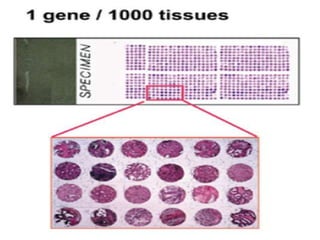
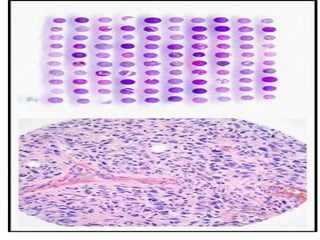
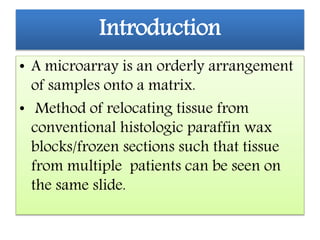
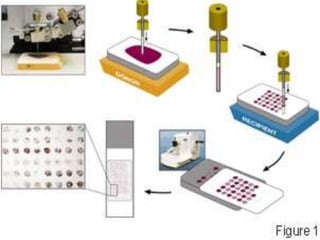
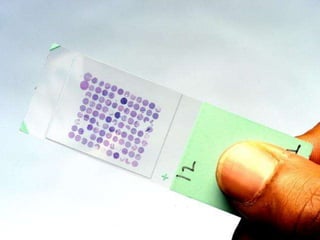
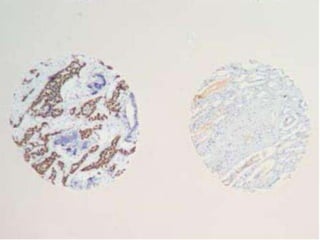
This document discusses tissue microarrays (TMAs), which allow analysis of hundreds of tissue samples on a single slide. It describes how TMAs are constructed by taking small tissue cores from donor blocks and embedding them in a recipient block. The advantages of TMAs include high throughput analysis and relatively low cost. Various types of TMAs are used for applications like immunohistochemistry, in situ hybridization, and analyzing protein/DNA expression. The document outlines the steps to construct a TMA, including defining the research question, selecting cases, determining core size and number, making a map, and embedding the cores. Quality controls and limitations are also discussed.