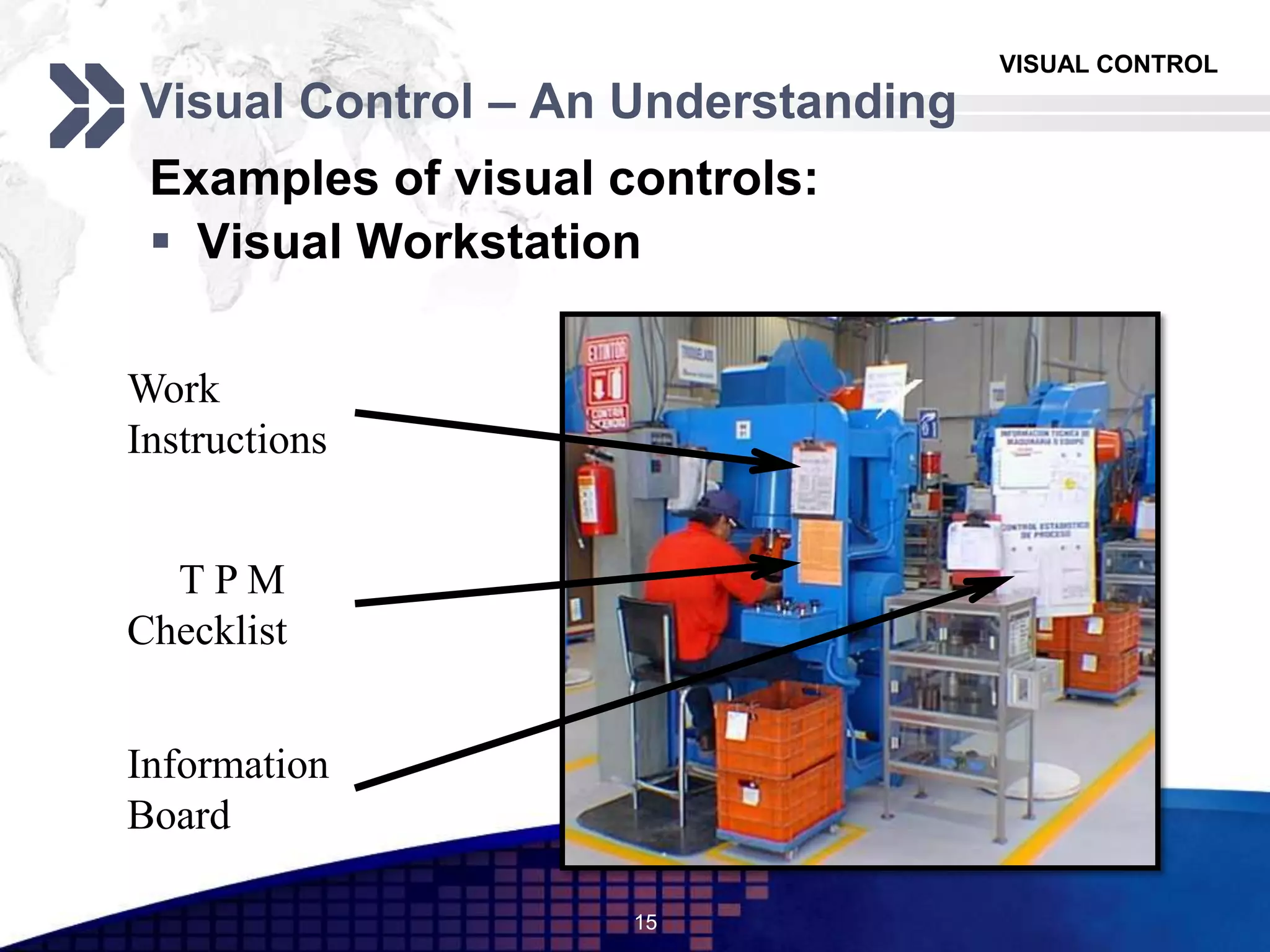
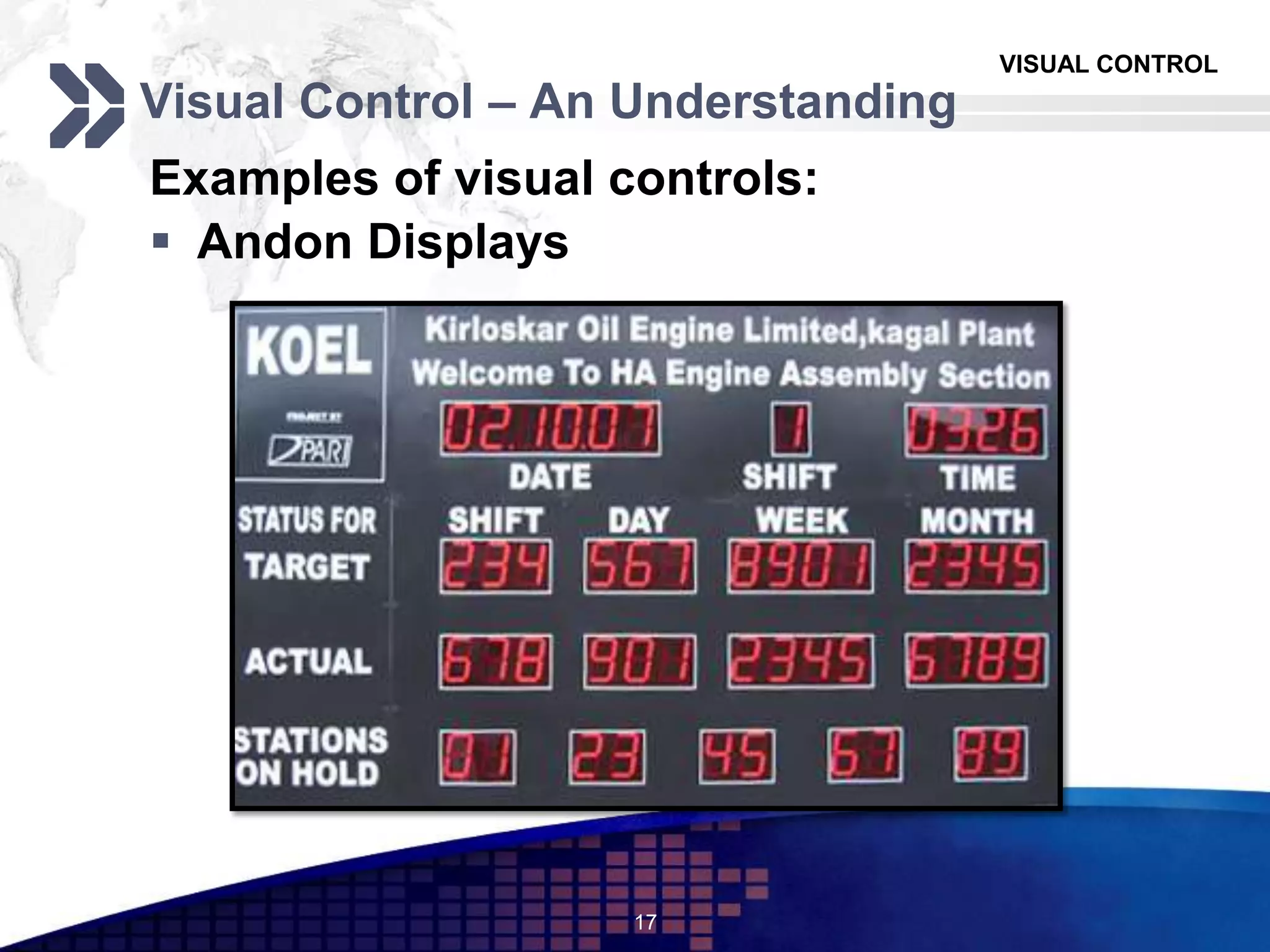
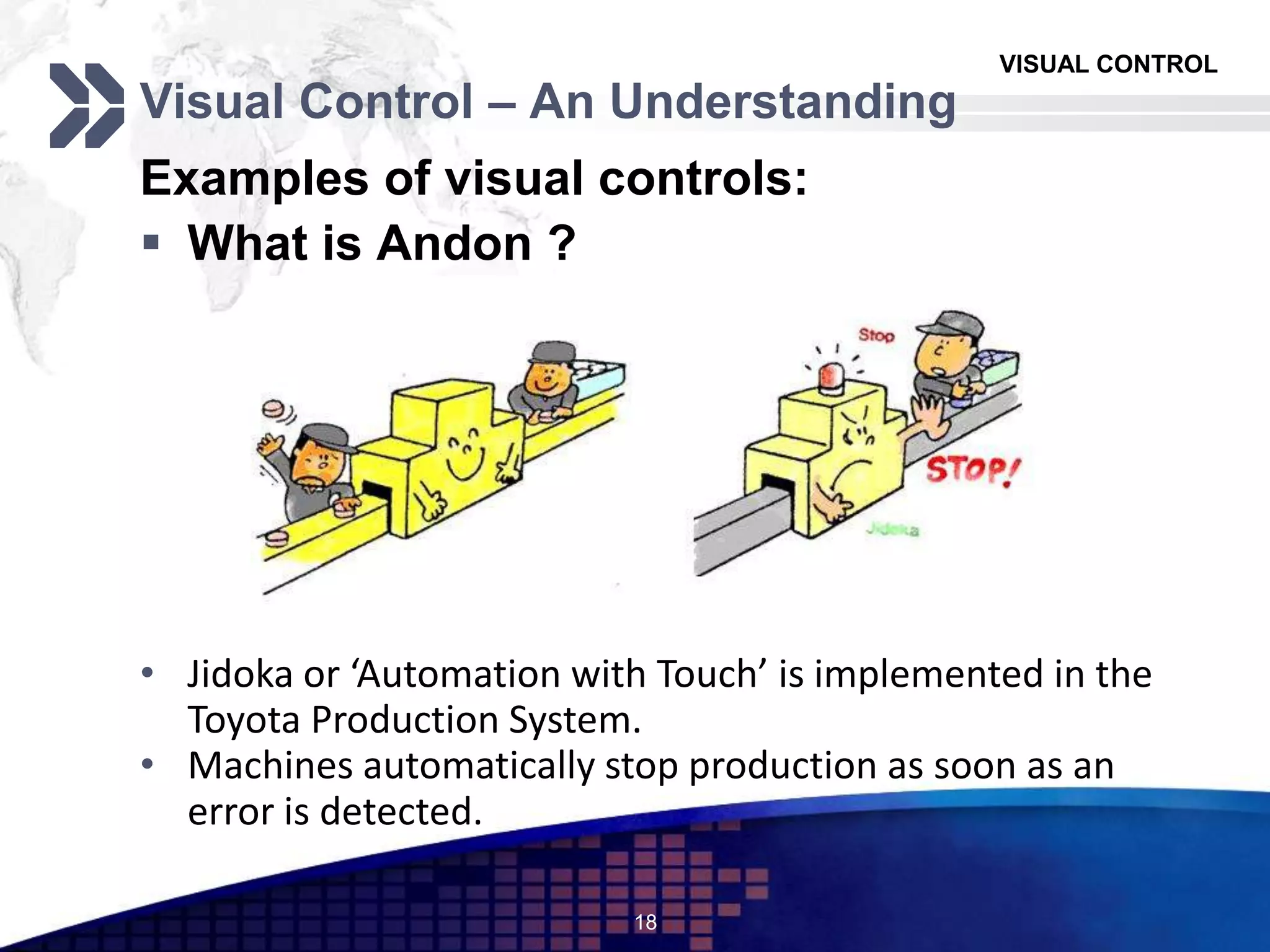
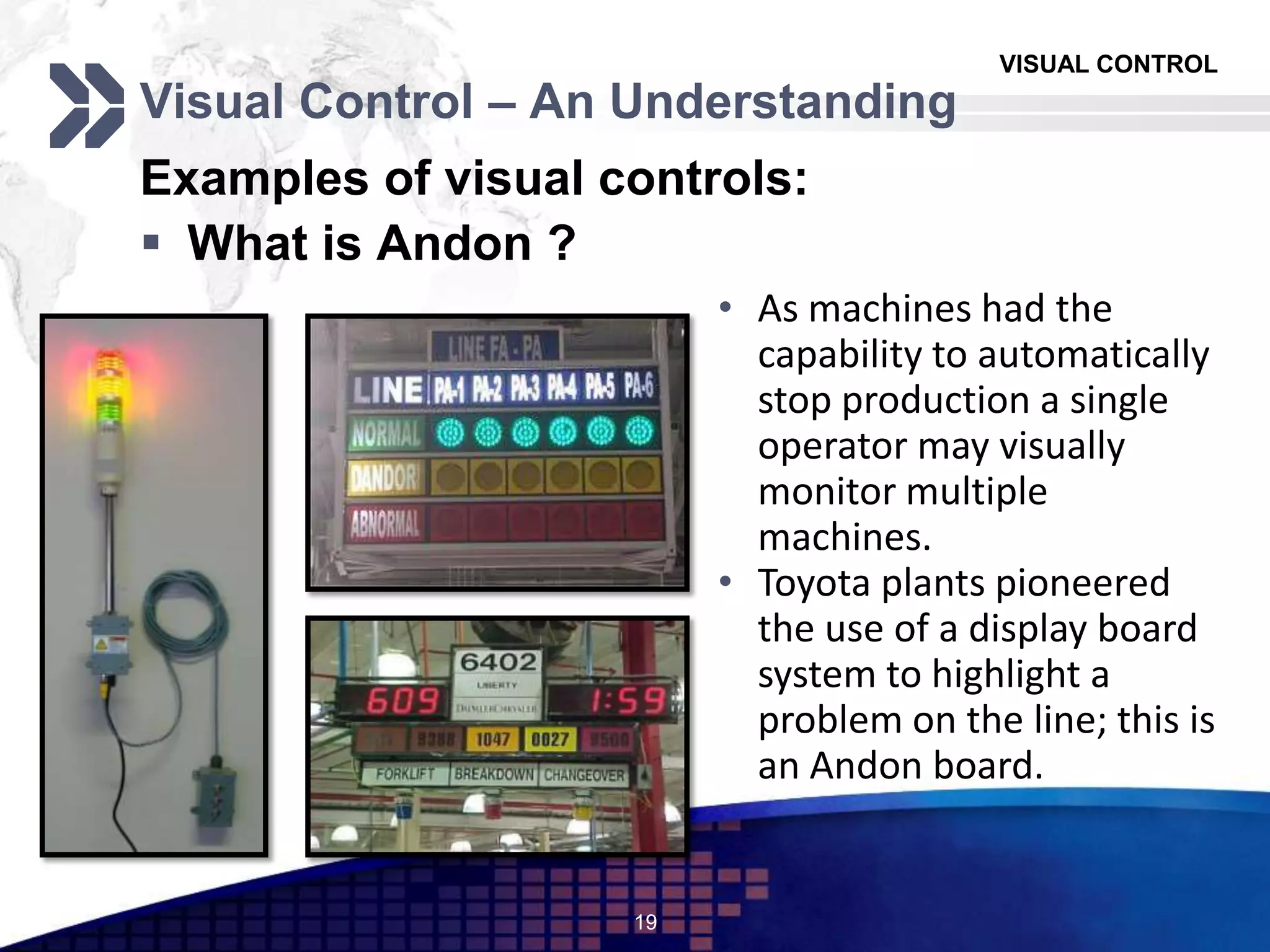
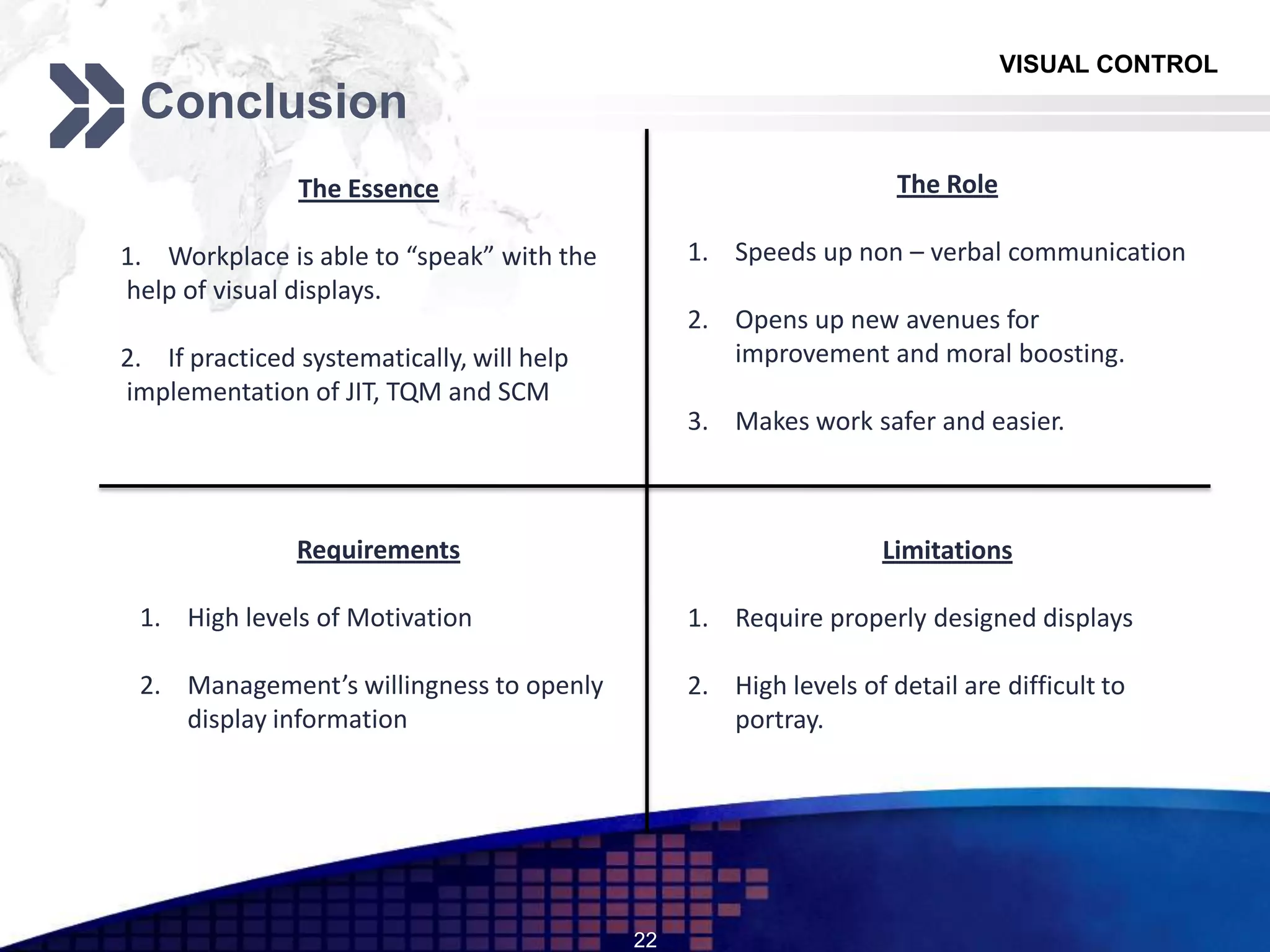
The document discusses visual control in the workplace, emphasizing its role in enhancing education, morale, and productivity through visual elements. It outlines the types of visual controls, including identification, informative, instructional, and planning tools, and highlights their advantages such as improved communication and rapid corrective action, as well as limitations like the potential to obscure facts if poorly designed. Ultimately, the document asserts that effective visual control fosters transparency and motivates employees, contributing to better operational management.