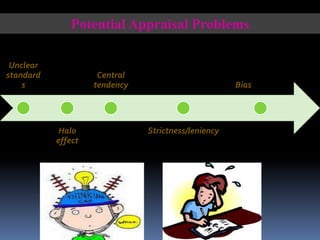
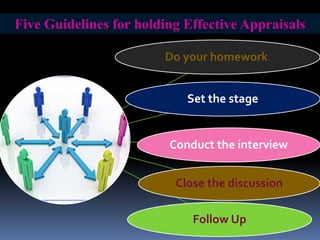
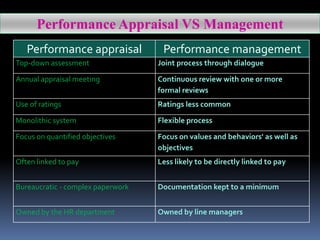
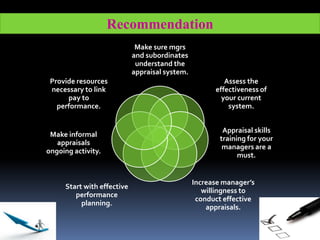
Performance management and appraisal involve ongoing evaluation of employee performance and development. Performance appraisal is the formal review, usually annual, that is the last step in the performance management process. Appraisals help identify employee strengths and weaknesses, provide feedback, and inform salary and career decisions. The supervisor plays a key role by observing performance, providing coaching, and conducting the formal review. Effective appraisals involve preparation, assessment, review, and follow up.