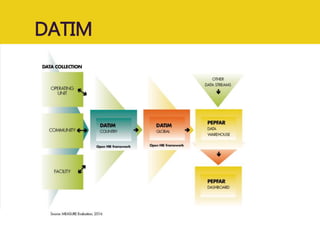
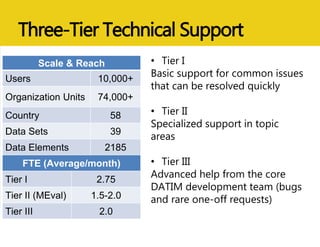
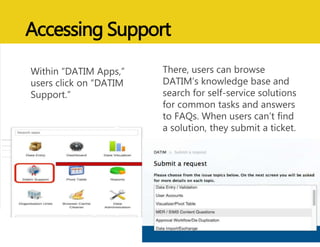
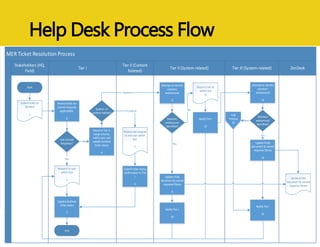
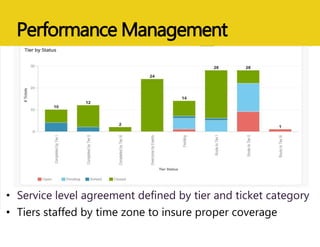
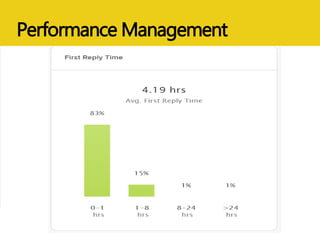
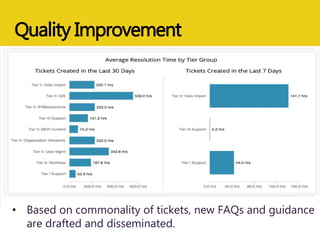
The document discusses MEASURE Evaluation's management of a global help desk for DATIM, a PEPFAR-specific version of DHIS 2 used by over 10,000 people across 58 countries. It describes the implementation of a three-tier support system to provide timely assistance to diverse and geographically dispersed users. Key lessons learned include setting clear policies, building support teams, providing training, and ensuring integration and expansion of services at low cost. Continuous quality improvement is achieved through surveying users and implementing suggested changes.