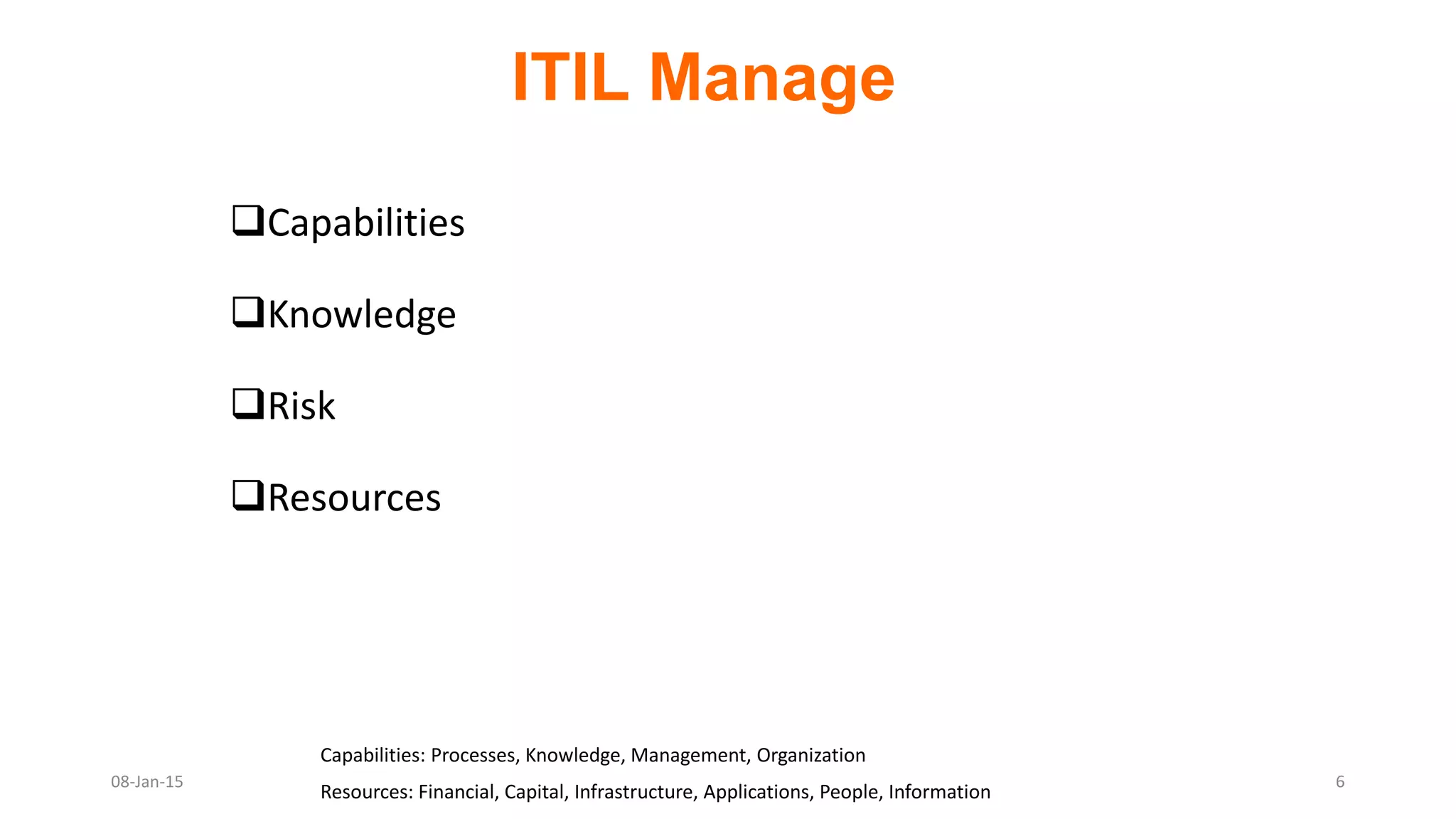
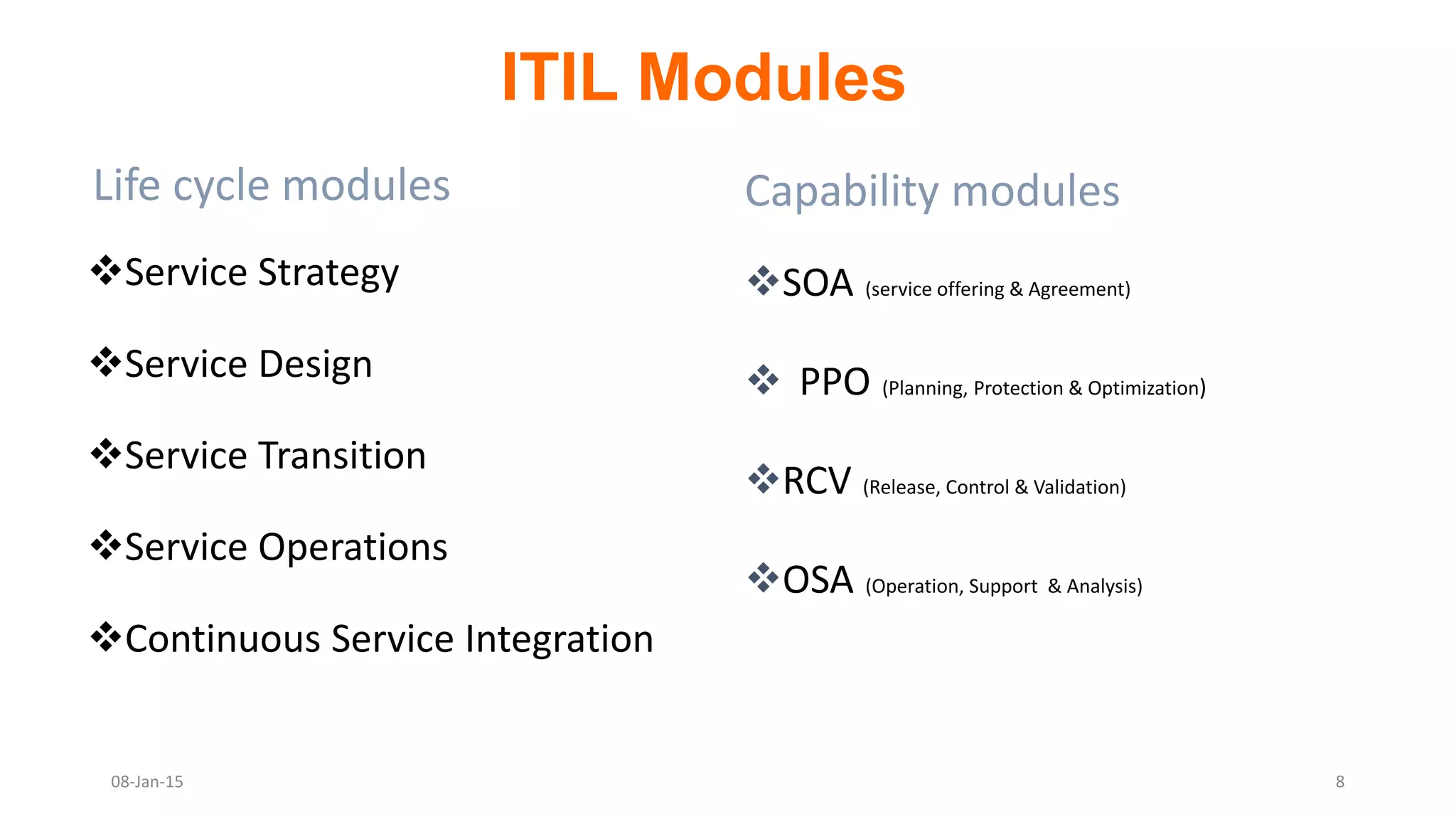
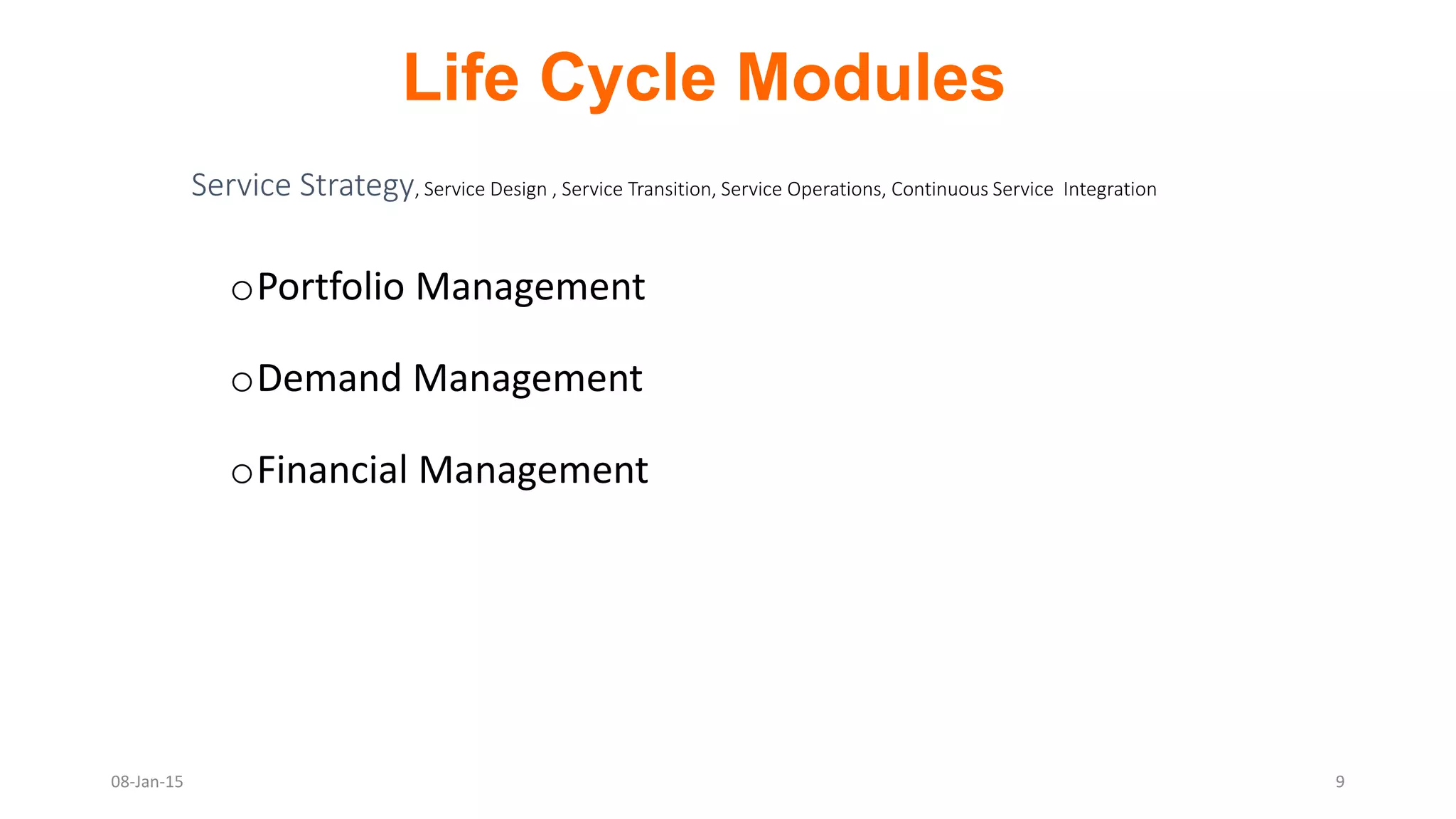
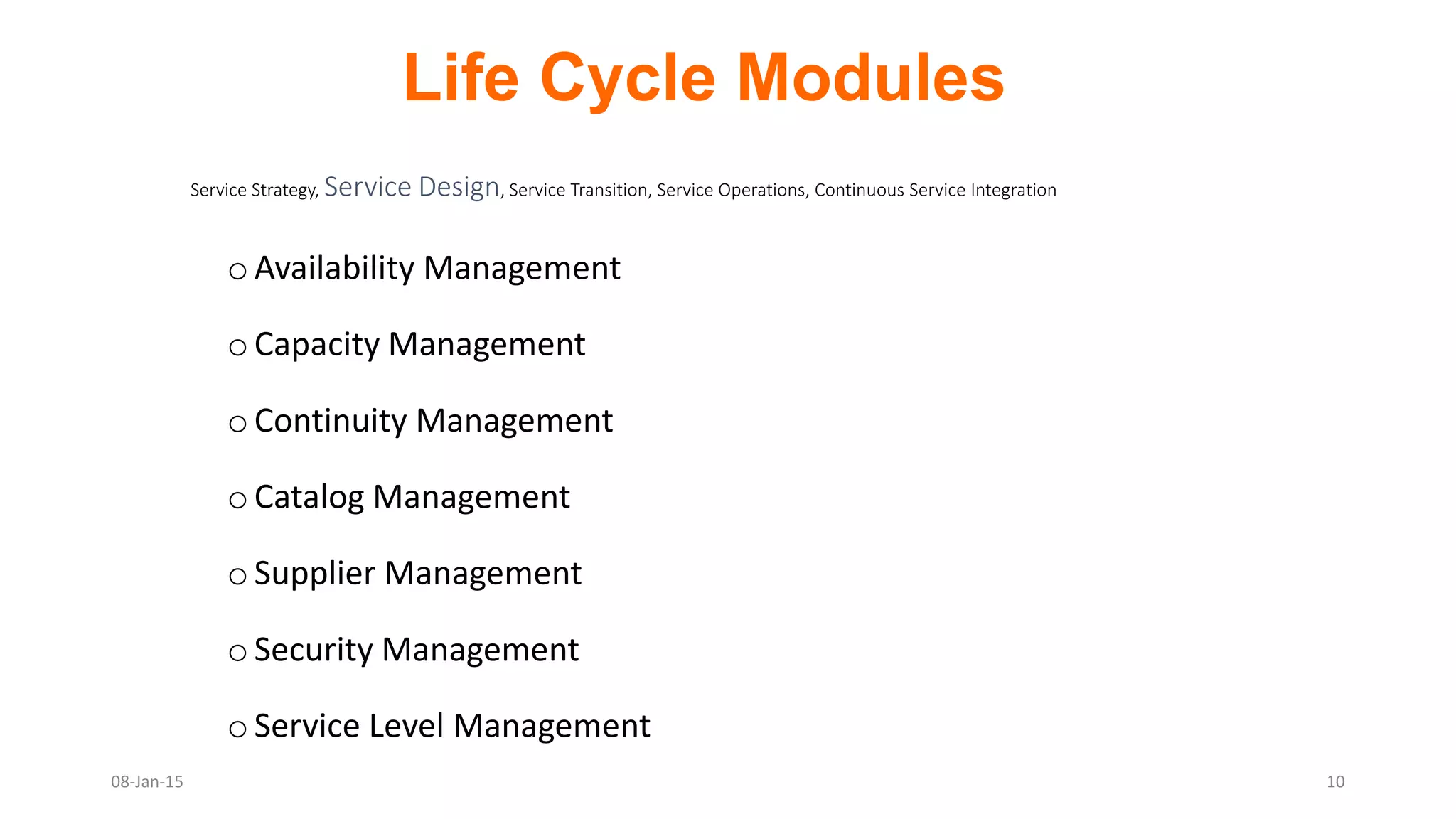
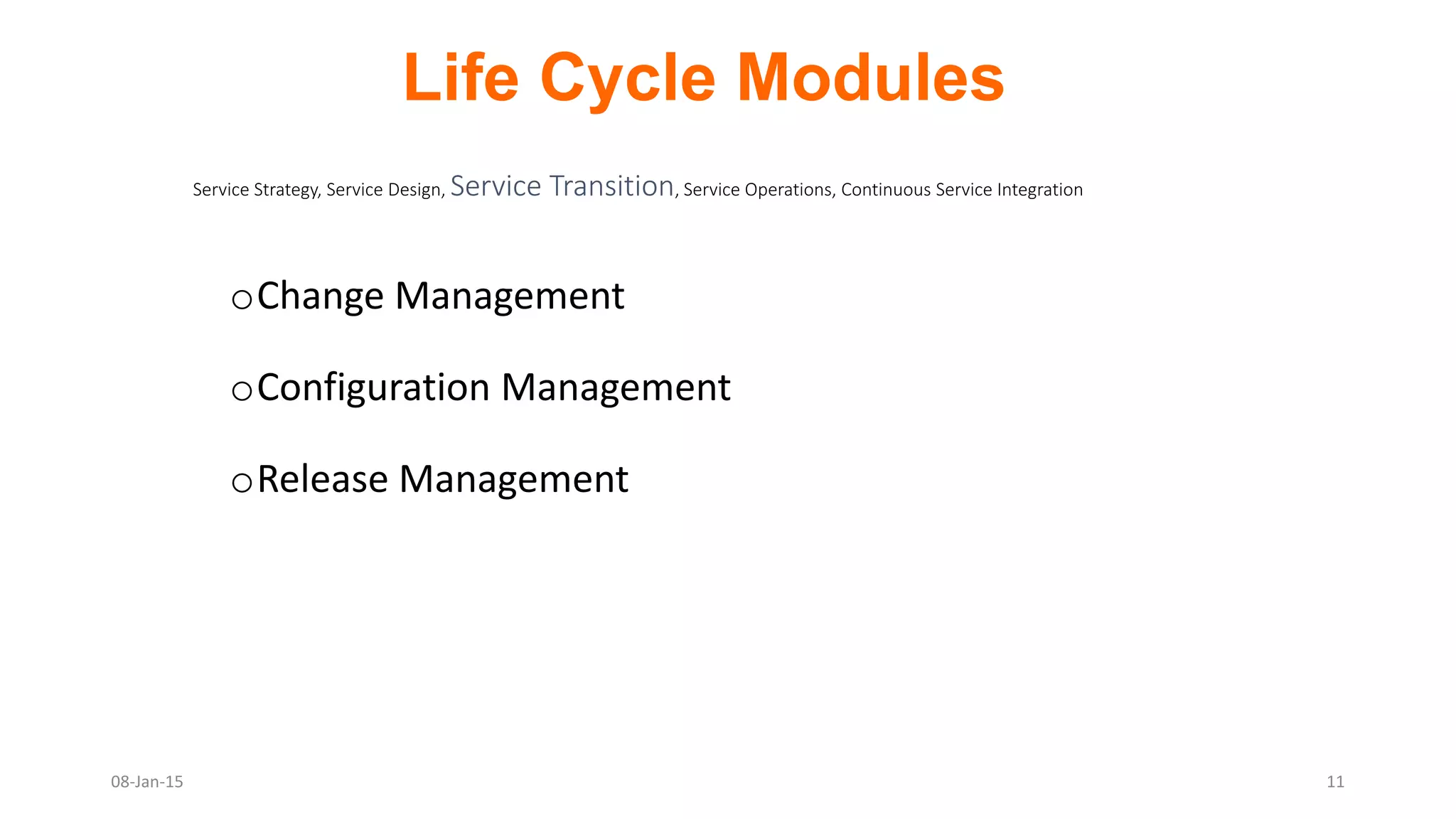
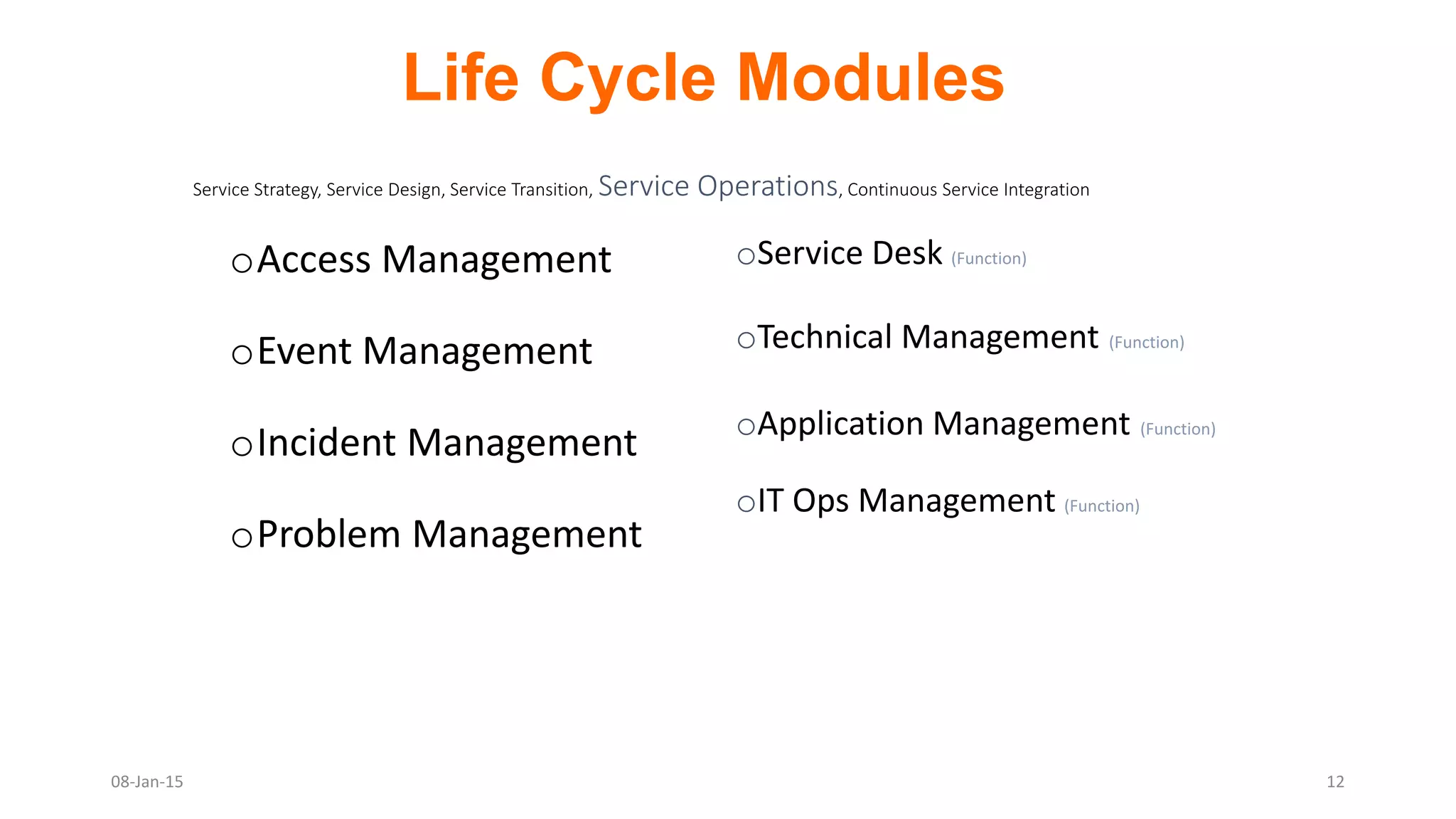
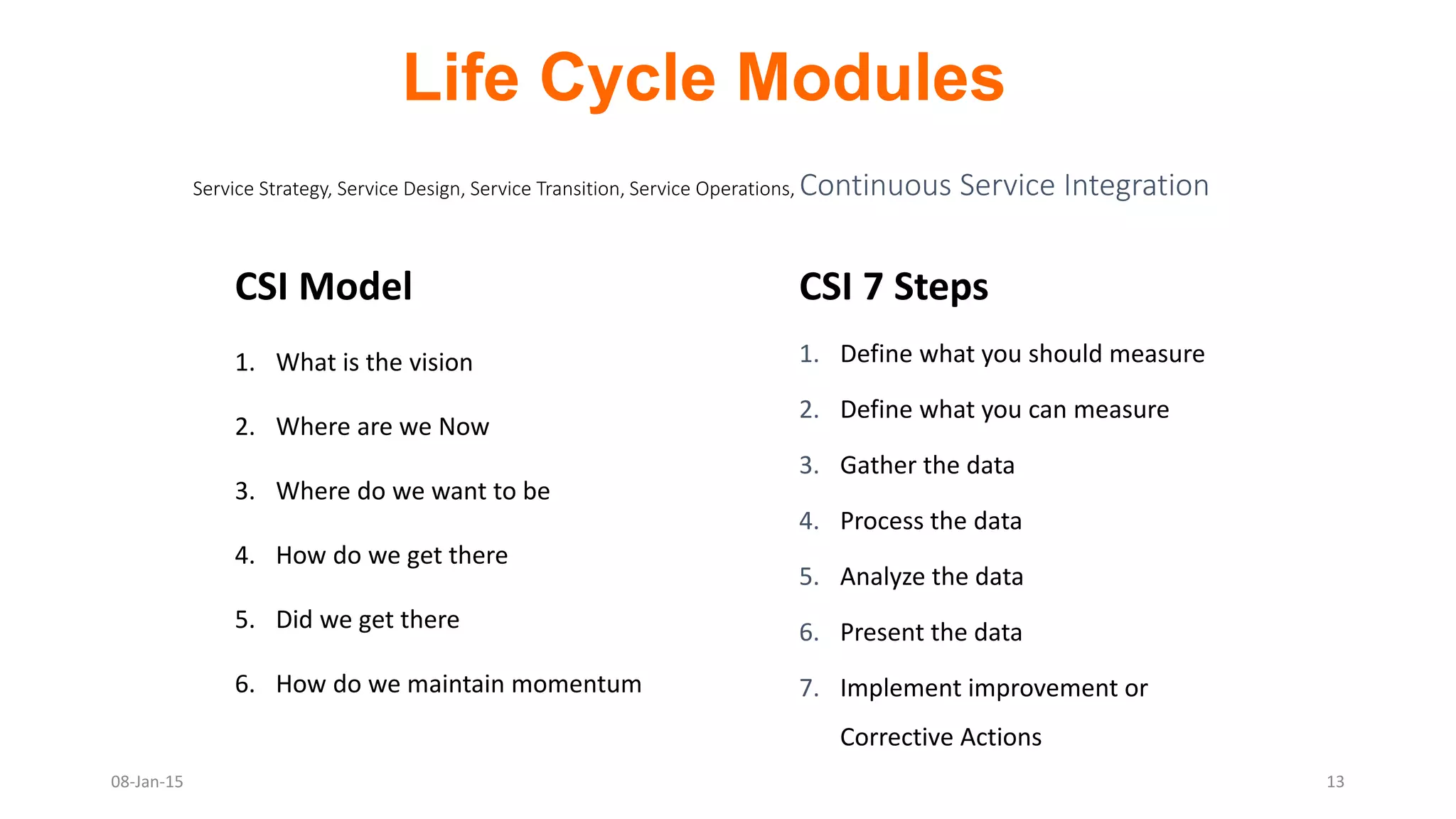
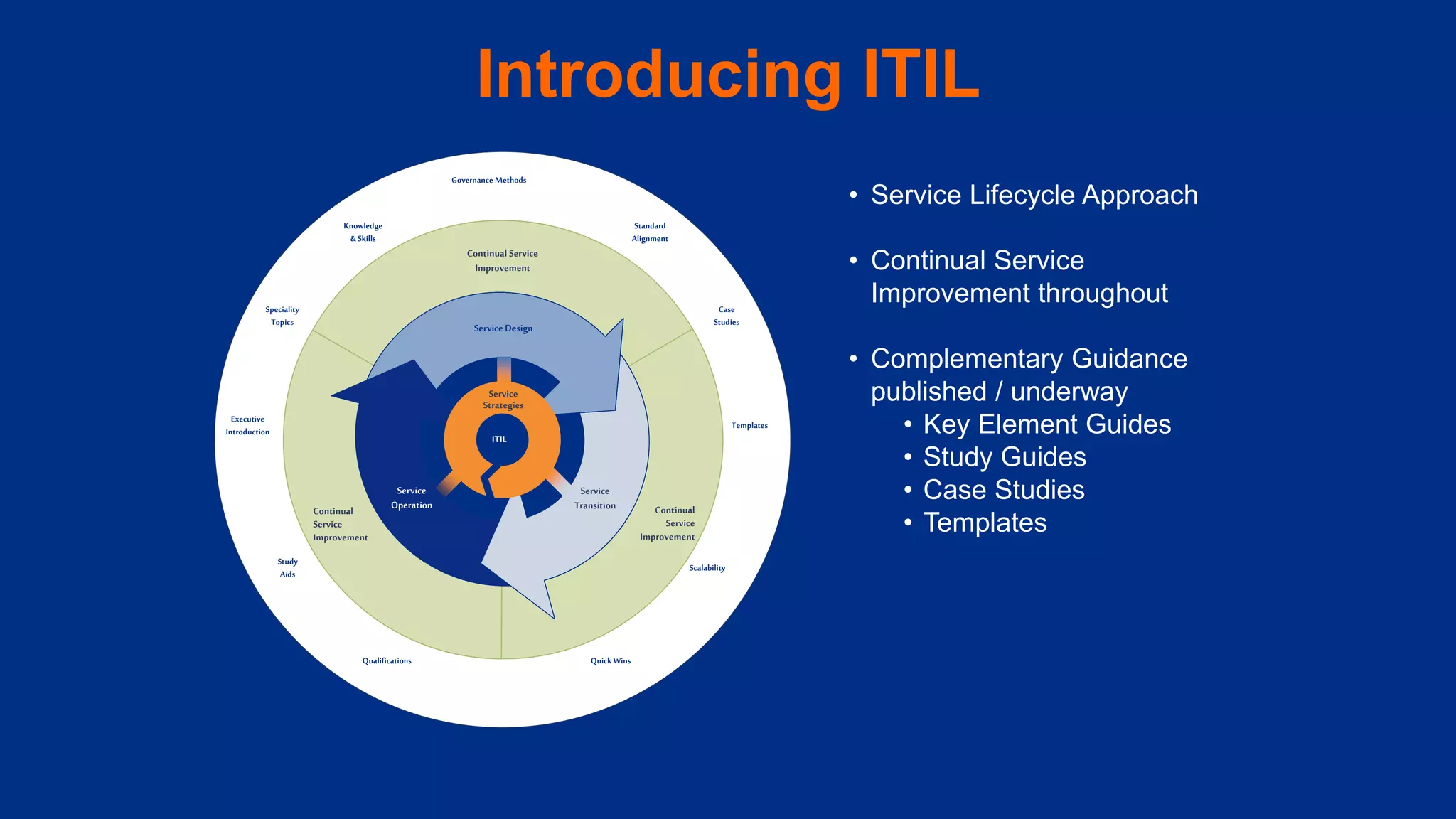
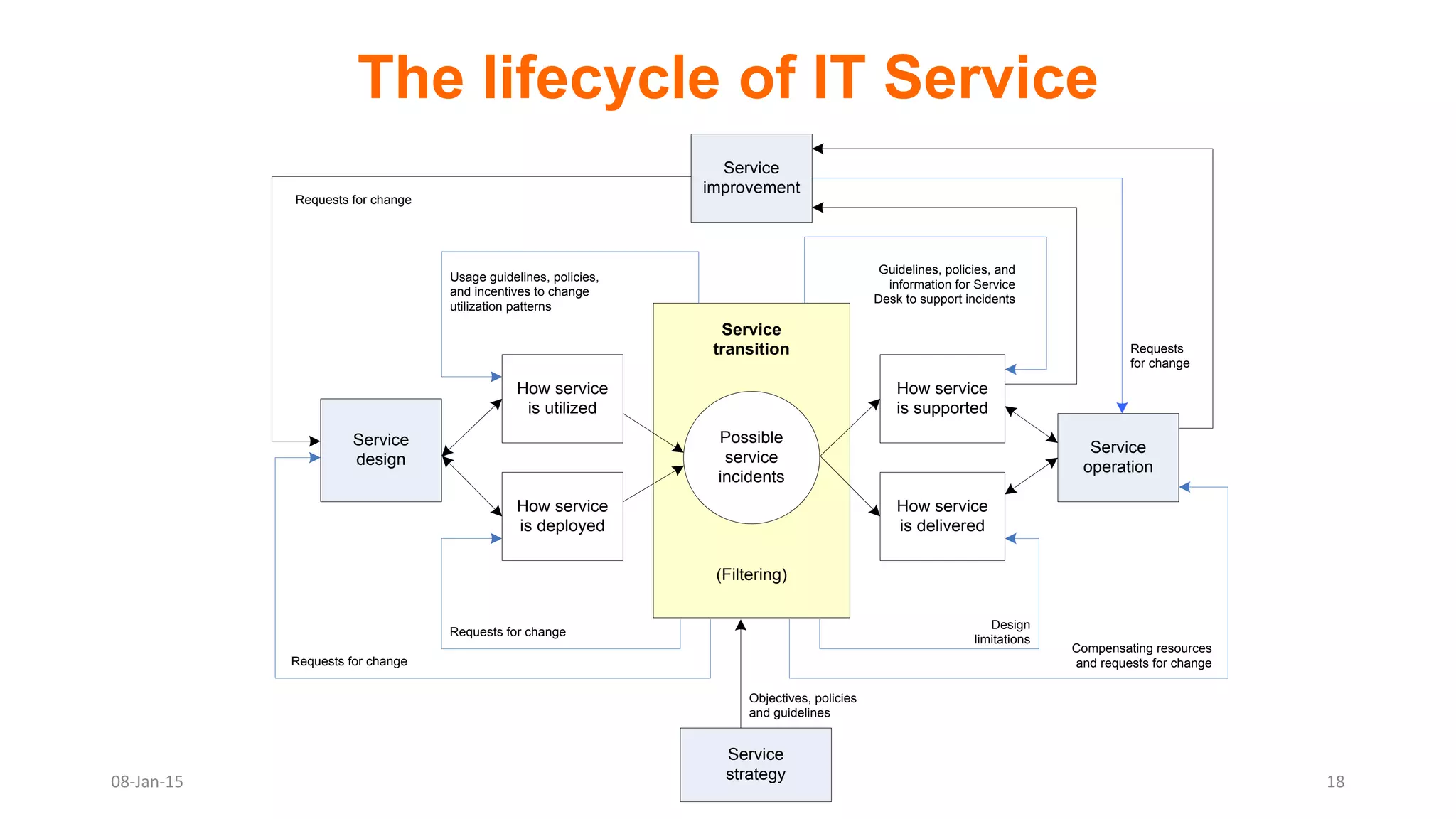
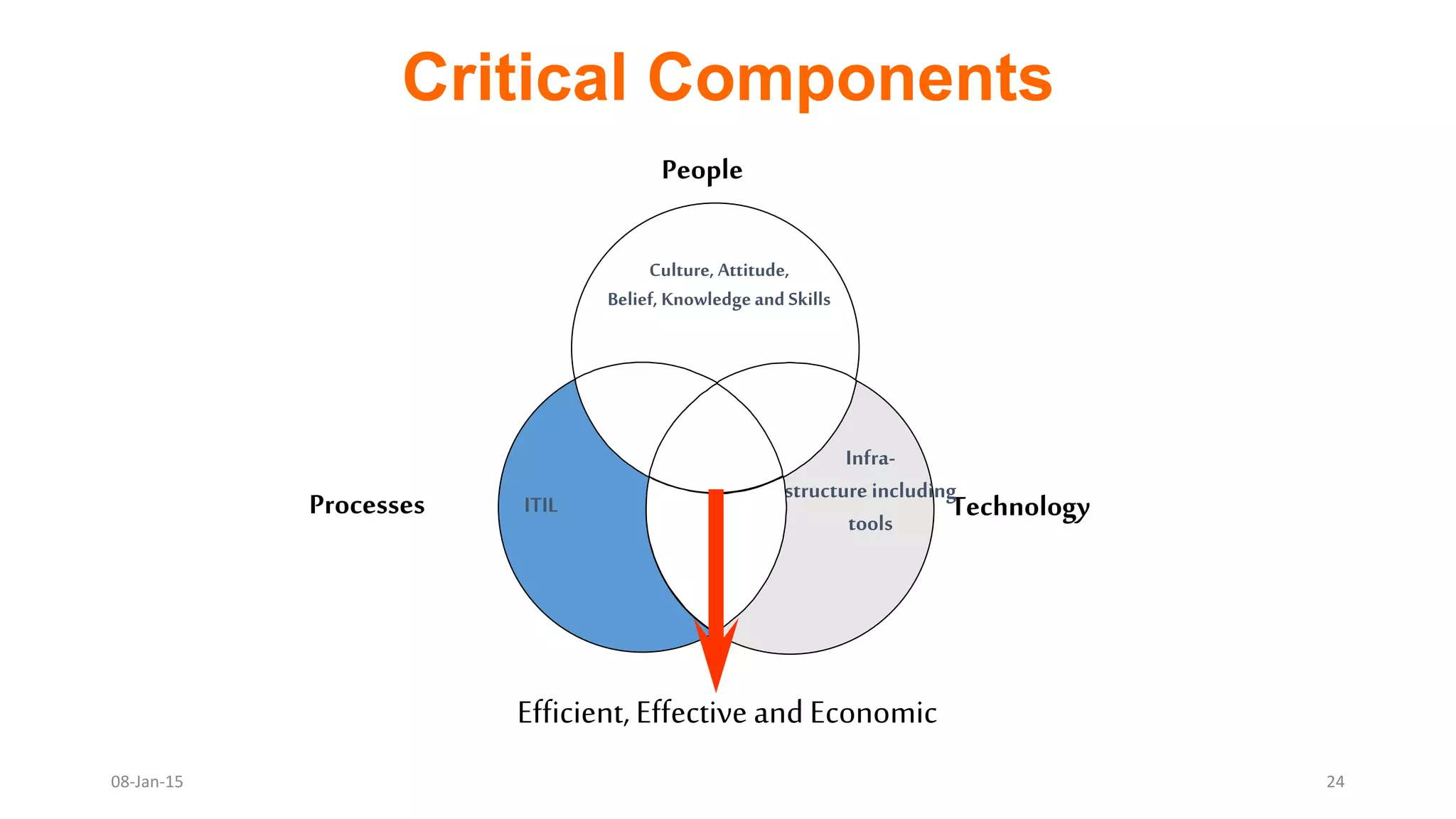
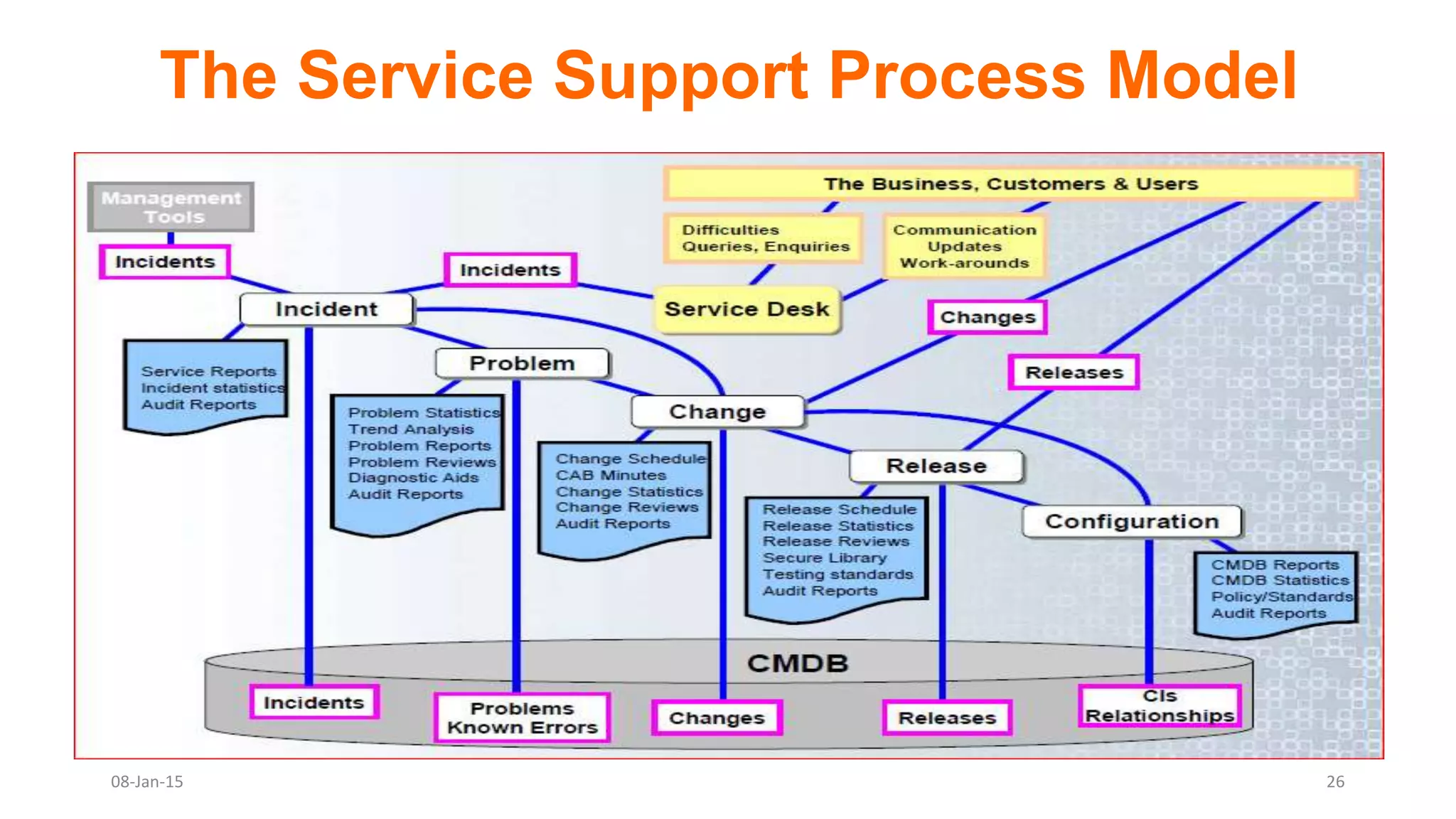
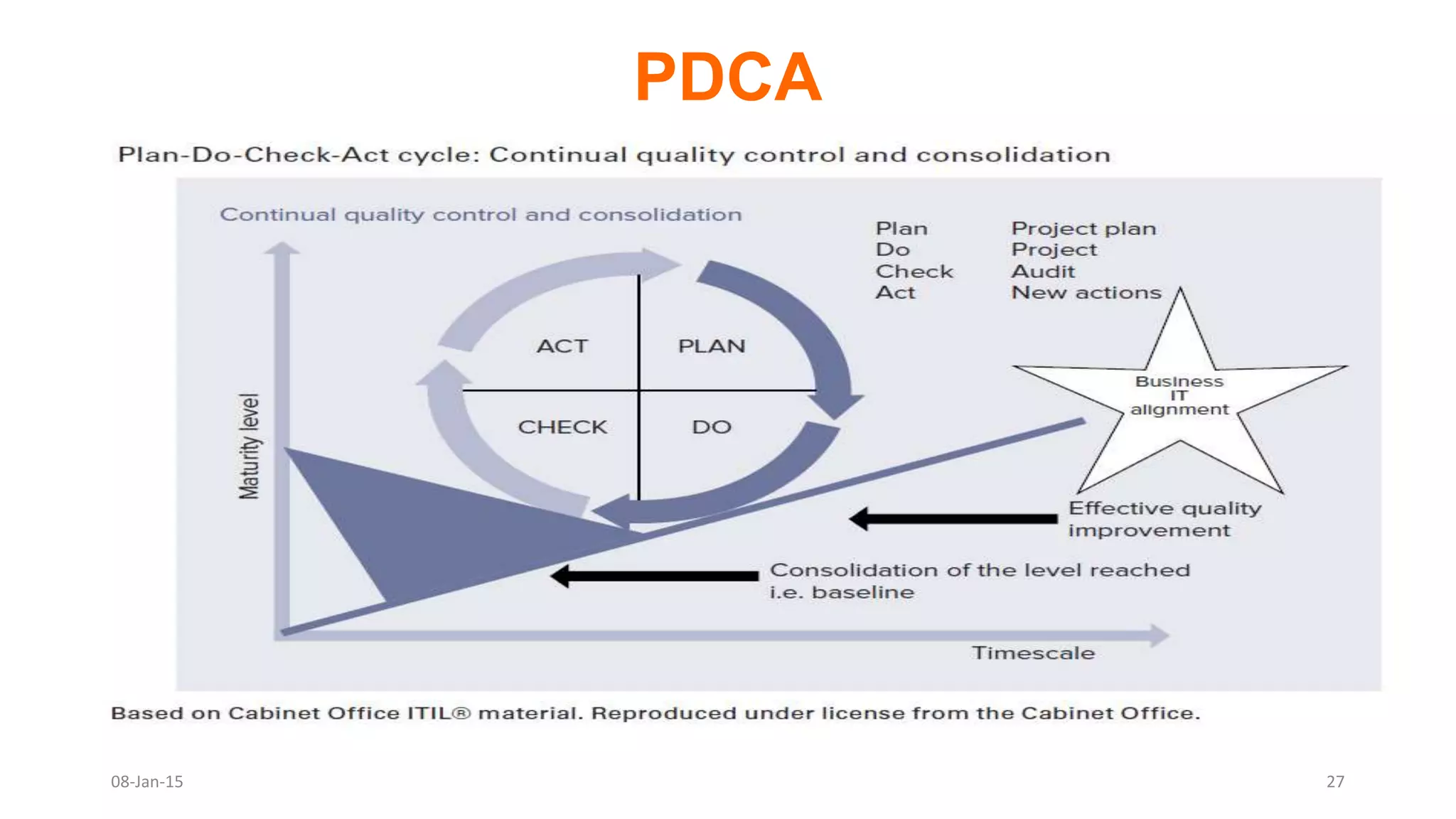
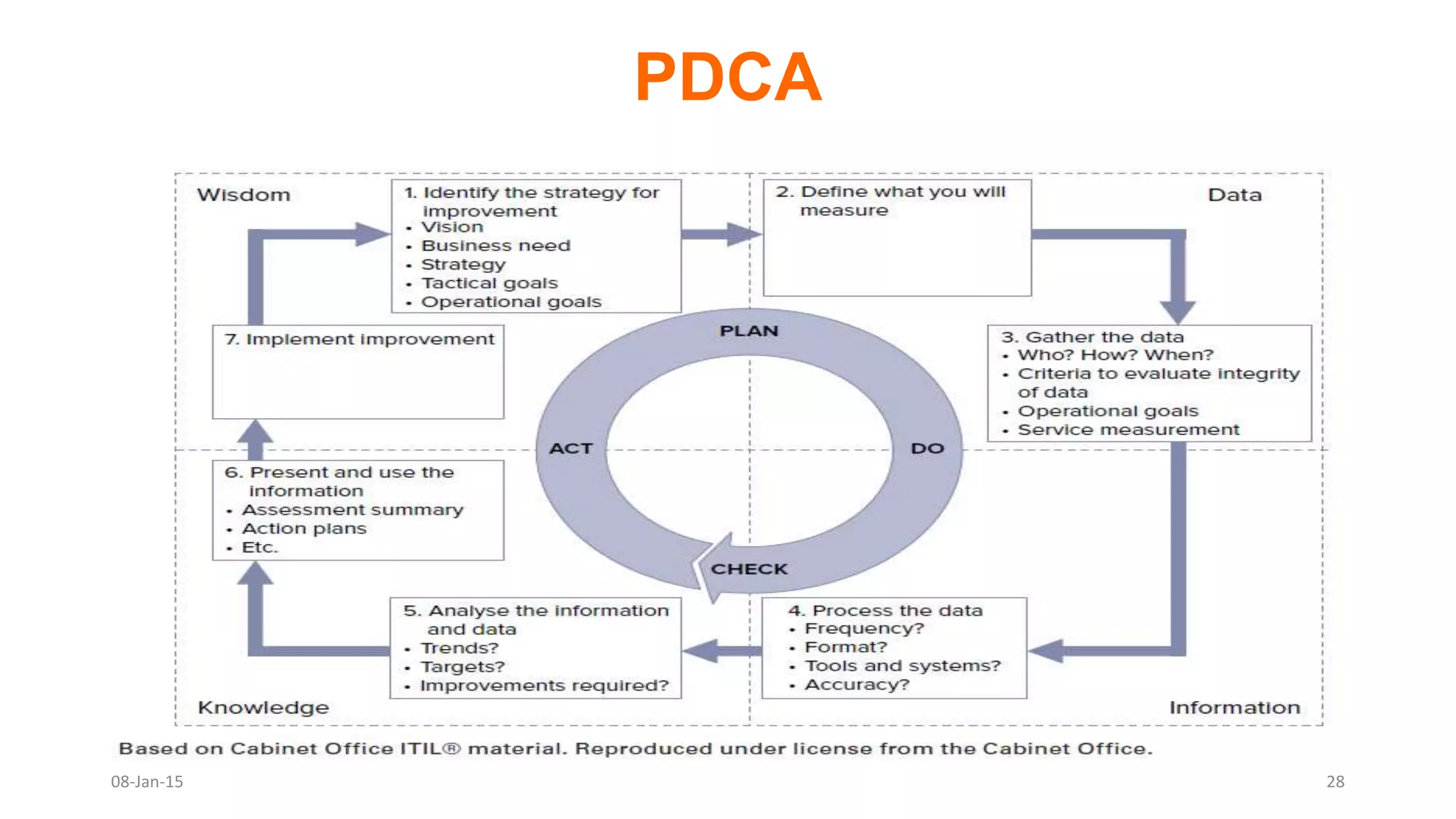
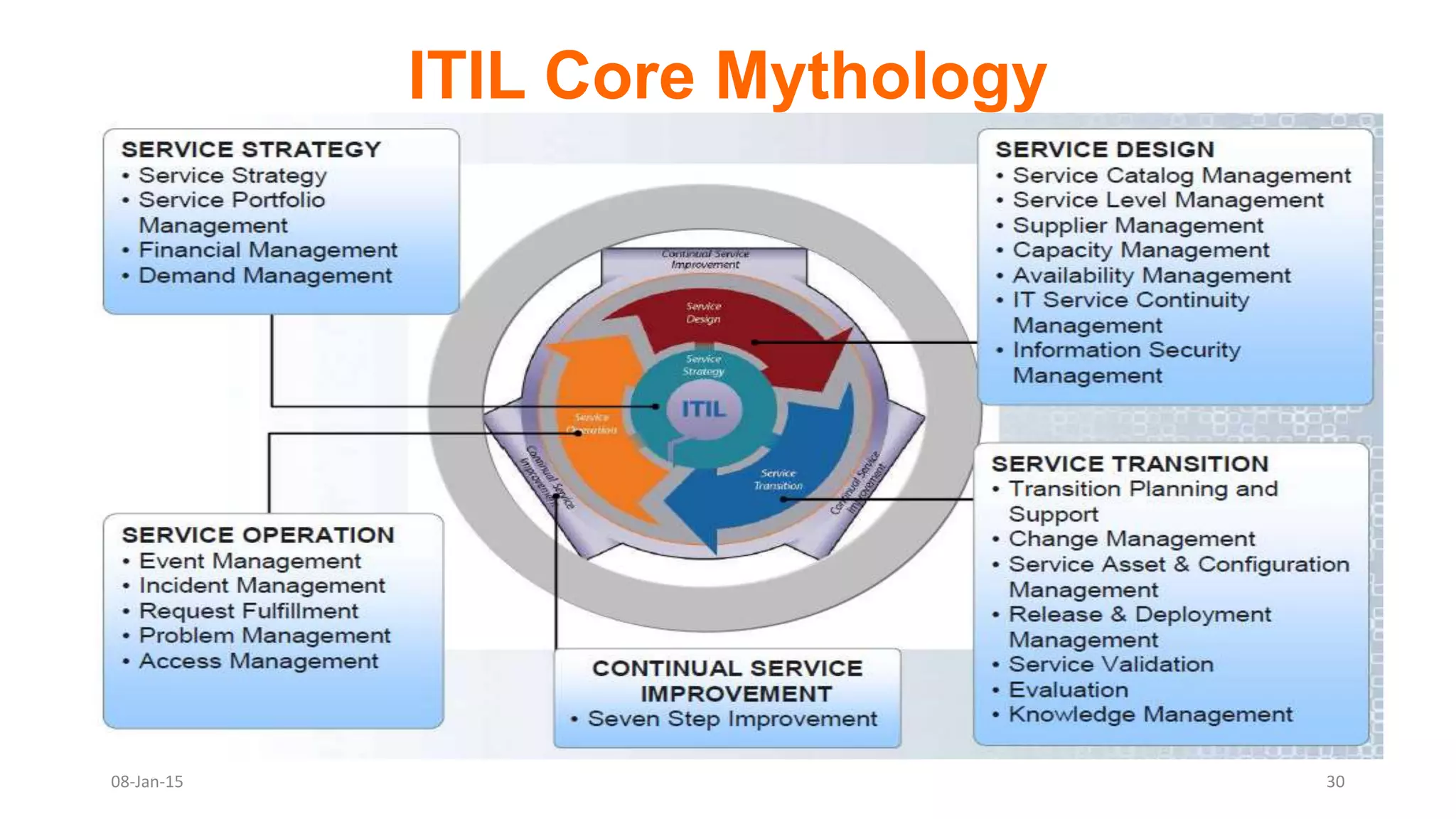
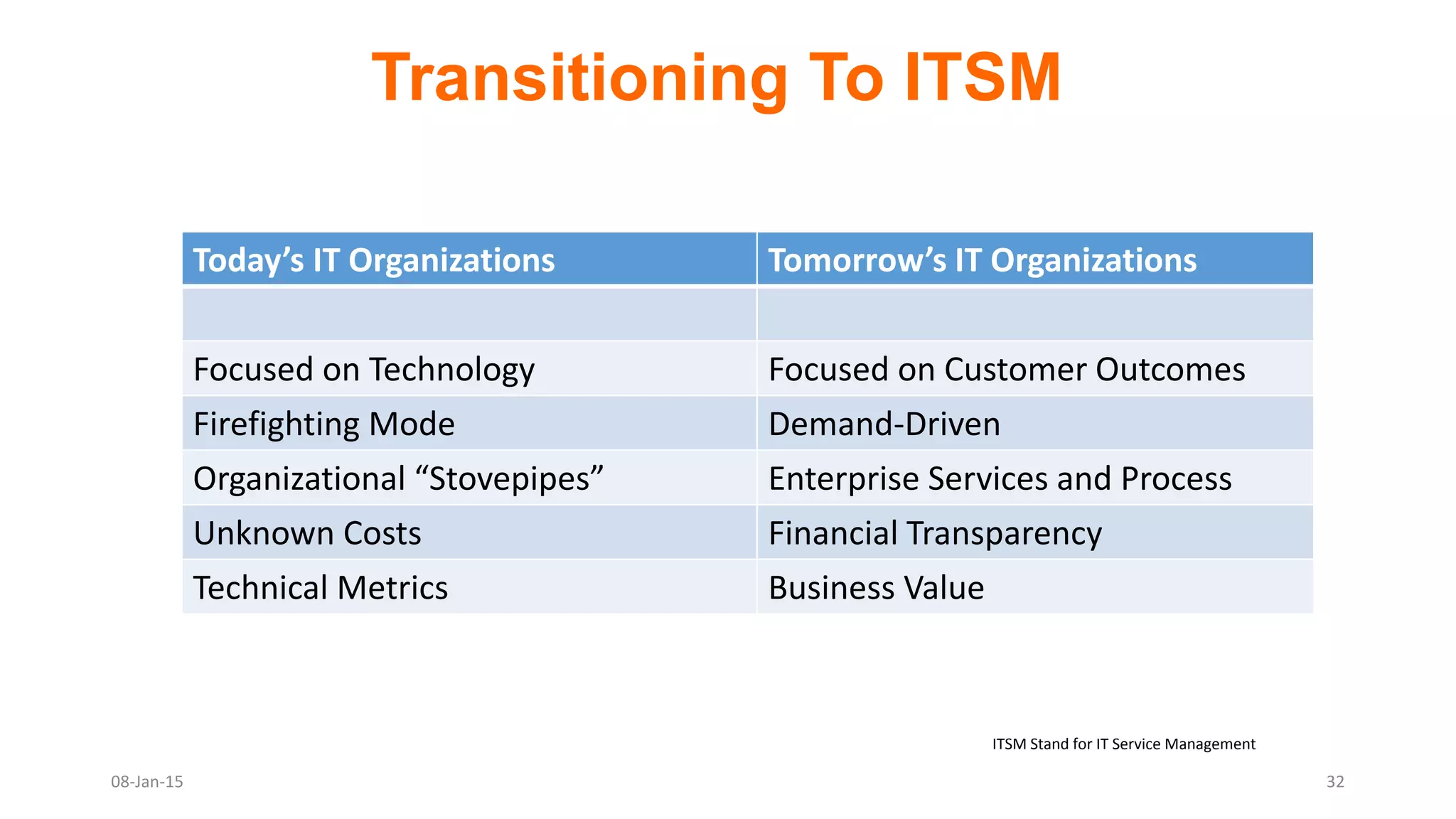
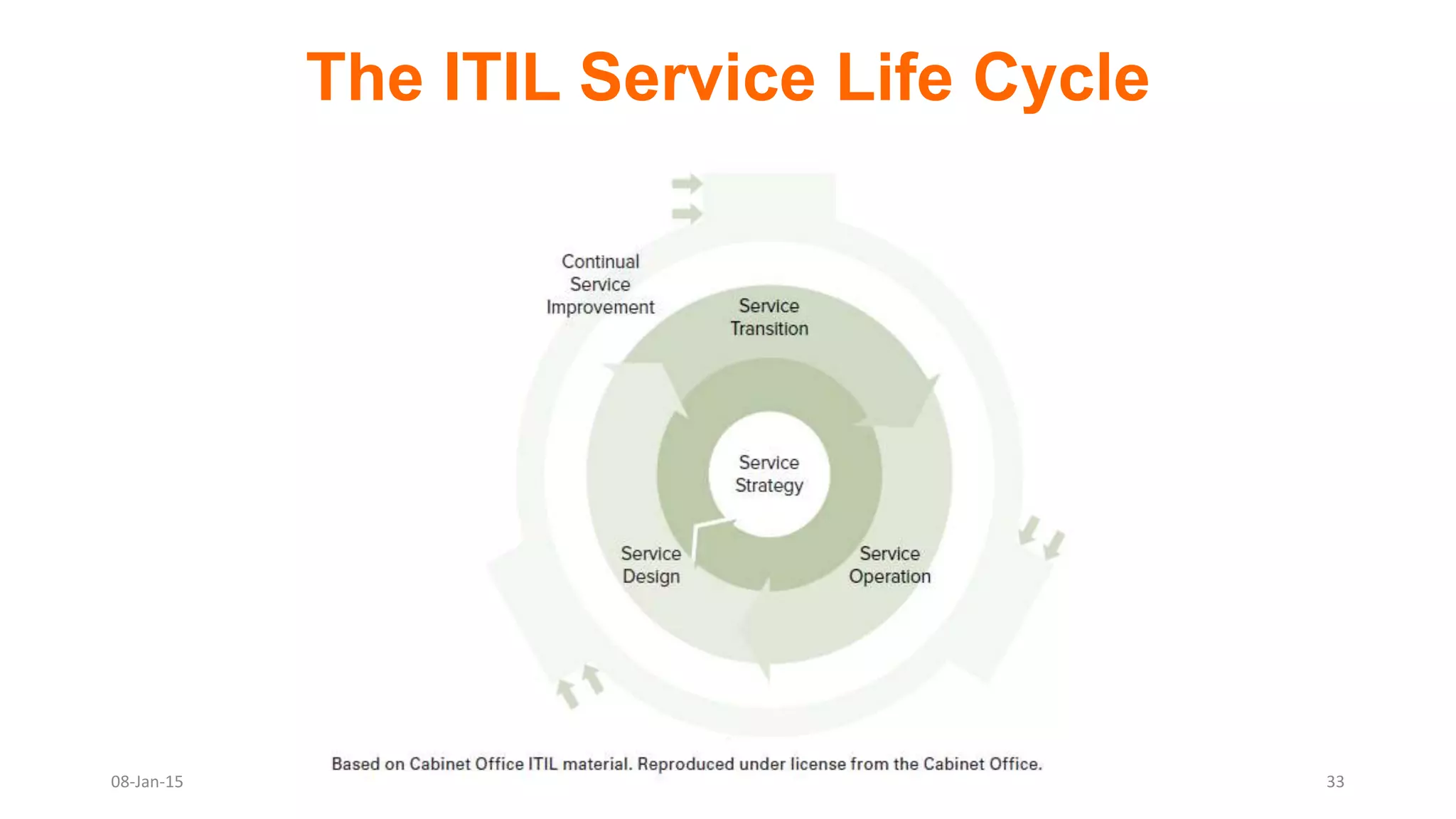
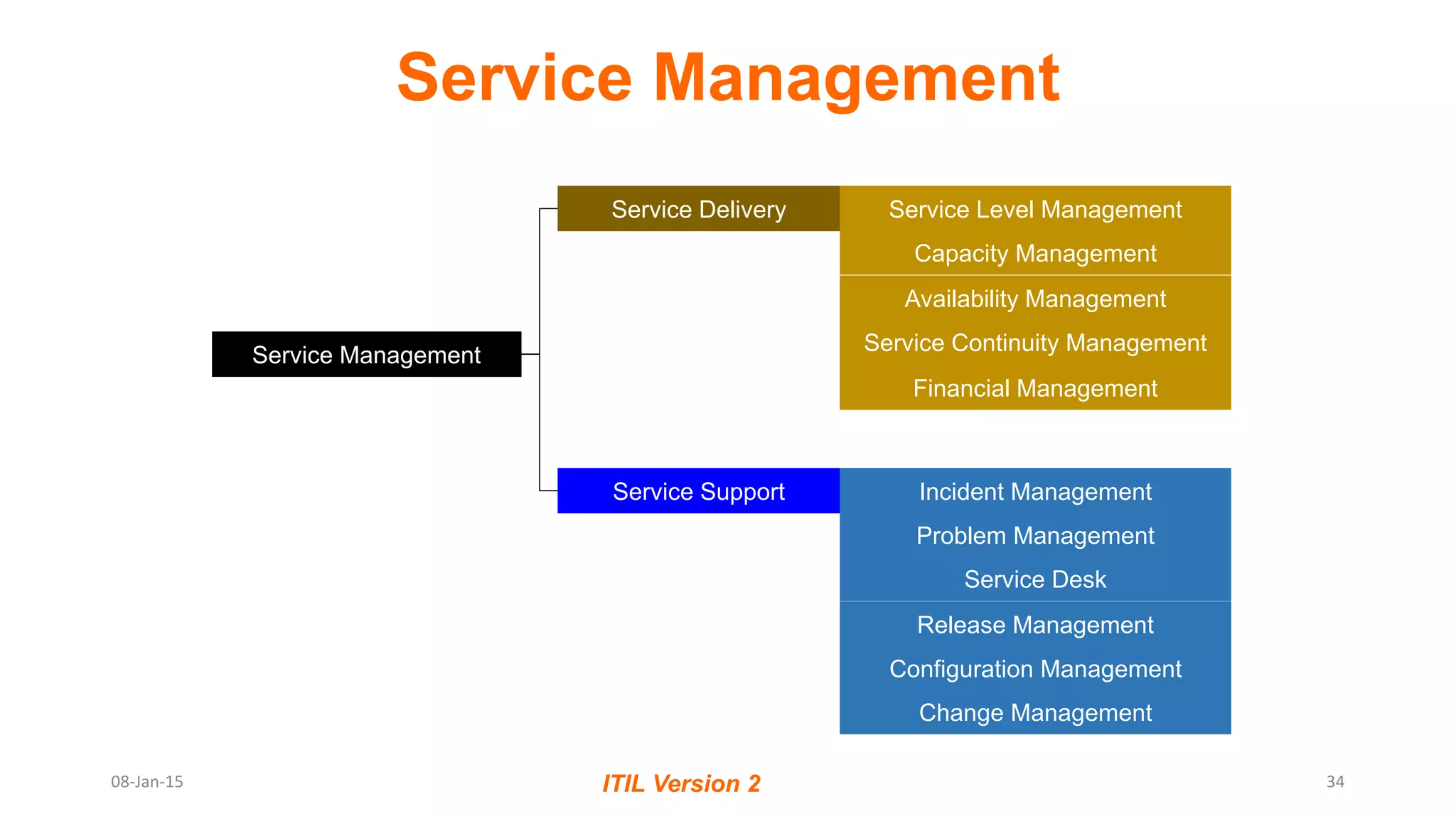
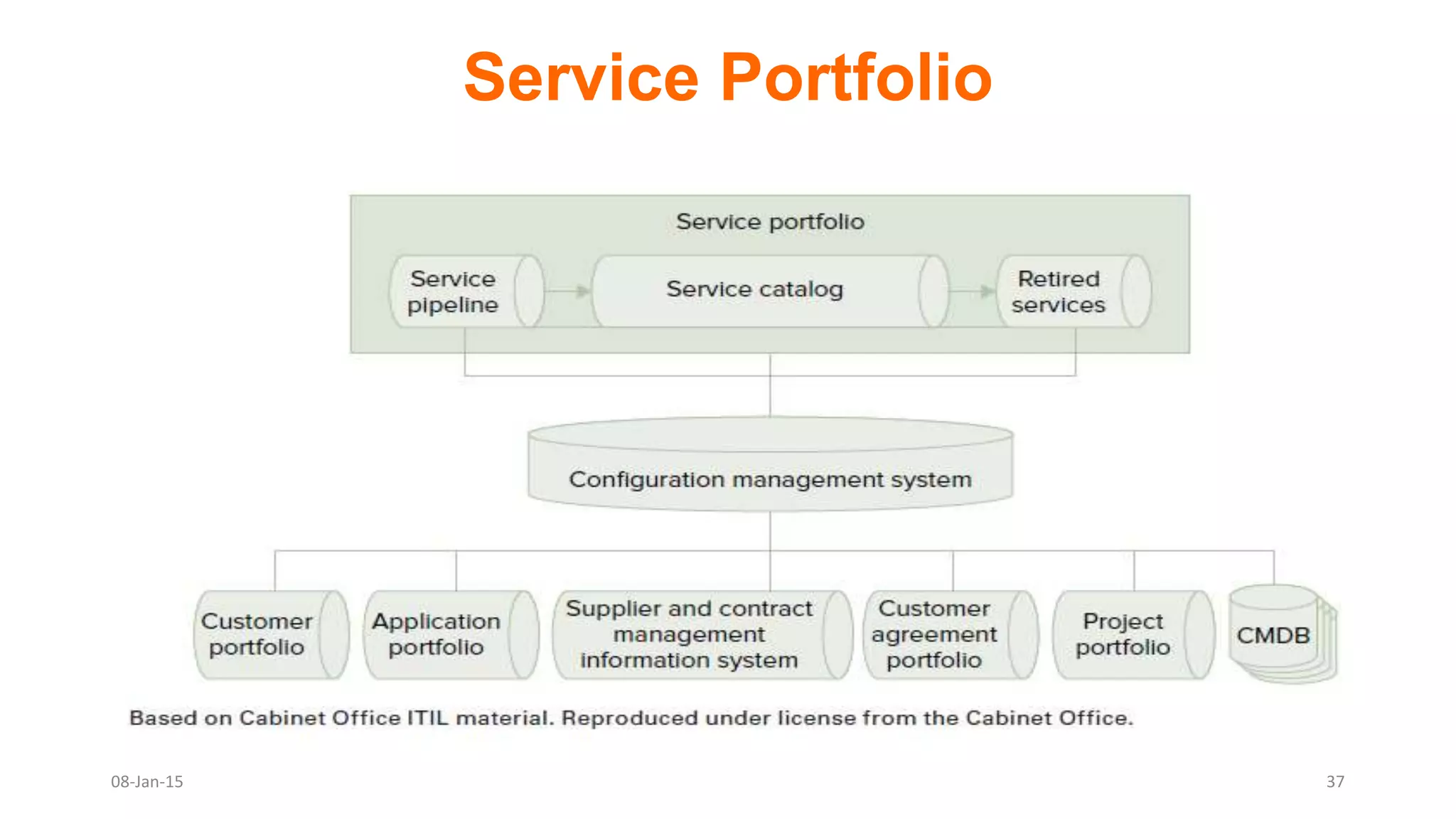
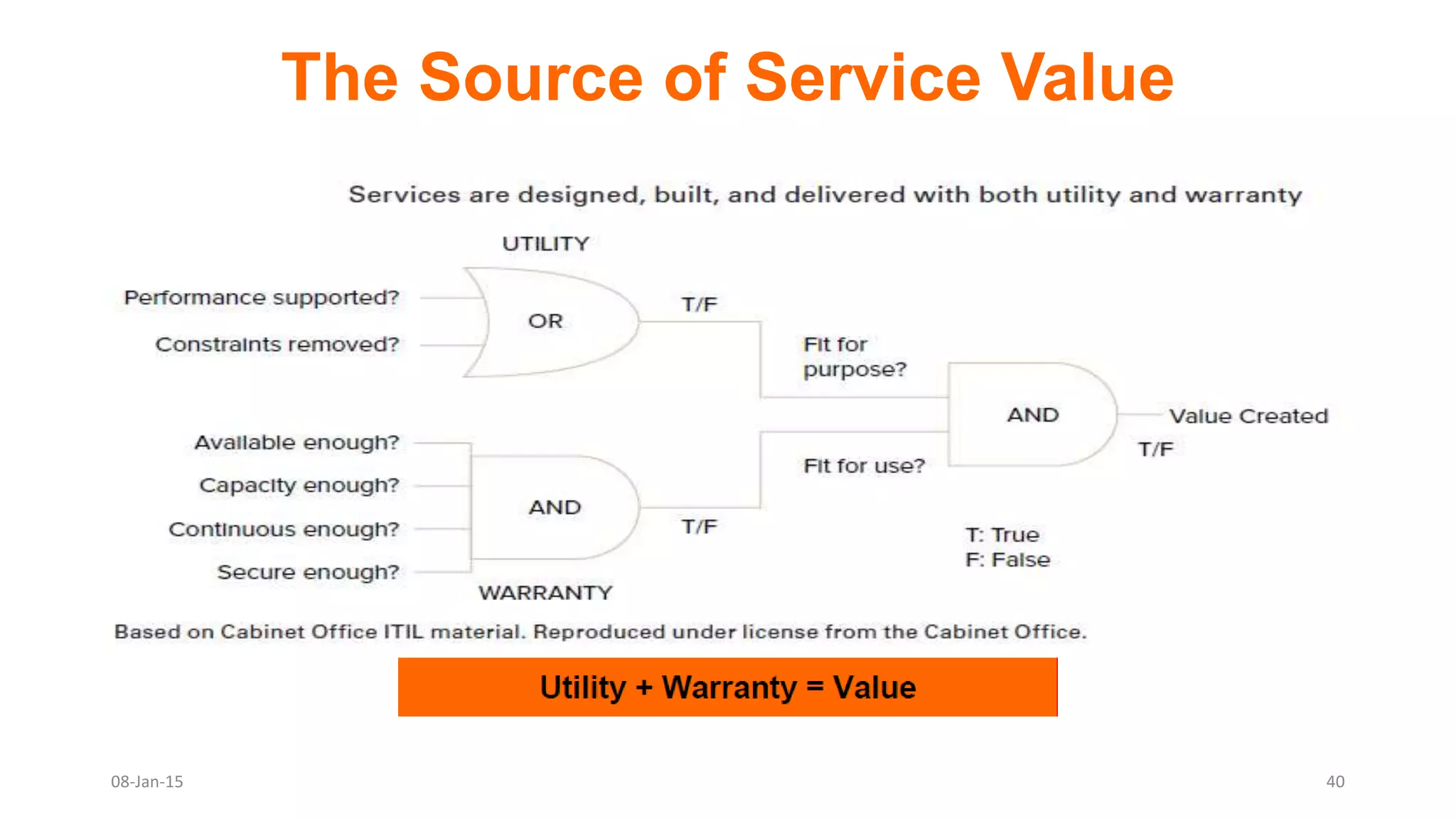
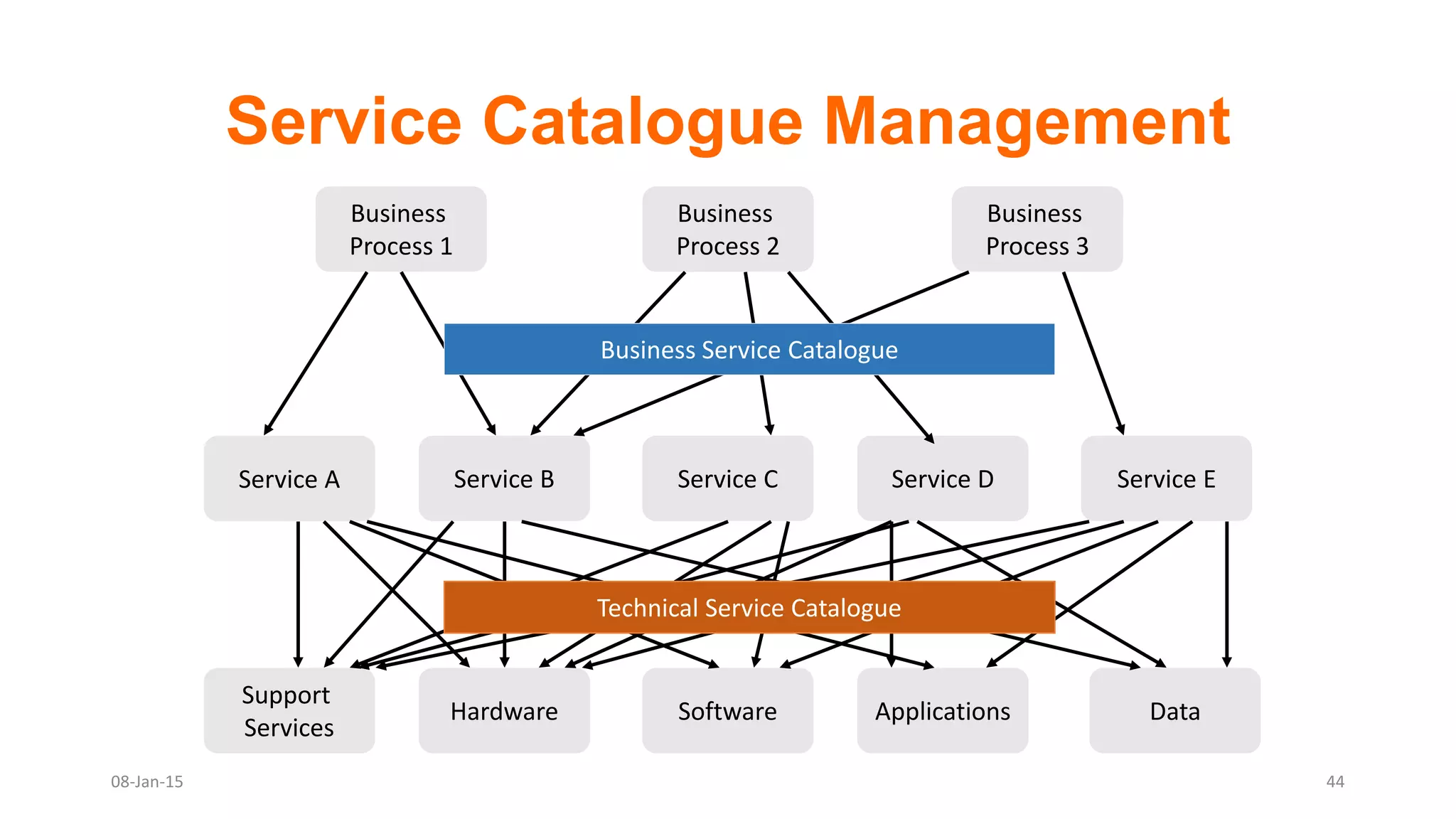
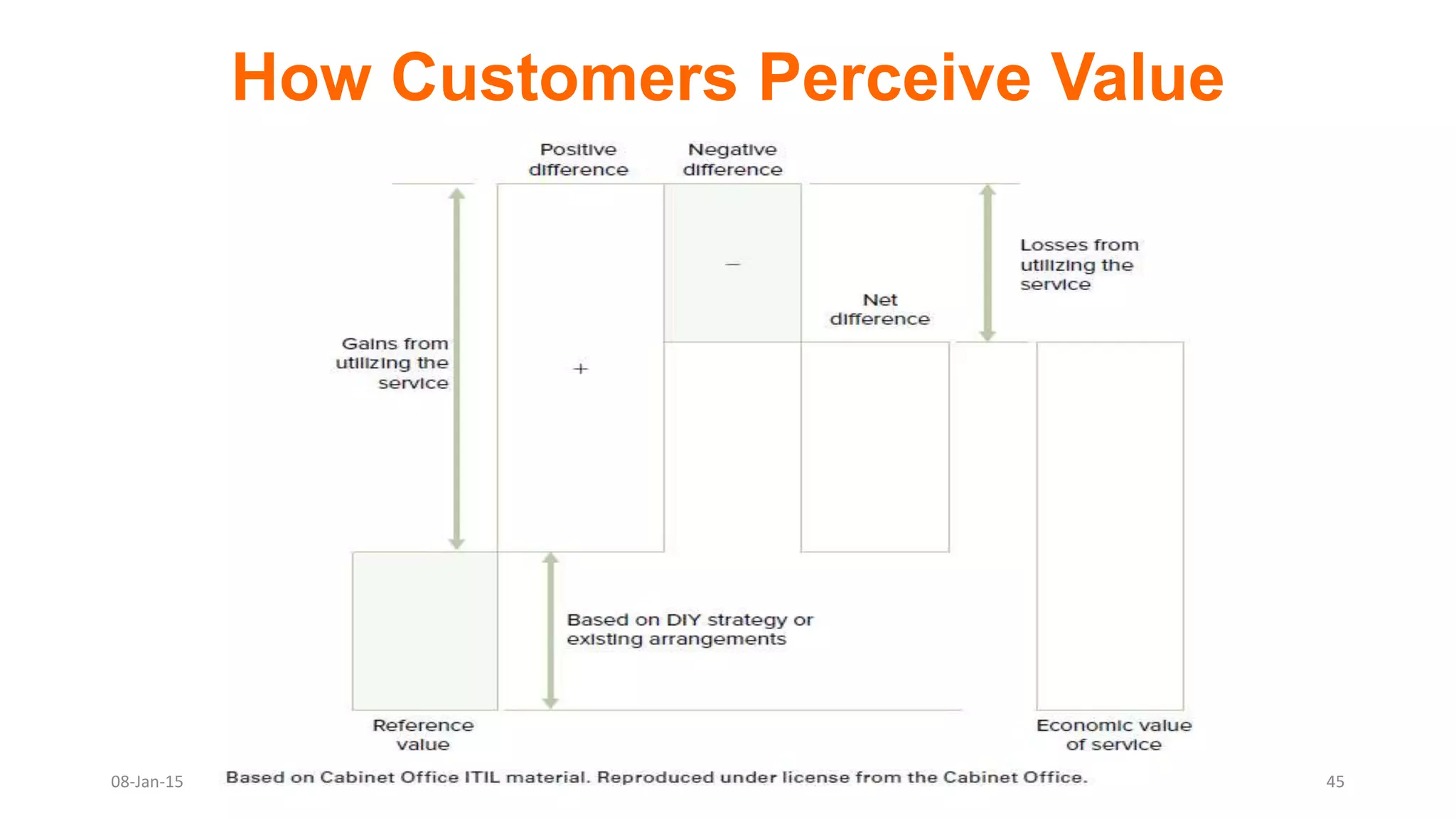
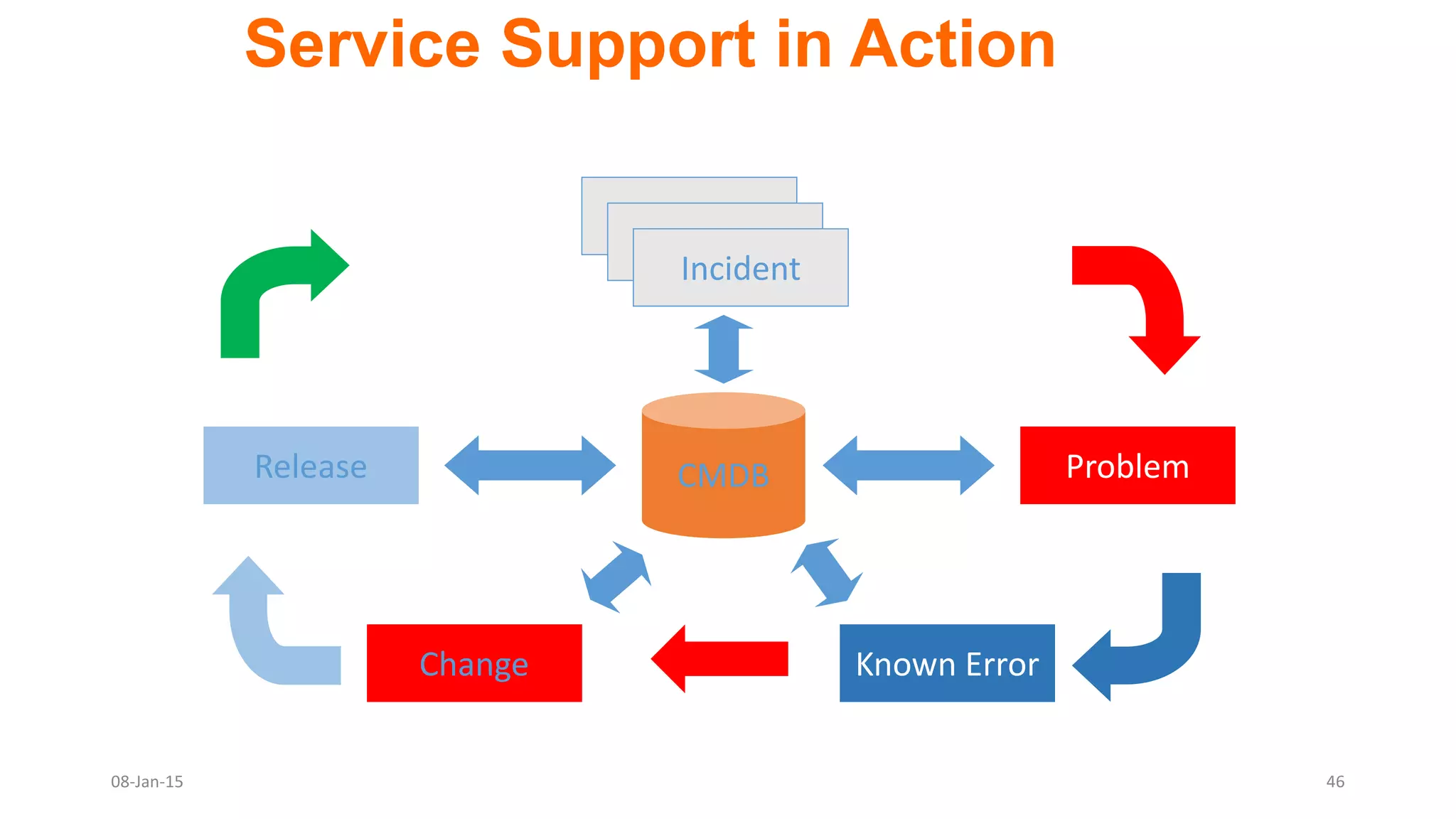
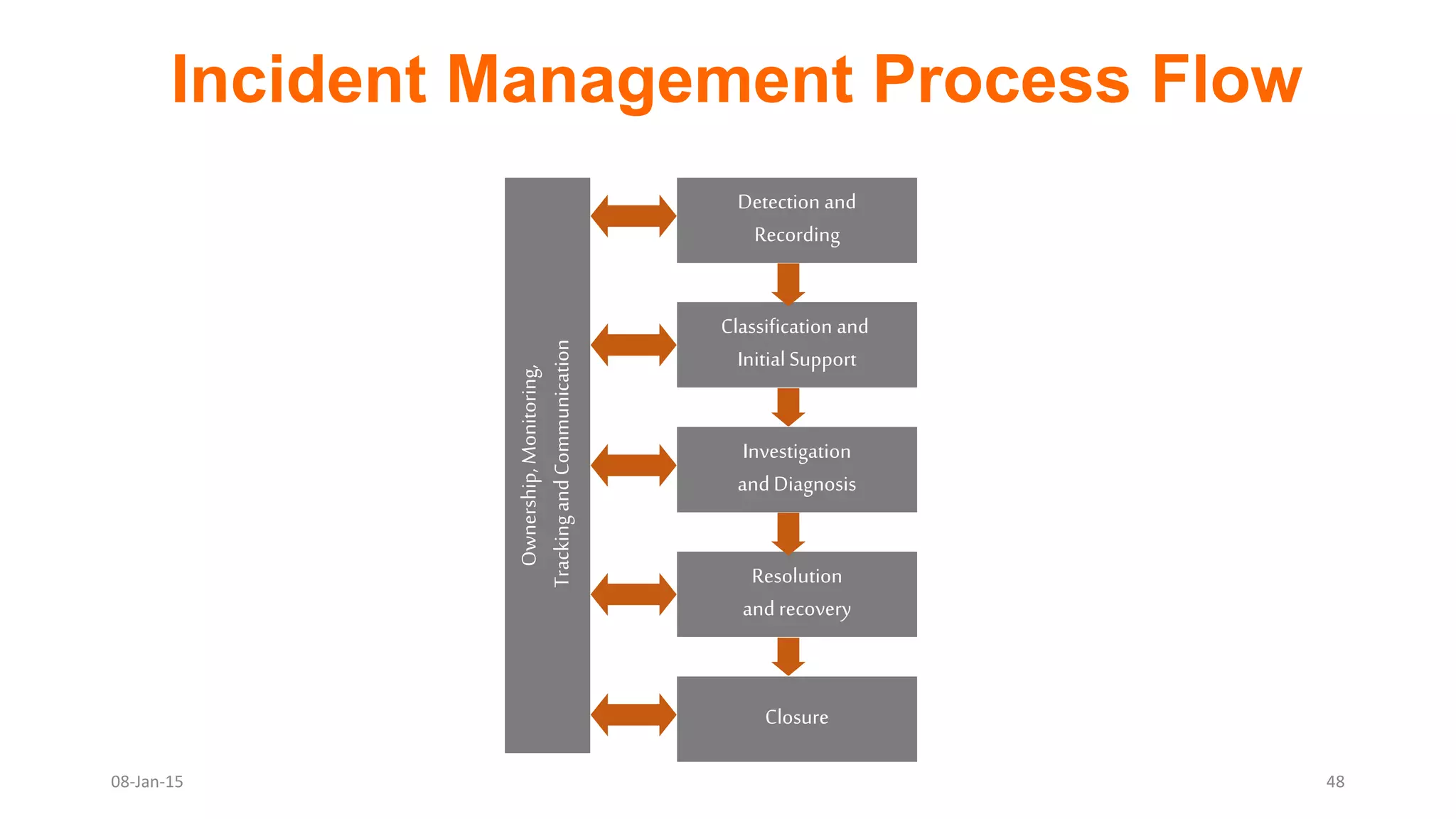
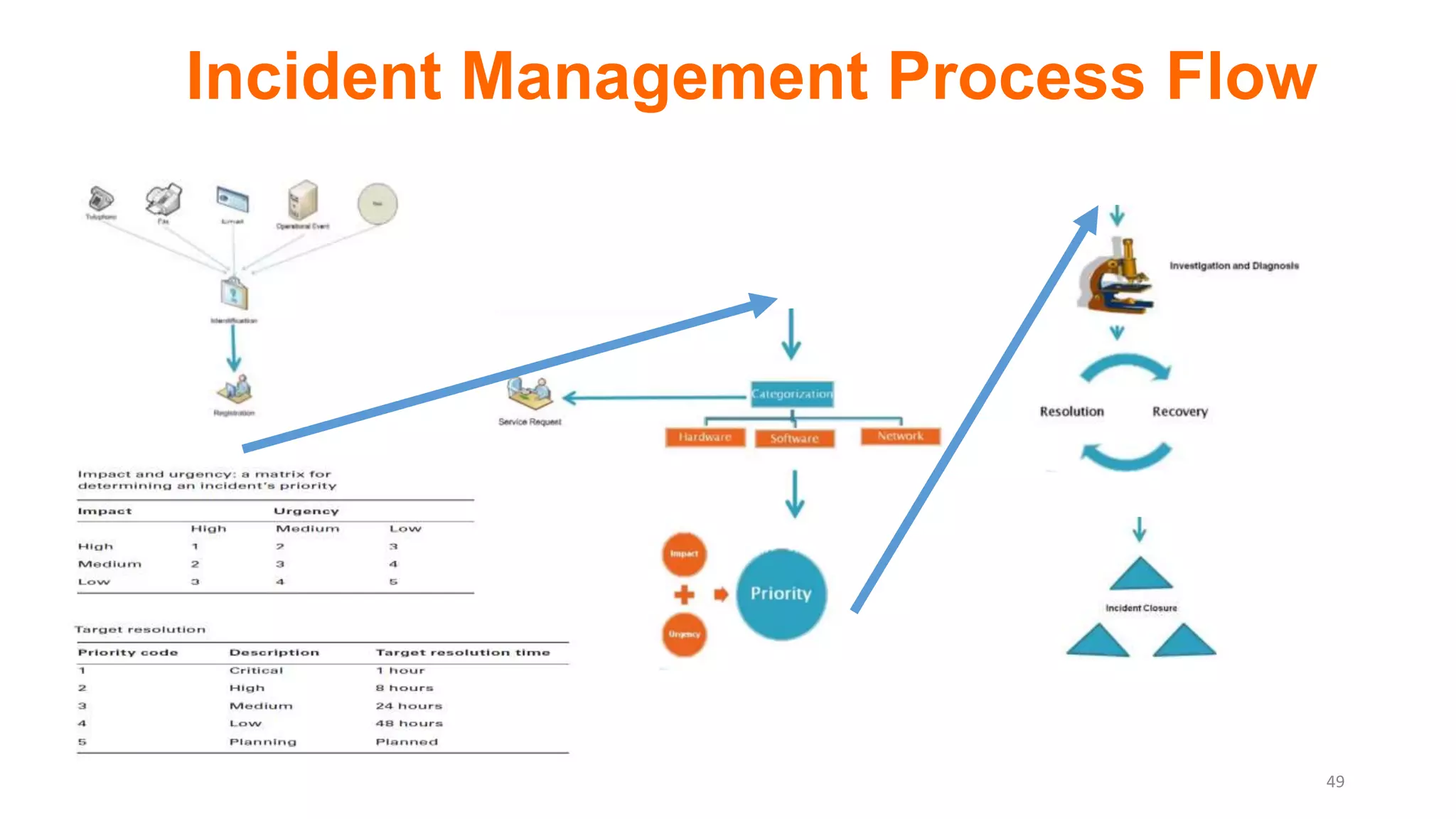
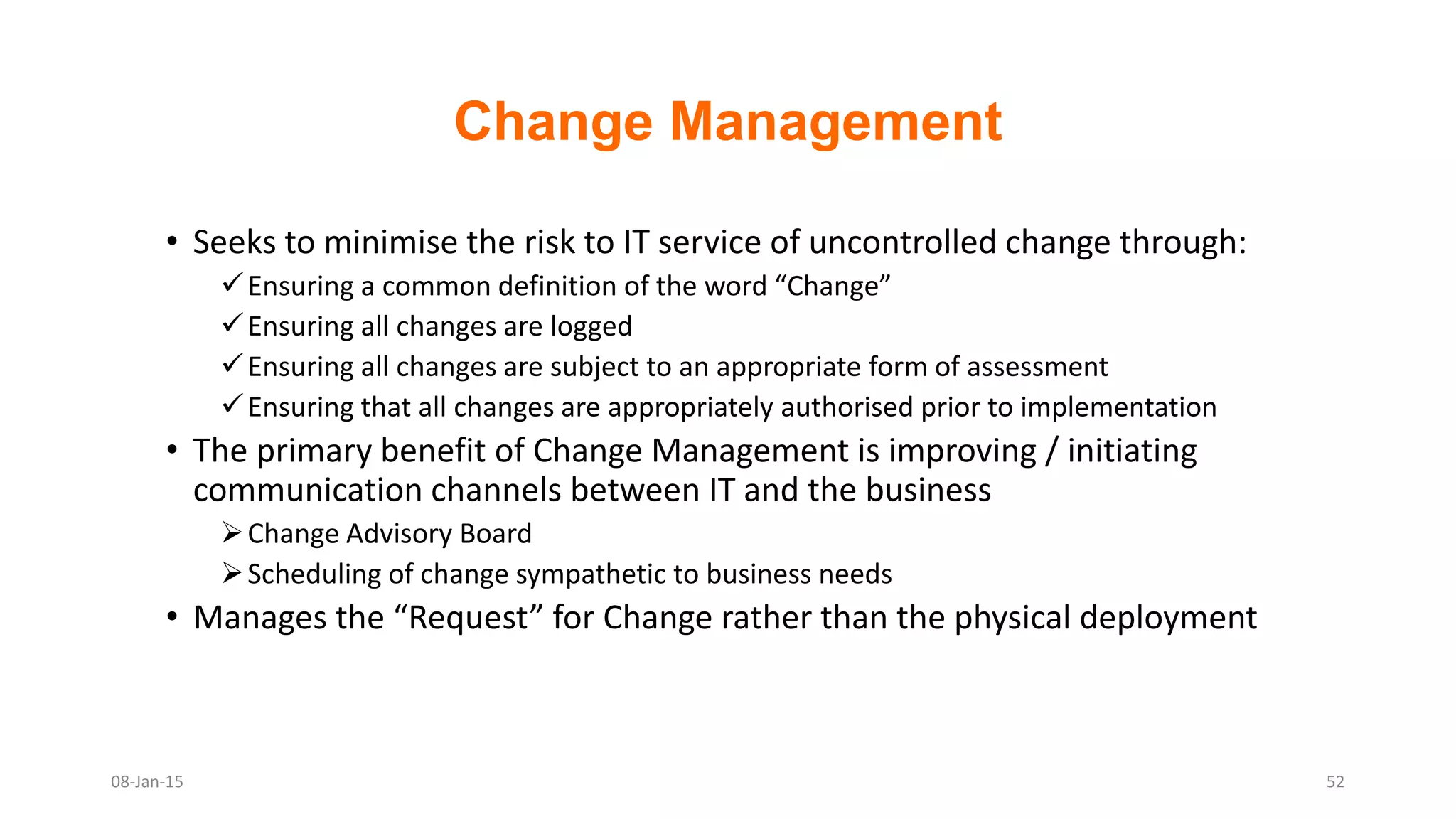
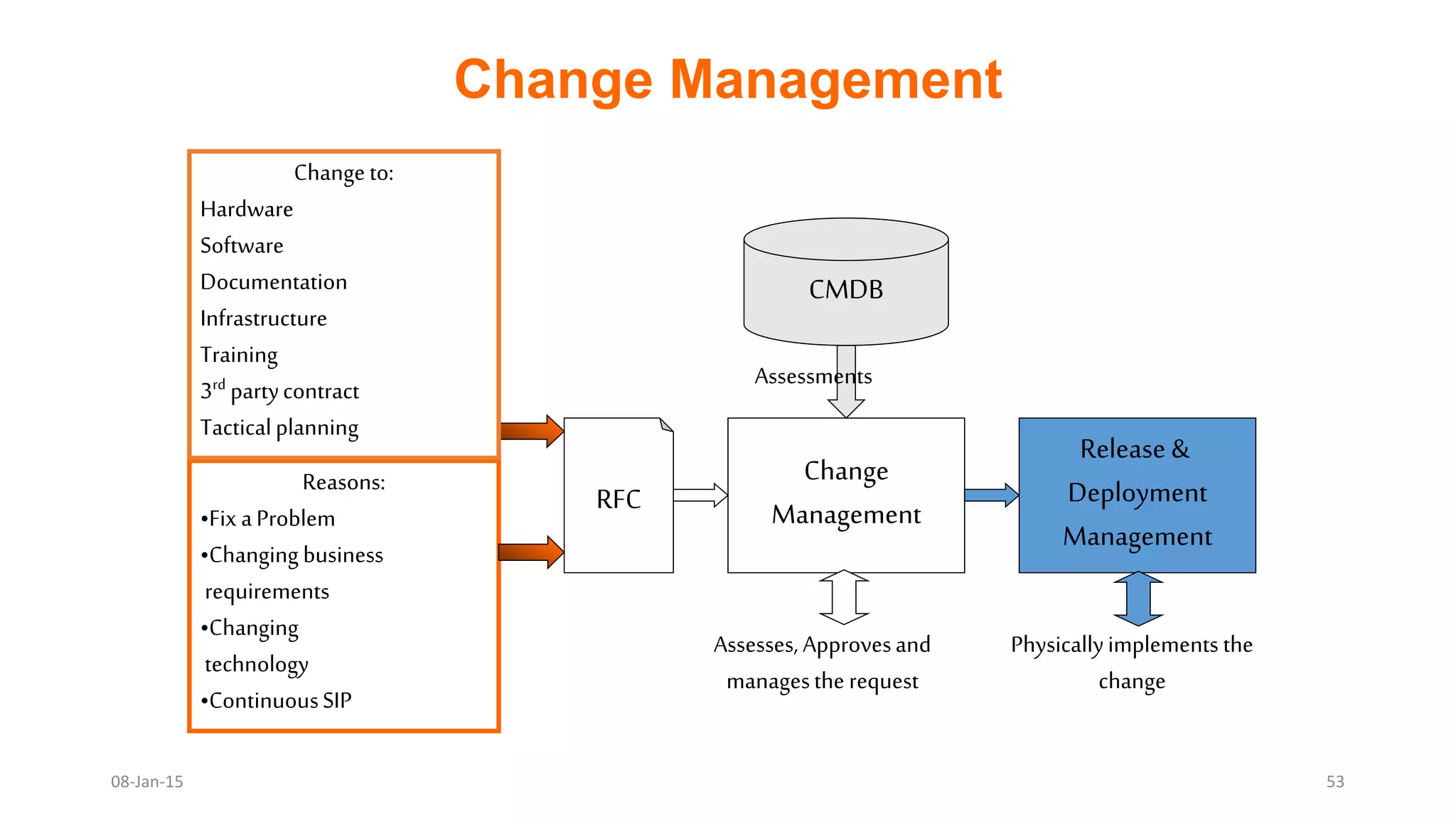
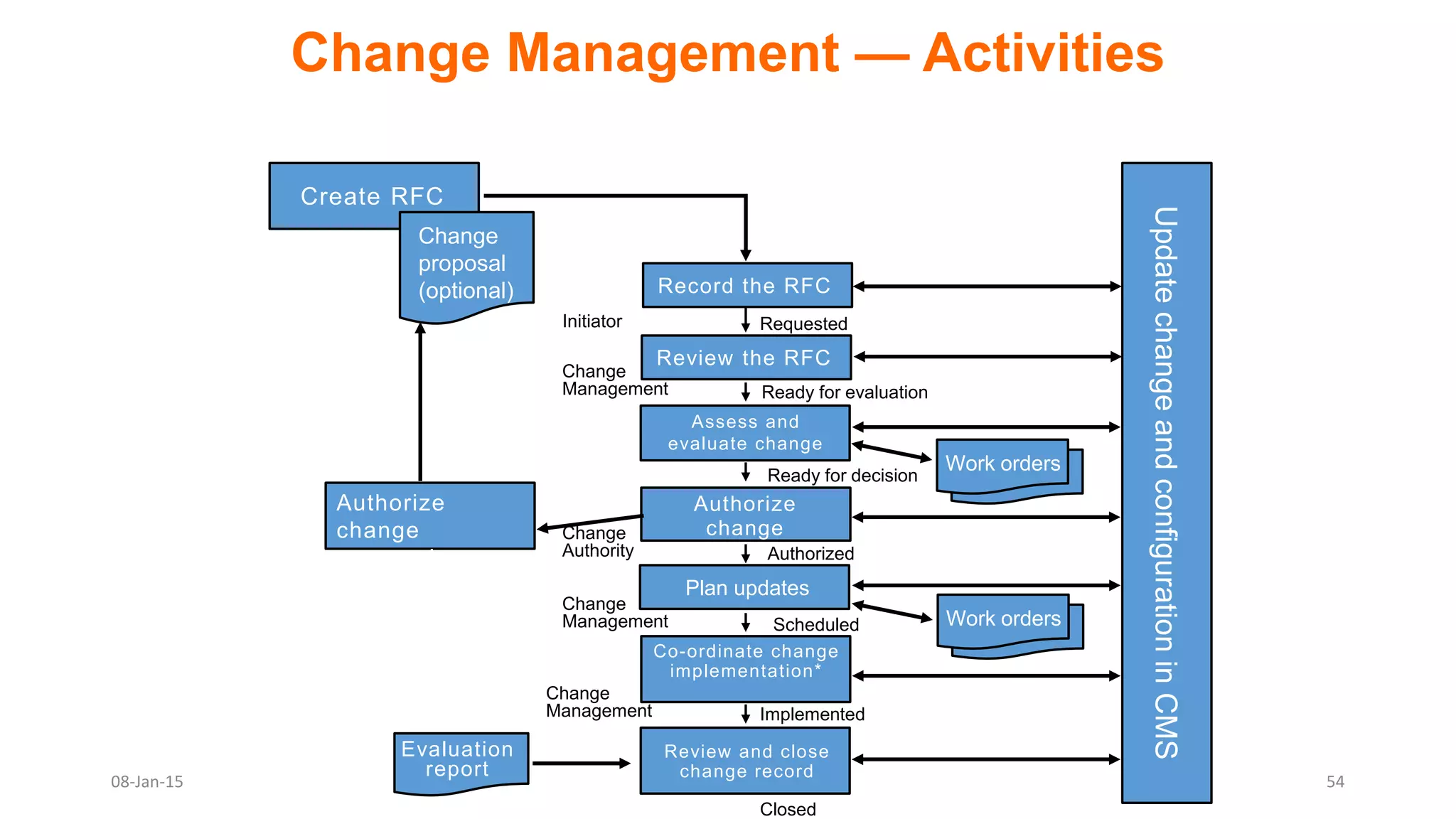
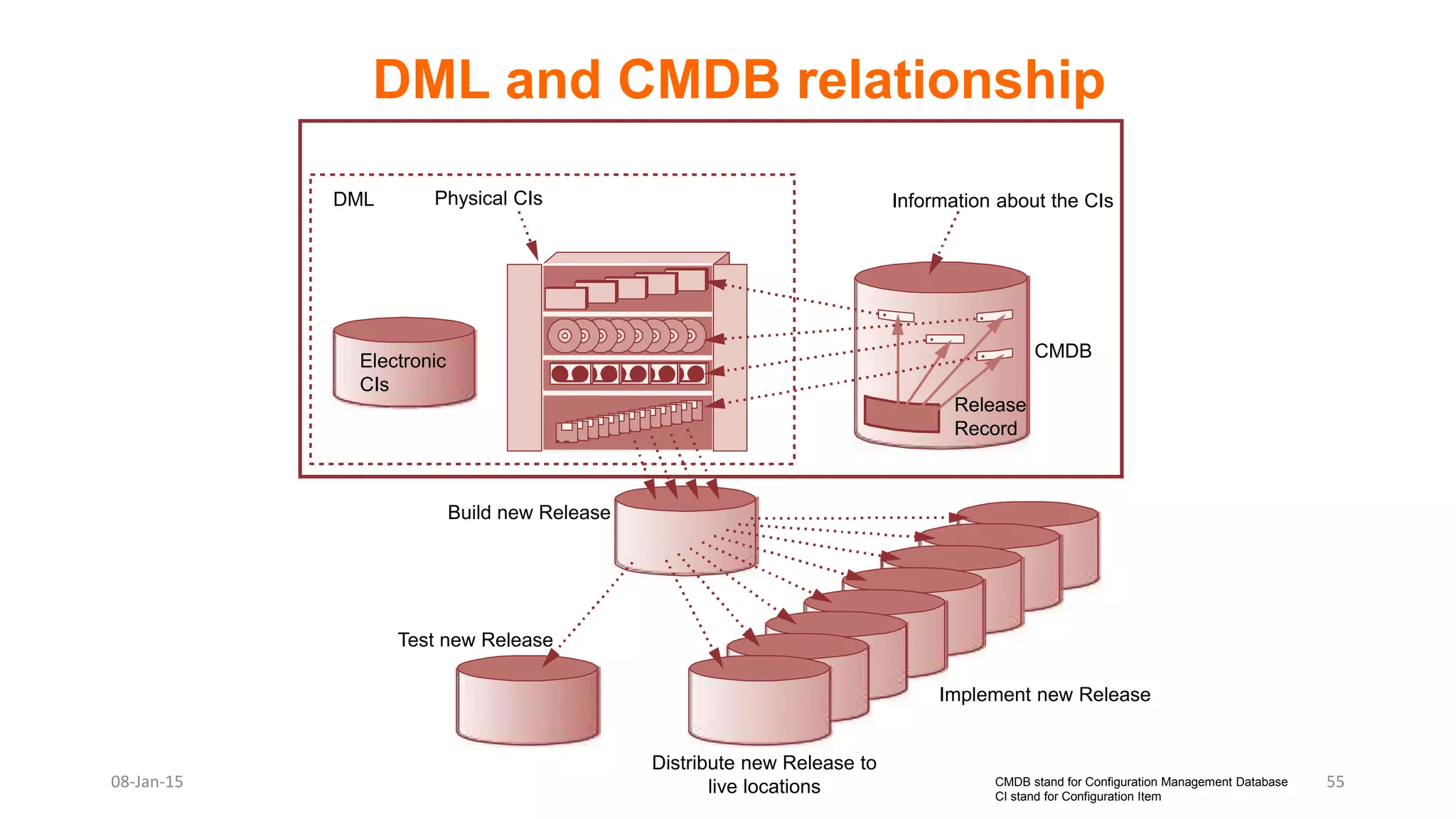
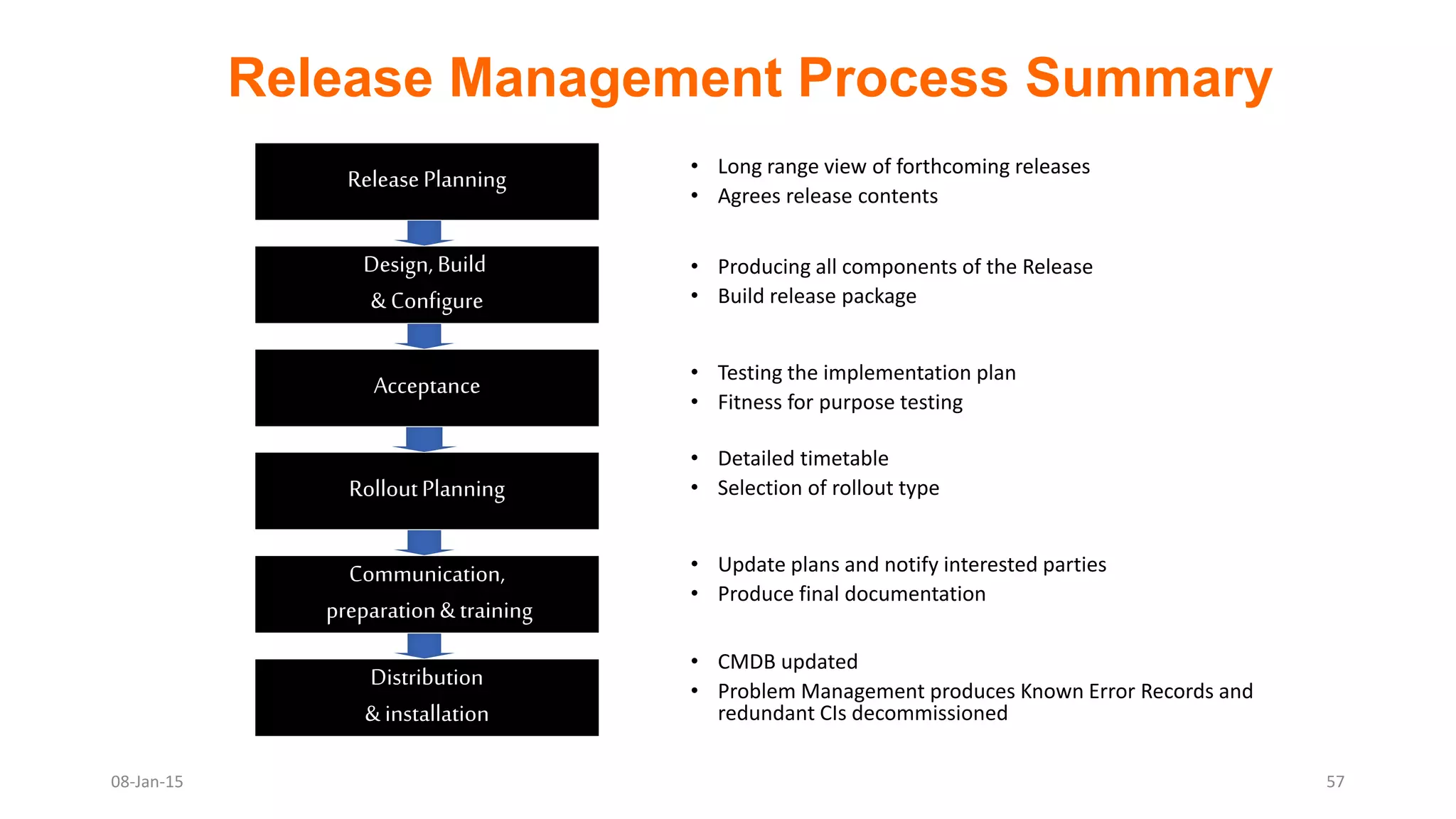
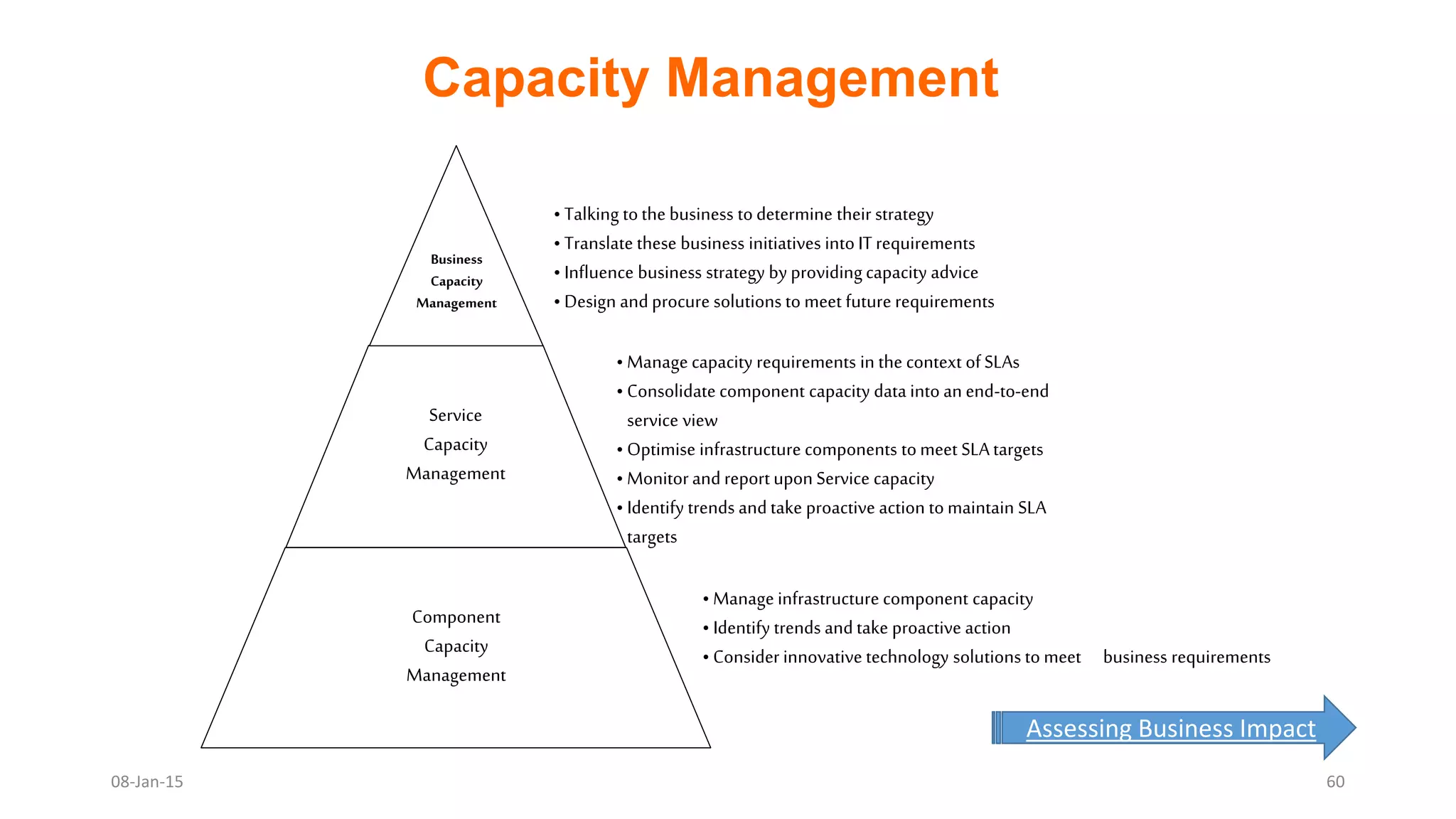
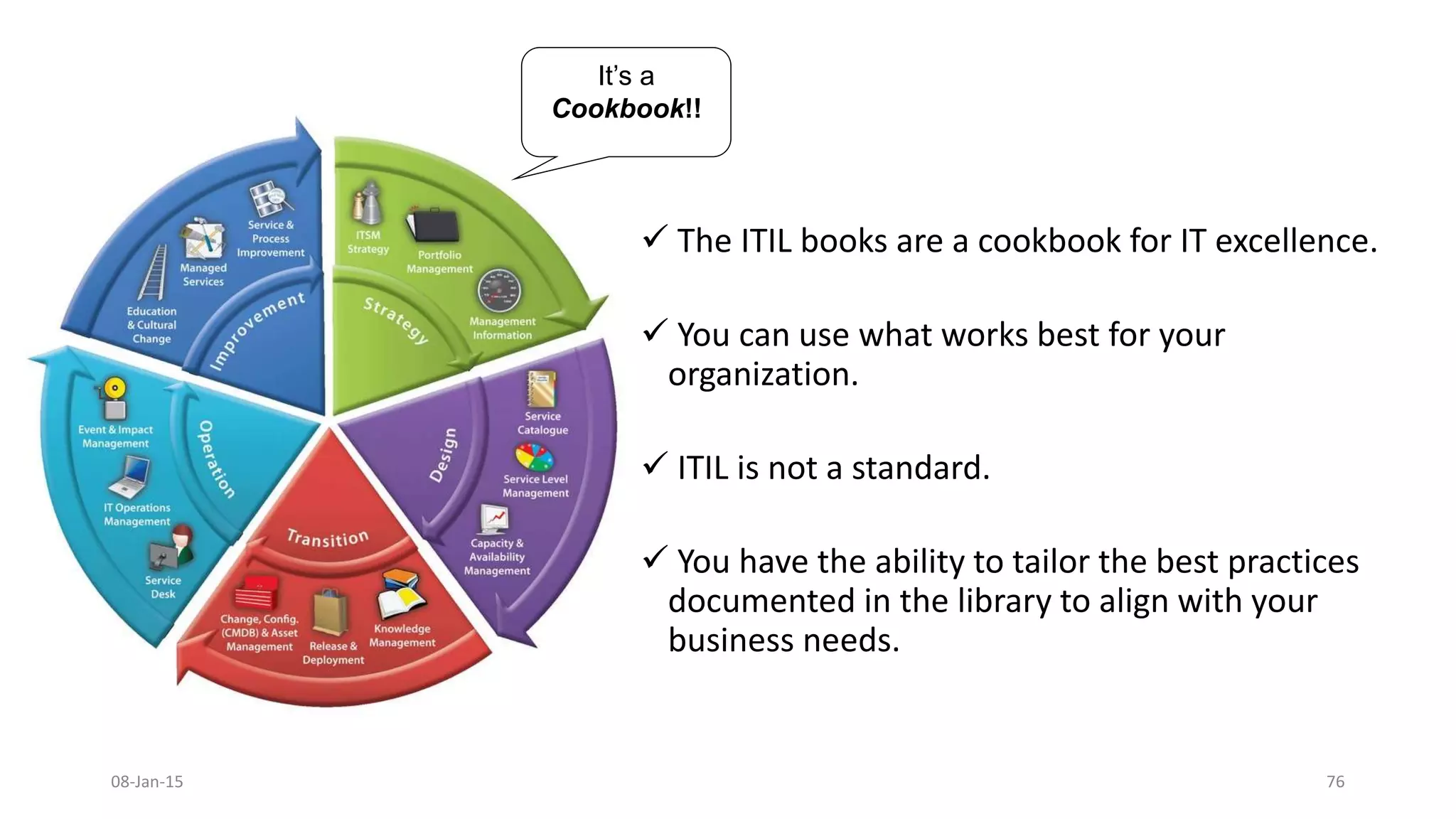
The document provides an overview of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), which is a framework for IT service management. It defines ITIL as a set of specialized organizational capabilities for providing value to customers in the form of IT services. The document then discusses the origins and evolution of ITIL, its key components such as processes, procedures, tasks and checklists. It also outlines the various ITIL modules like service strategy, service design, service transition, service operations and continuous service improvement.