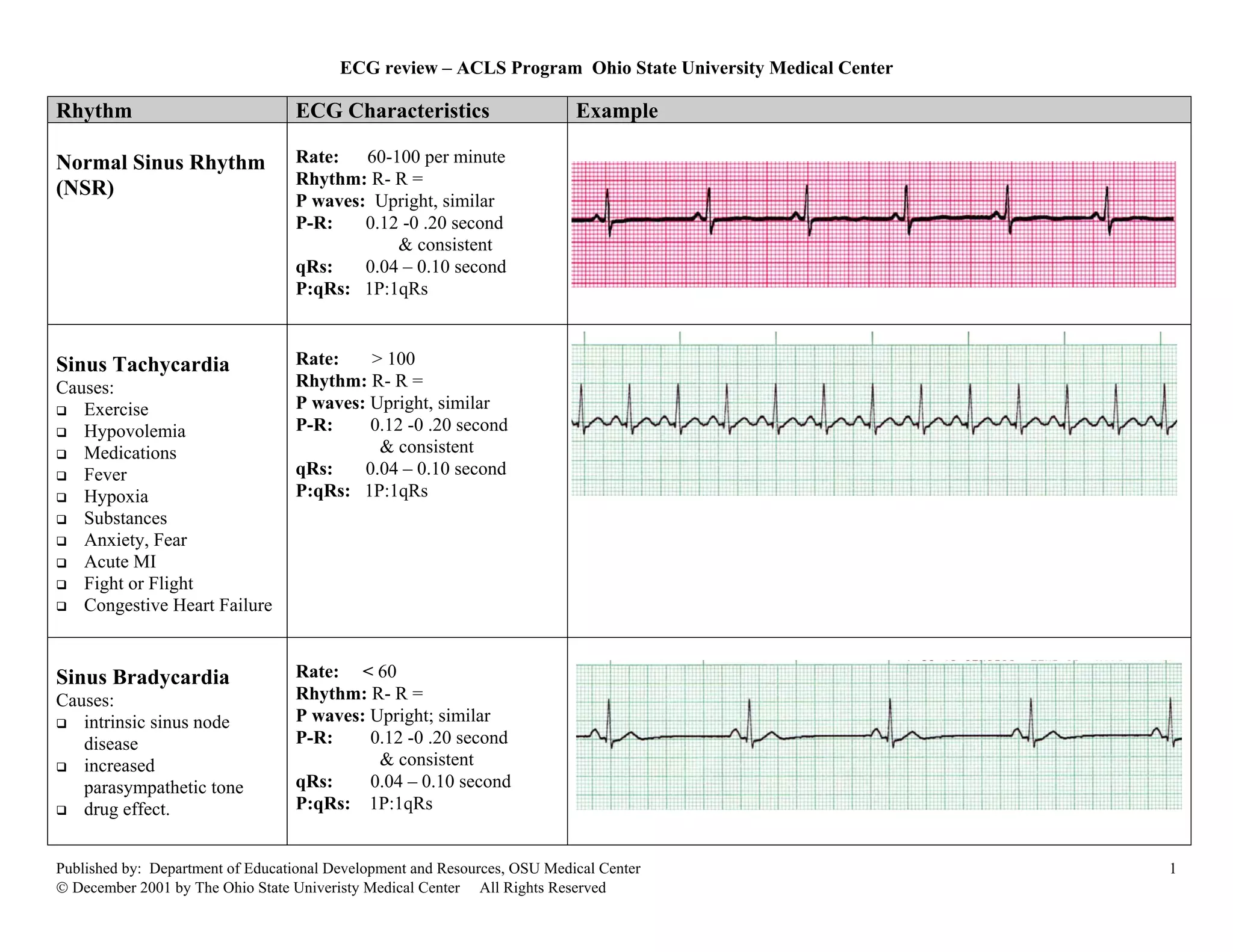
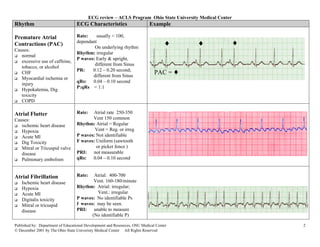
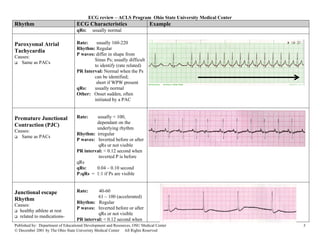
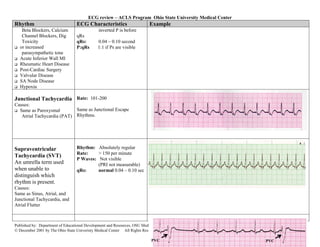
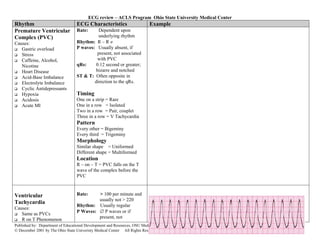
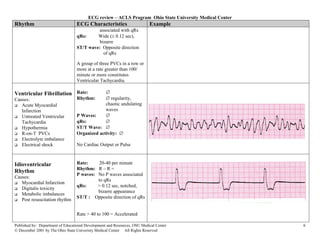
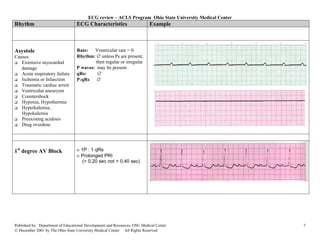
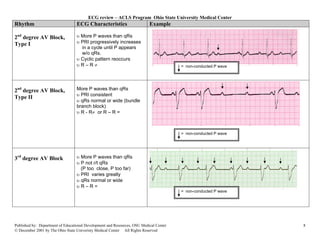
This document provides an overview of common cardiac rhythms seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs) including normal sinus rhythm, sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, premature atrial contractions, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, premature junctional contractions, junctional escape rhythm, junctional tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, premature ventricular complexes, and ventricular tachycardia. For each rhythm, the typical heart rate, rhythm, P wave characteristics, PR interval, QRS duration, and examples are described. Causes of each rhythm are also listed.