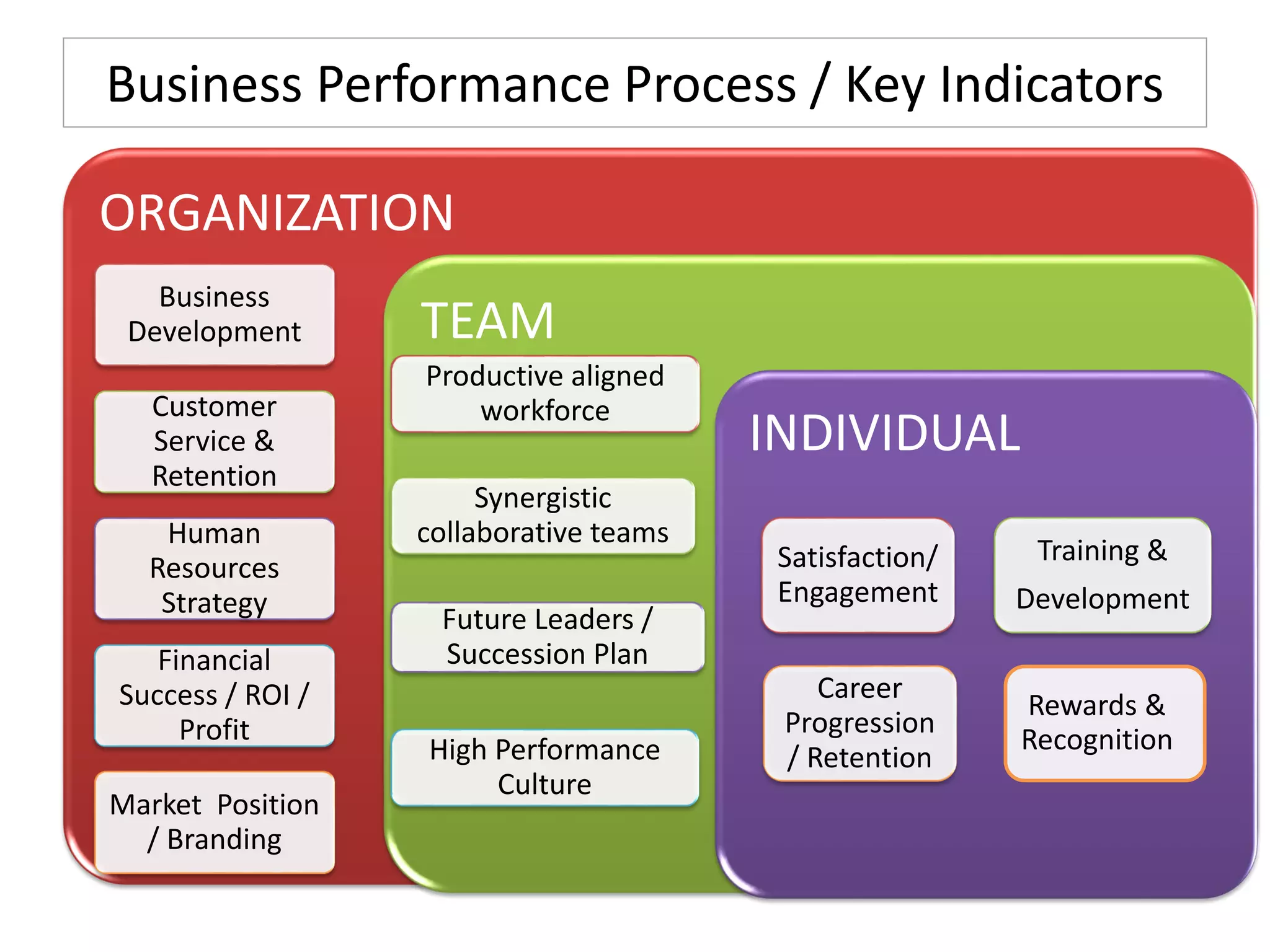
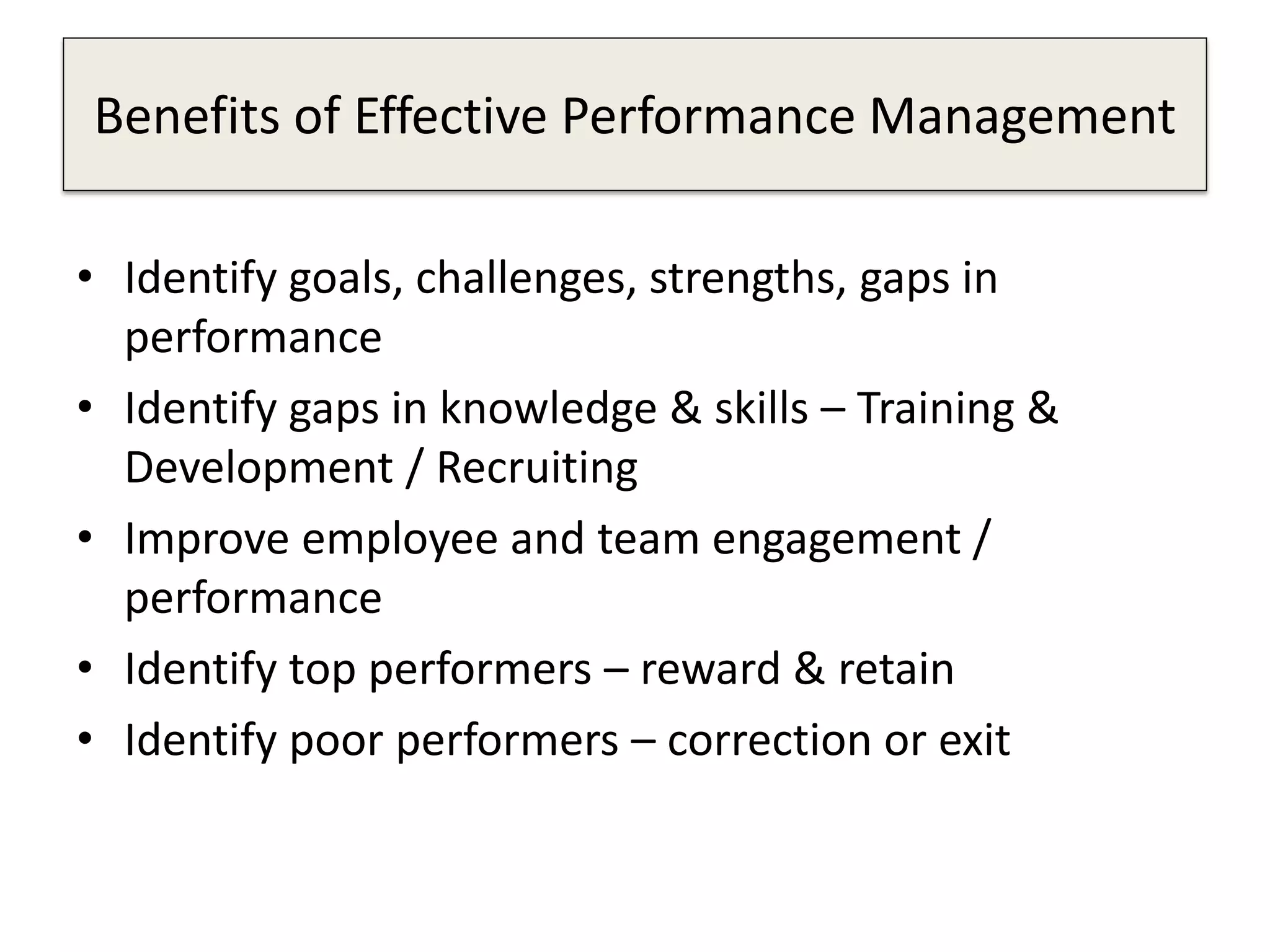
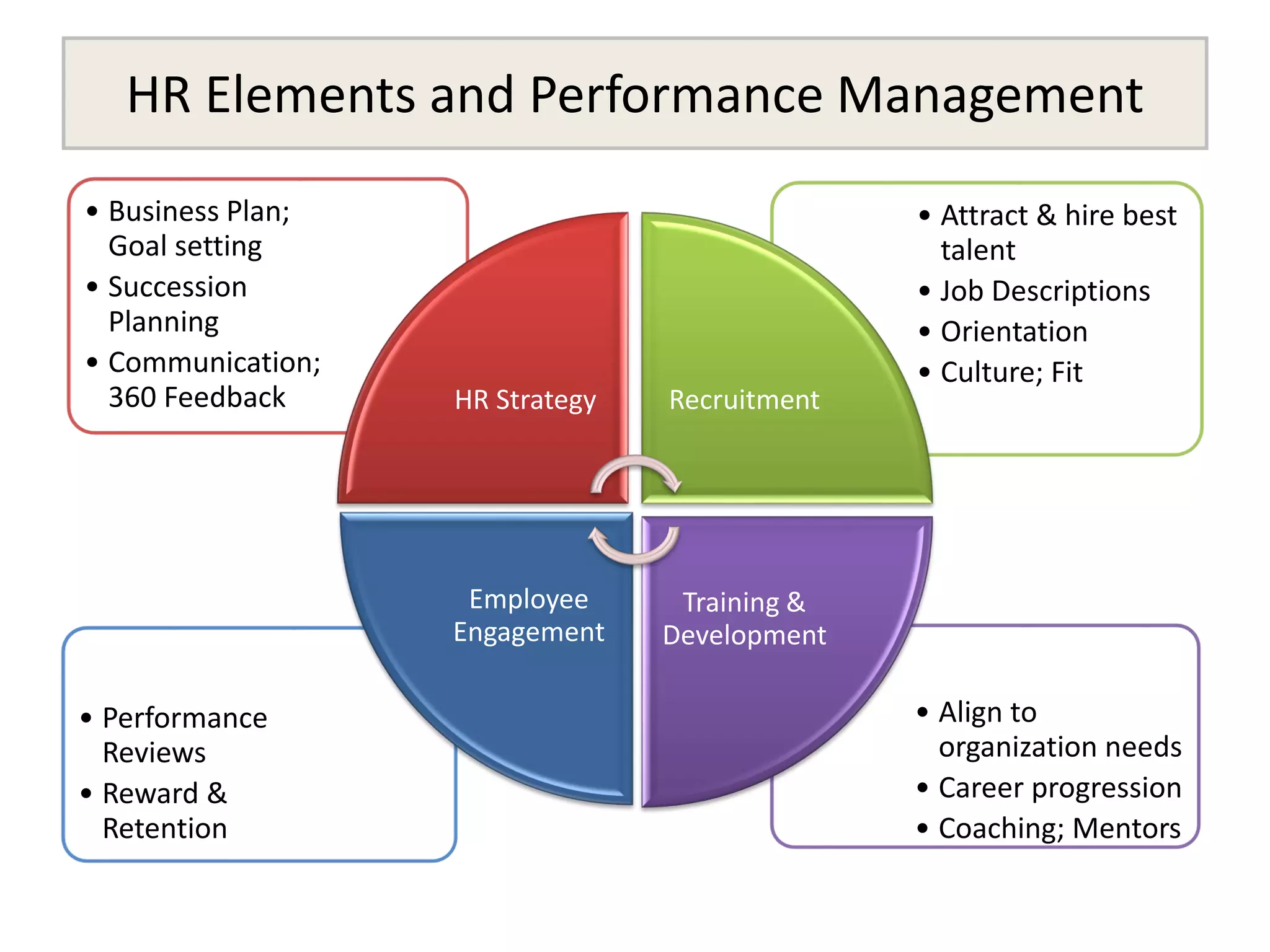
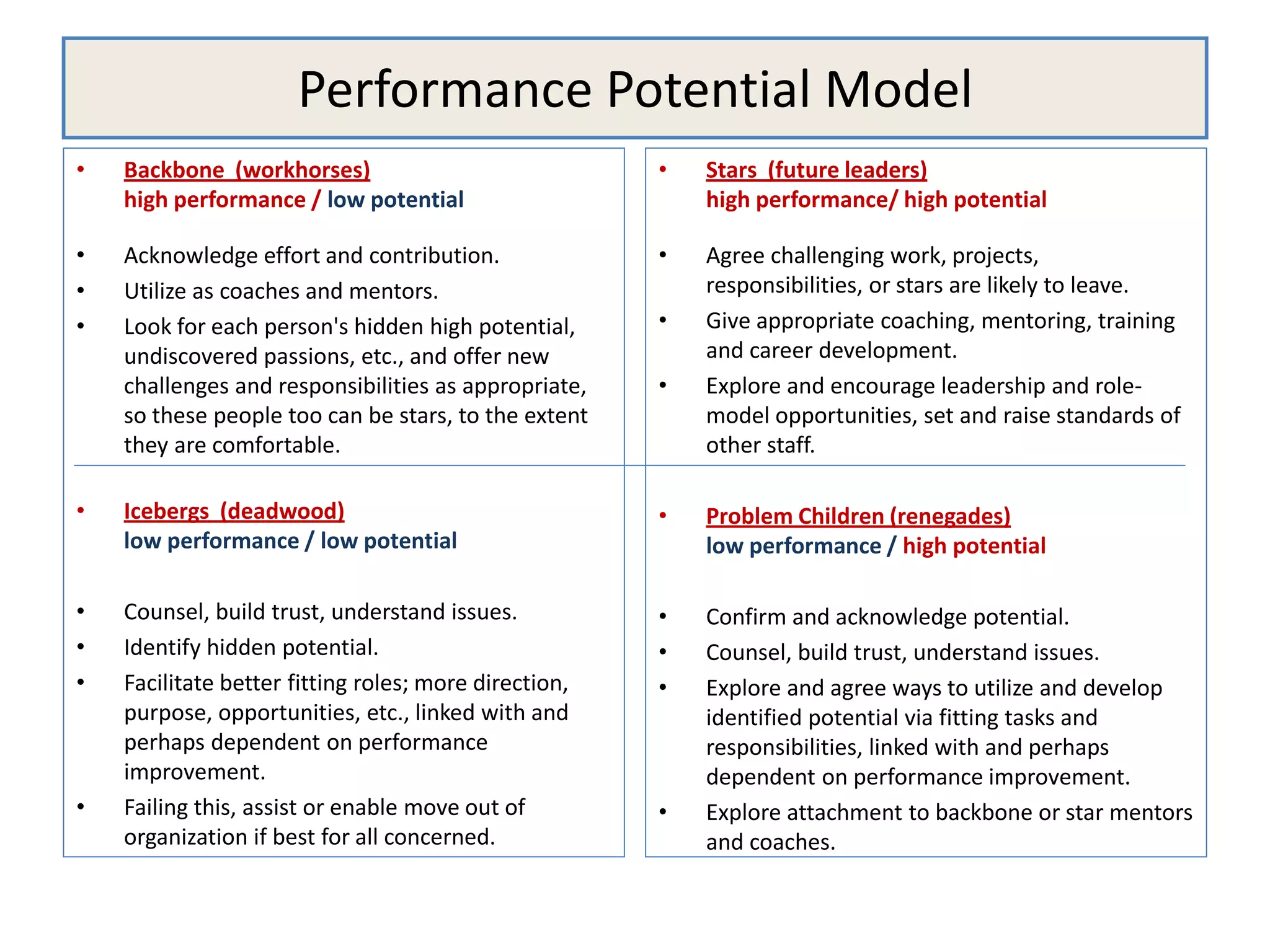
The document outlines the design and implementation of a performance management program, emphasizing the alignment of individual and team goals with organizational objectives. It highlights the importance of regular communication, benchmarking, and various performance management models to enhance employee engagement and performance. Additionally, it discusses HR elements crucial for effective performance management and the benefits of such programs, including improved productivity and reduced turnover.