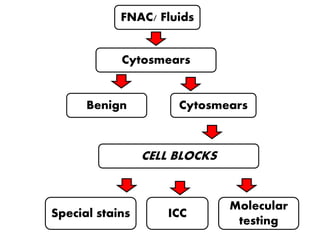
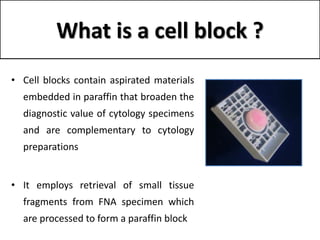
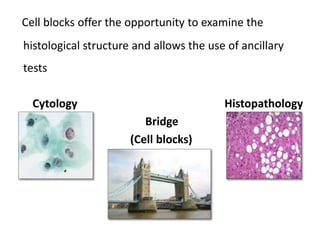
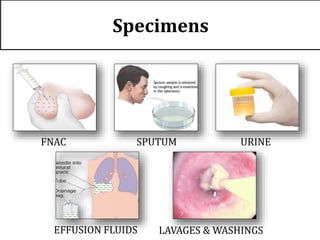
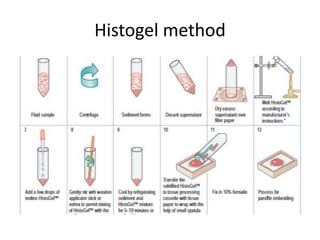
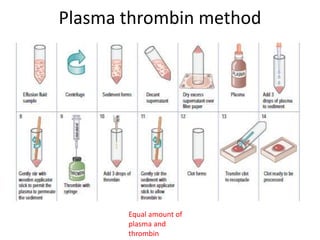
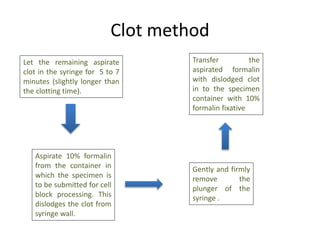
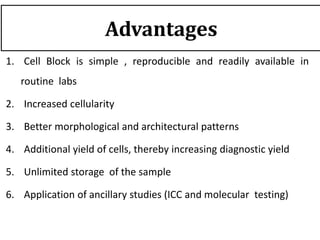
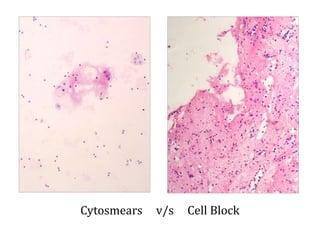
The document discusses the history, utility, and methods of preparing cell blocks from fine needle aspiration cytology samples. Cell blocks allow examination of histological structure and use of ancillary tests. Key methods include the fixed sedimentation method using a 1:1 ratio of 100% alcohol and 40% formalin, the plasma thrombin method using equal parts plasma and thrombin, and the bacterial agar method using 3% agar. Cell blocks provide increased diagnostic sensitivity and specificity compared to cytology alone through examination of tissue architecture and ability to perform special stains and molecular testing.