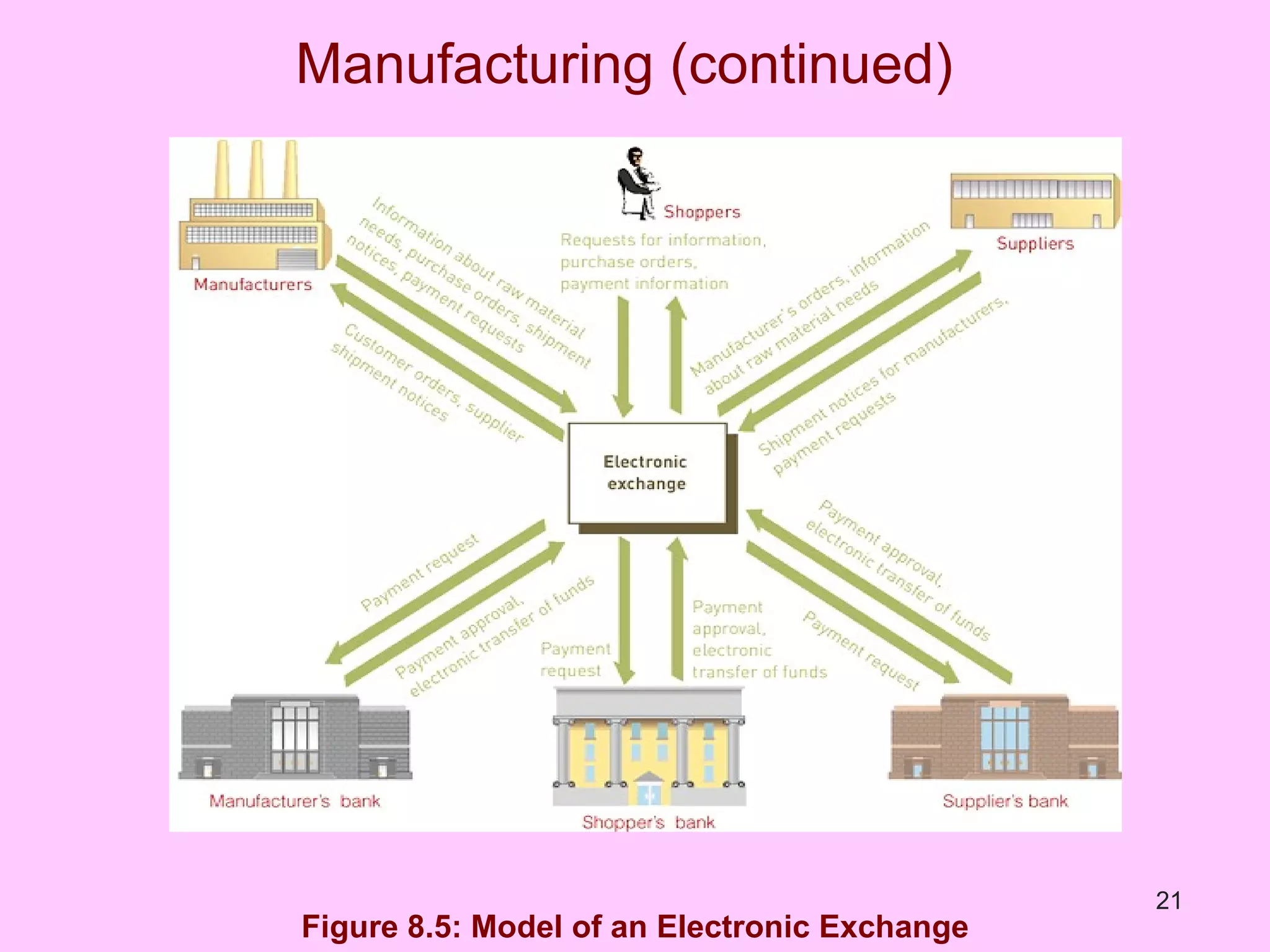
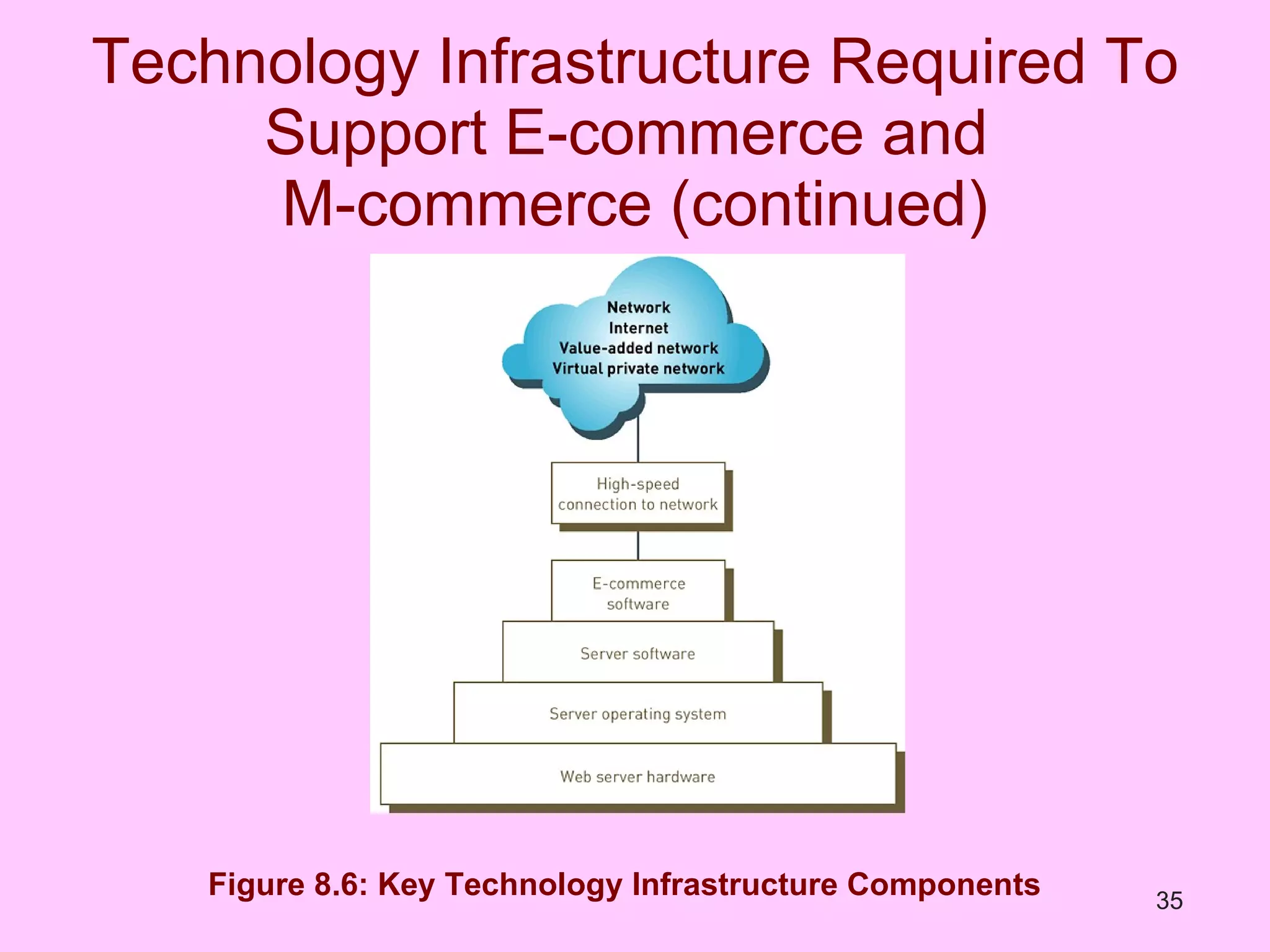
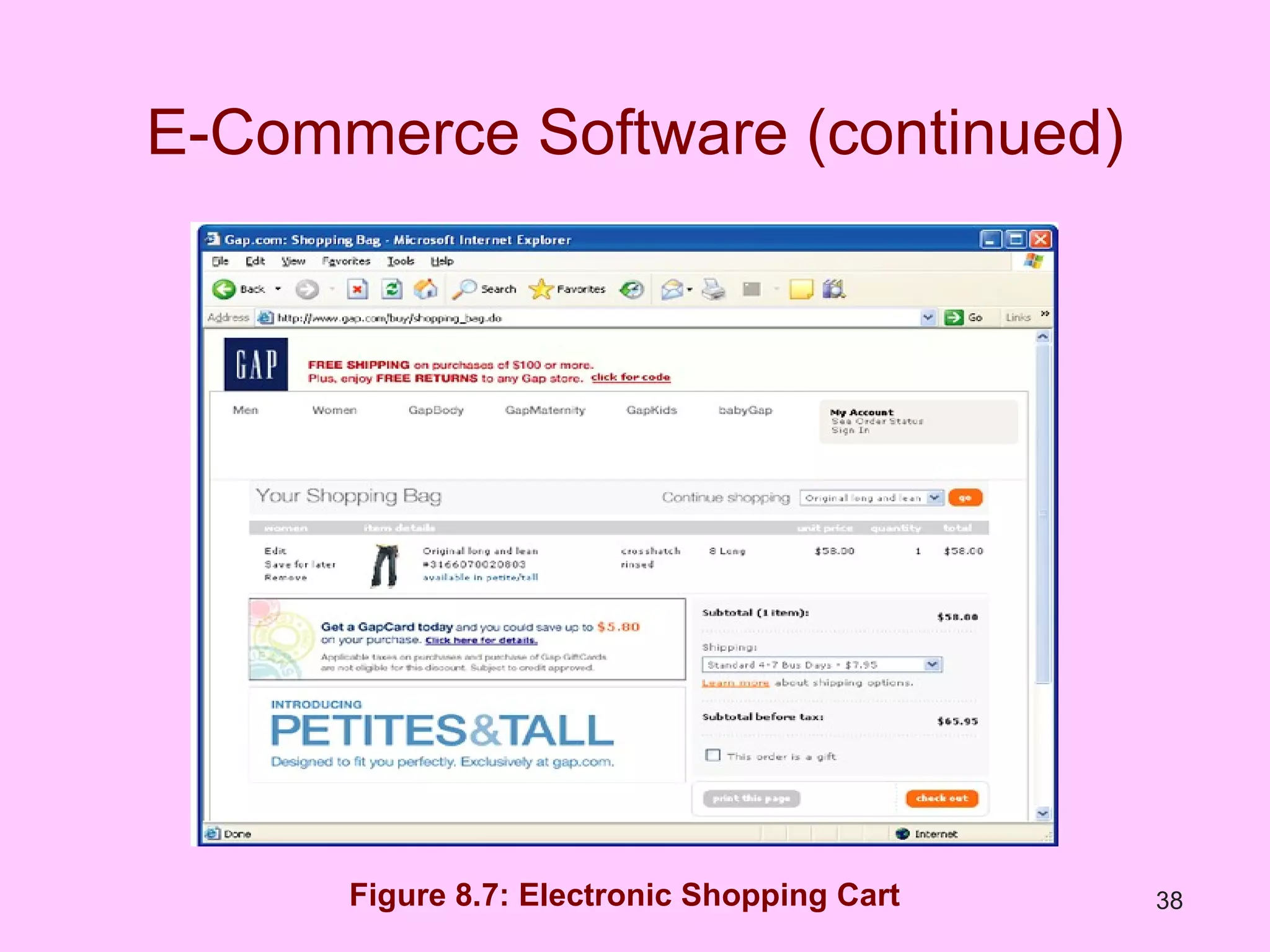
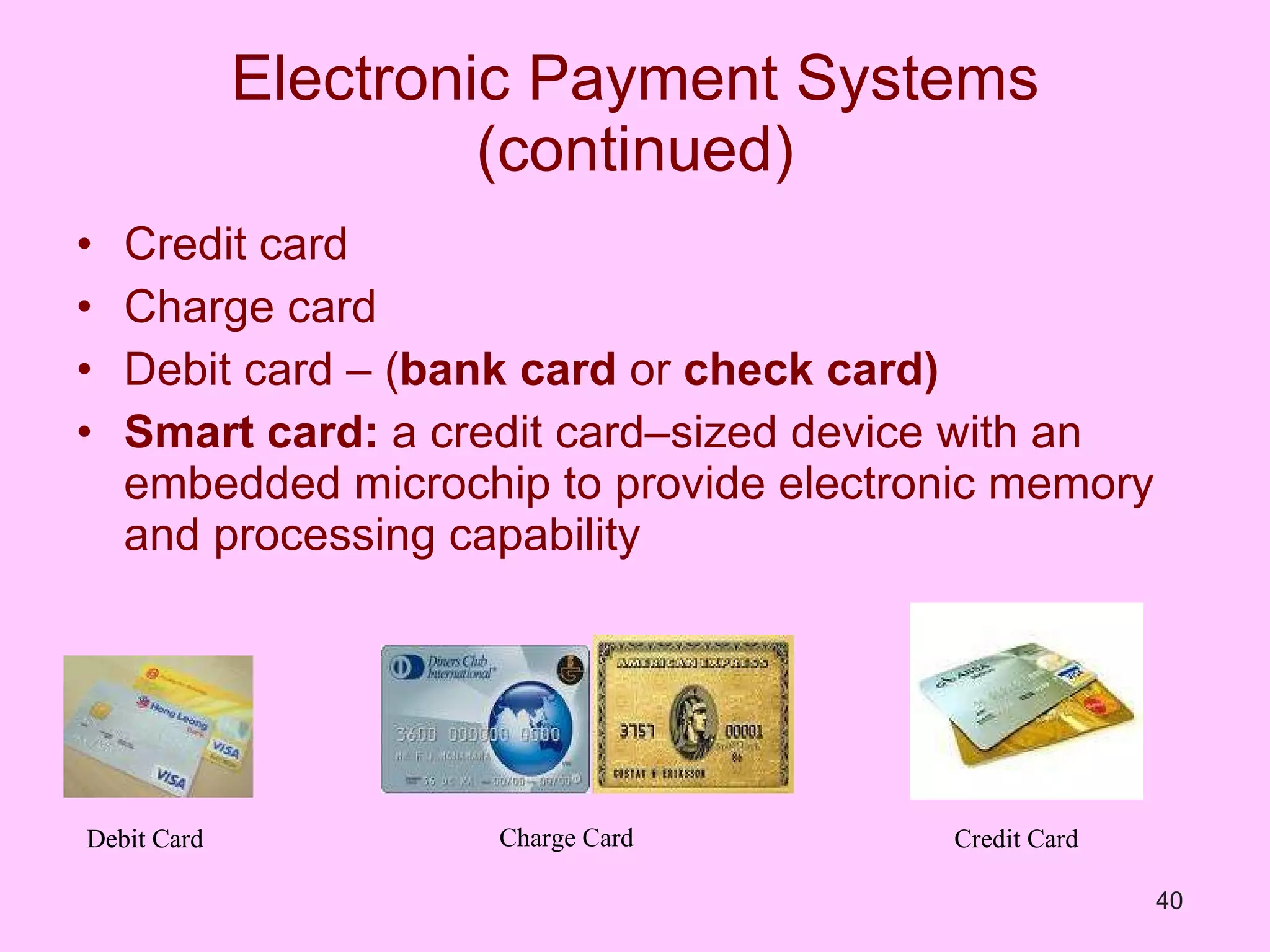
The document discusses electronic commerce (e-commerce) and mobile commerce (m-commerce). It outlines various forms of e-commerce like business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), and consumer-to-consumer (C2C). It also describes technologies needed for e-commerce and m-commerce like the wireless application protocol (WAP) and provides examples of applications in areas like retail, manufacturing, and finance. Finally, it discusses advantages and challenges of e-commerce and m-commerce including security, intellectual property theft, and lack of internet access.