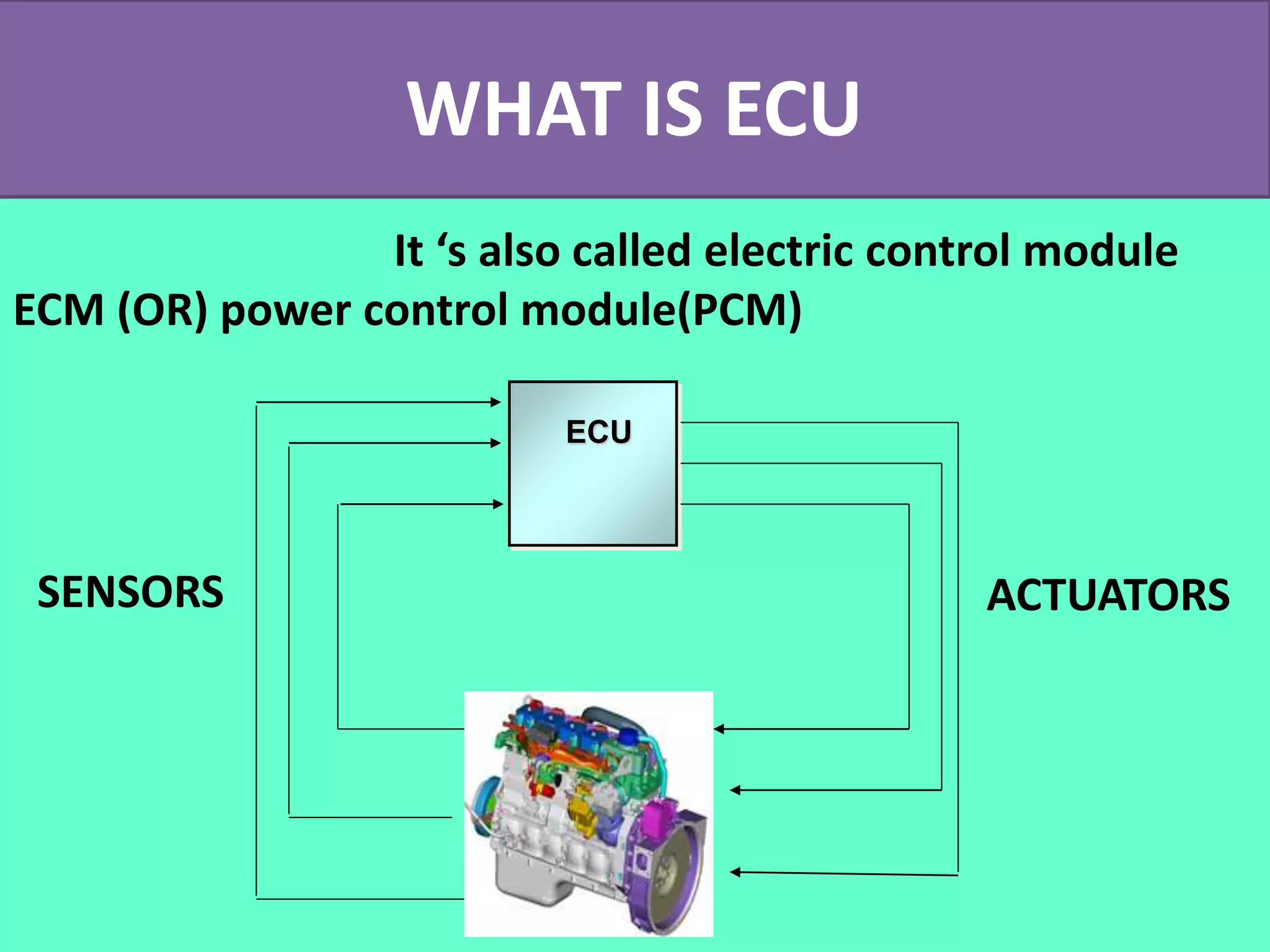
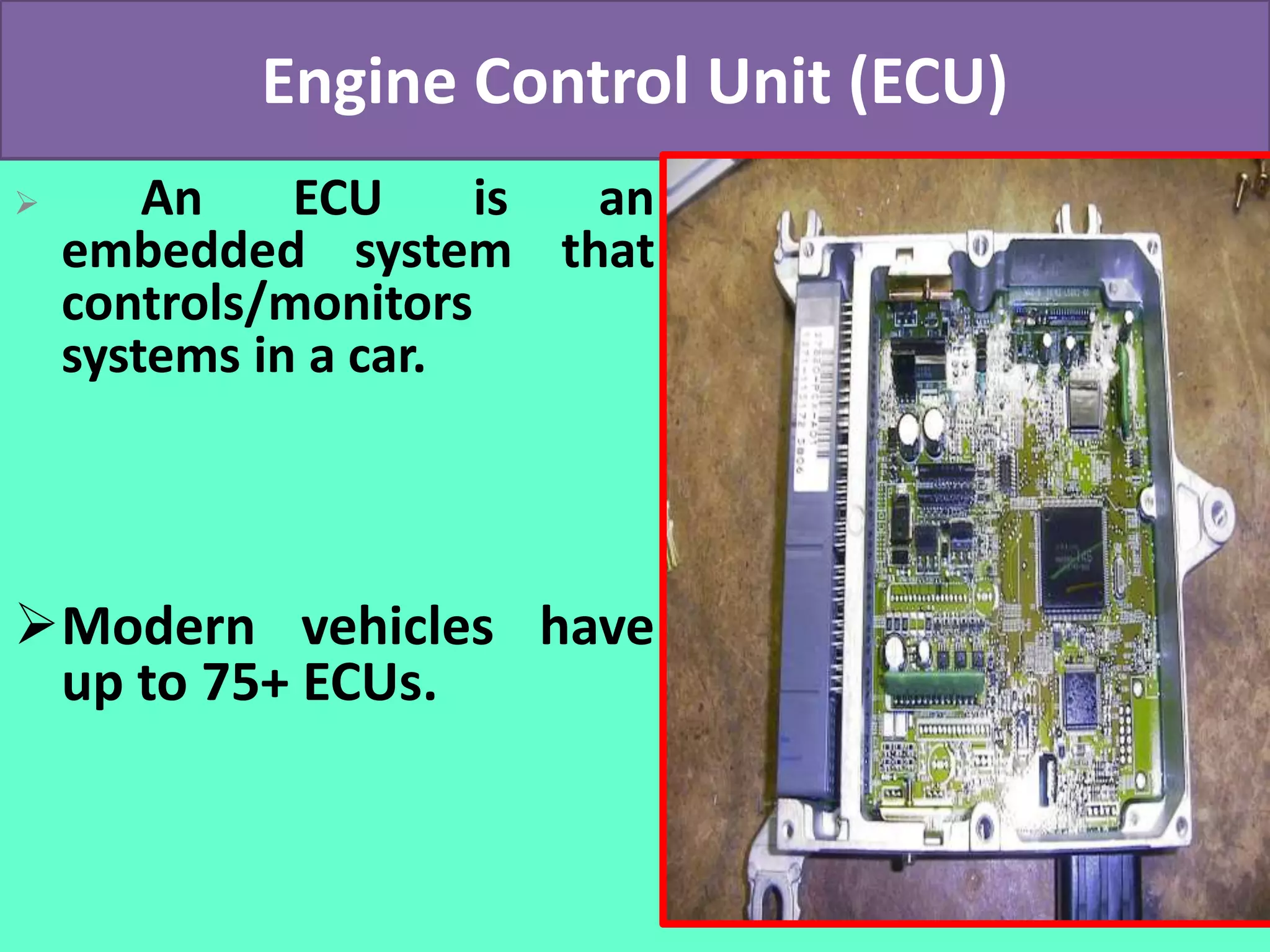
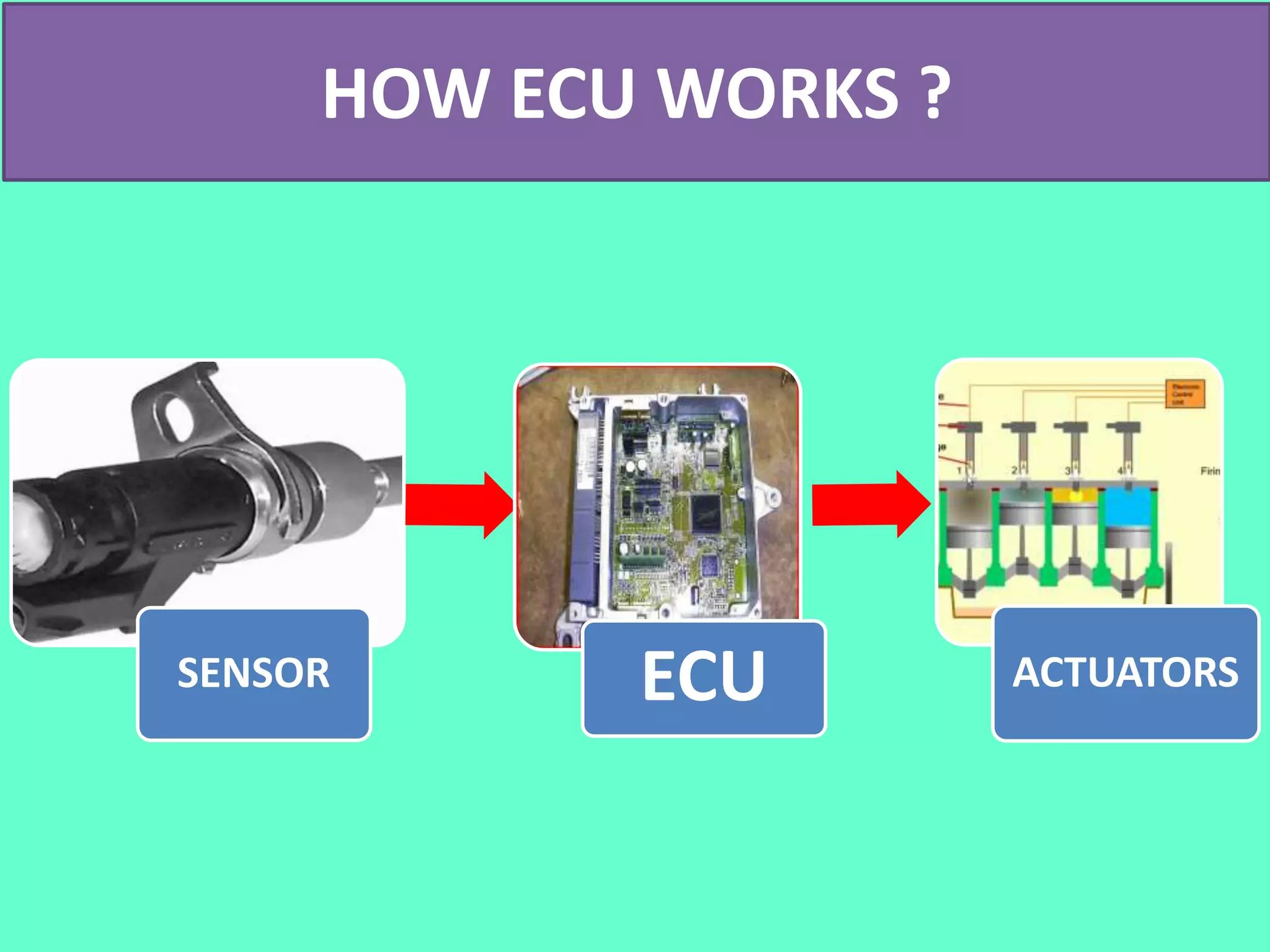
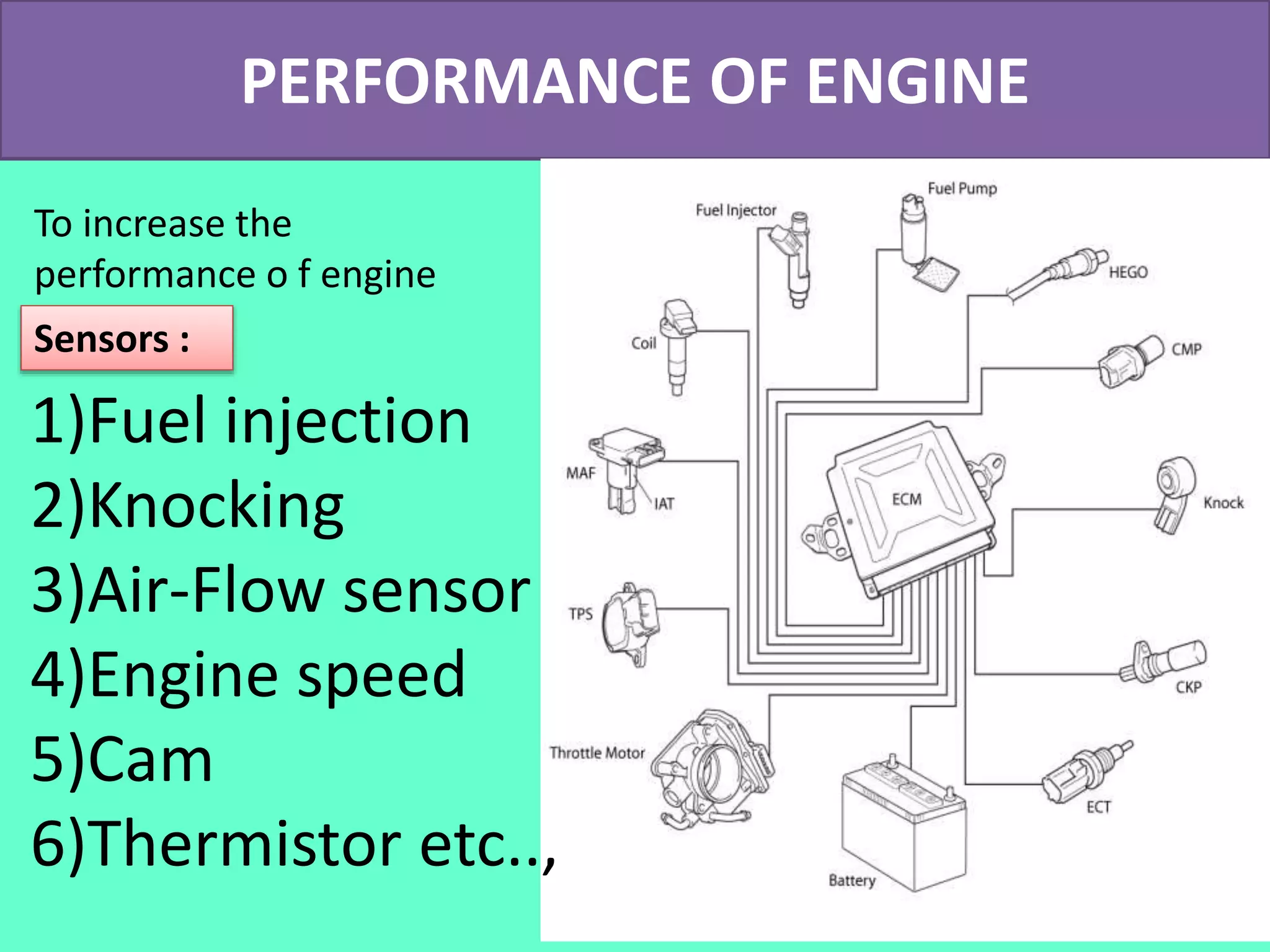
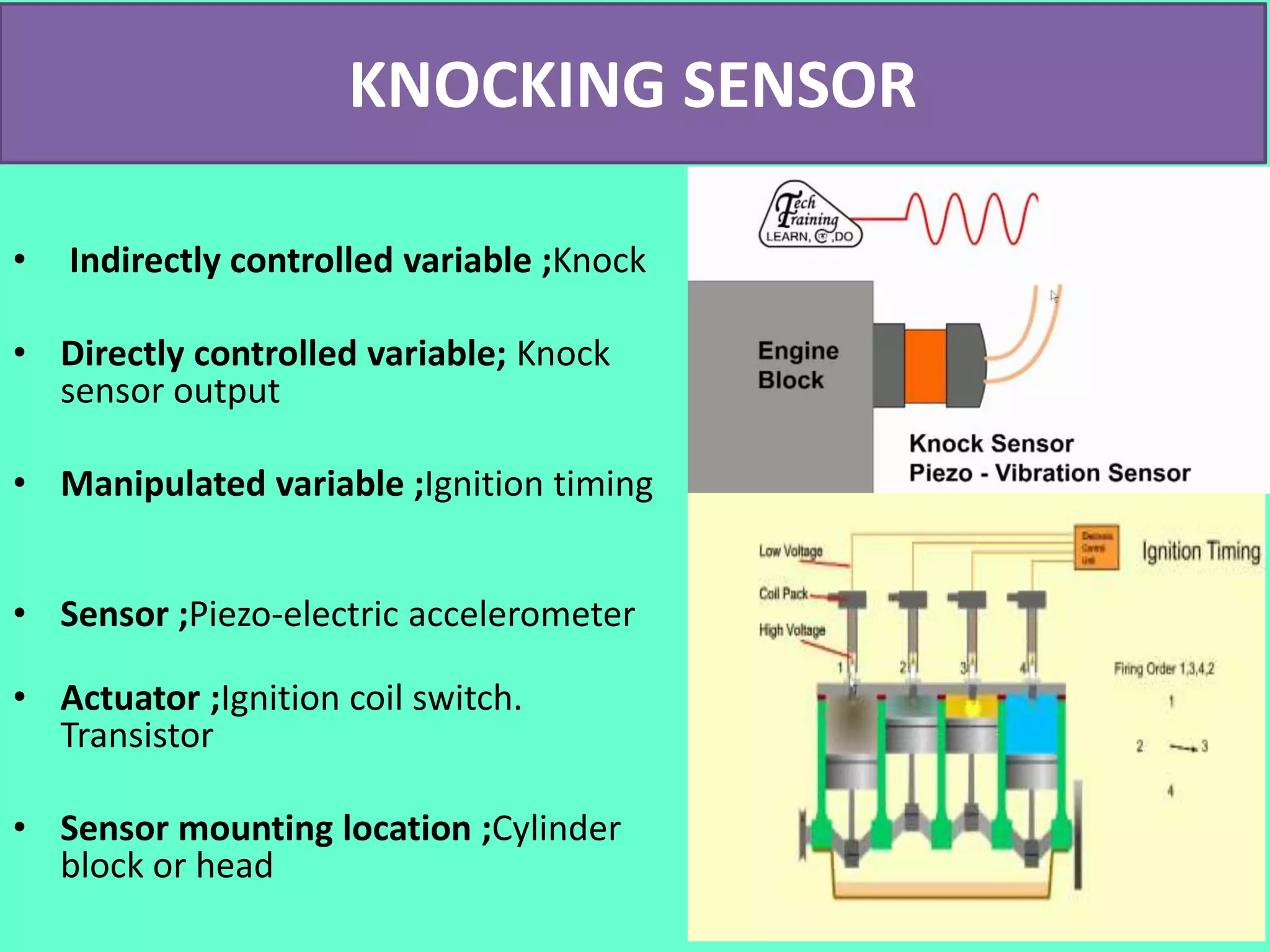
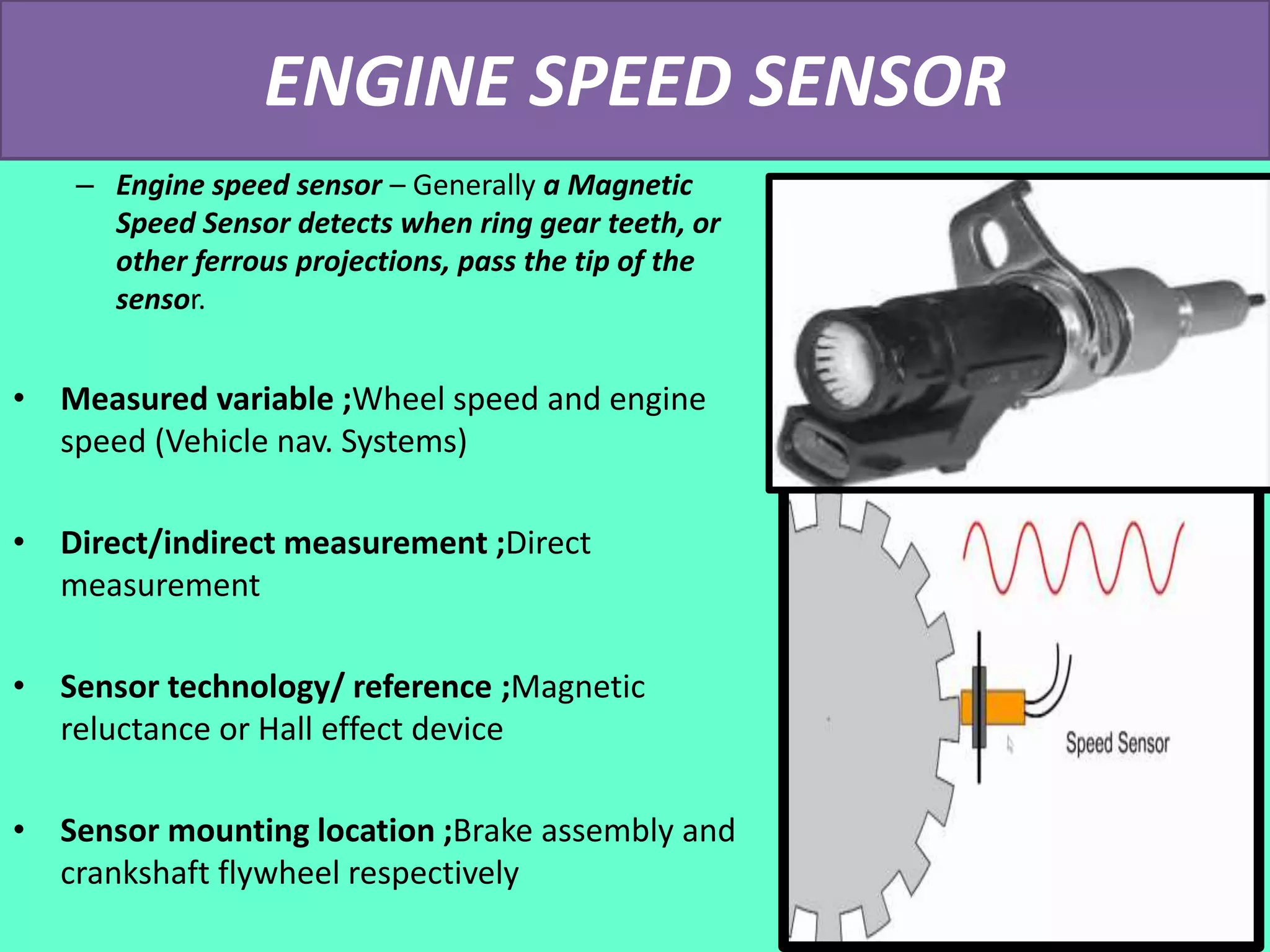
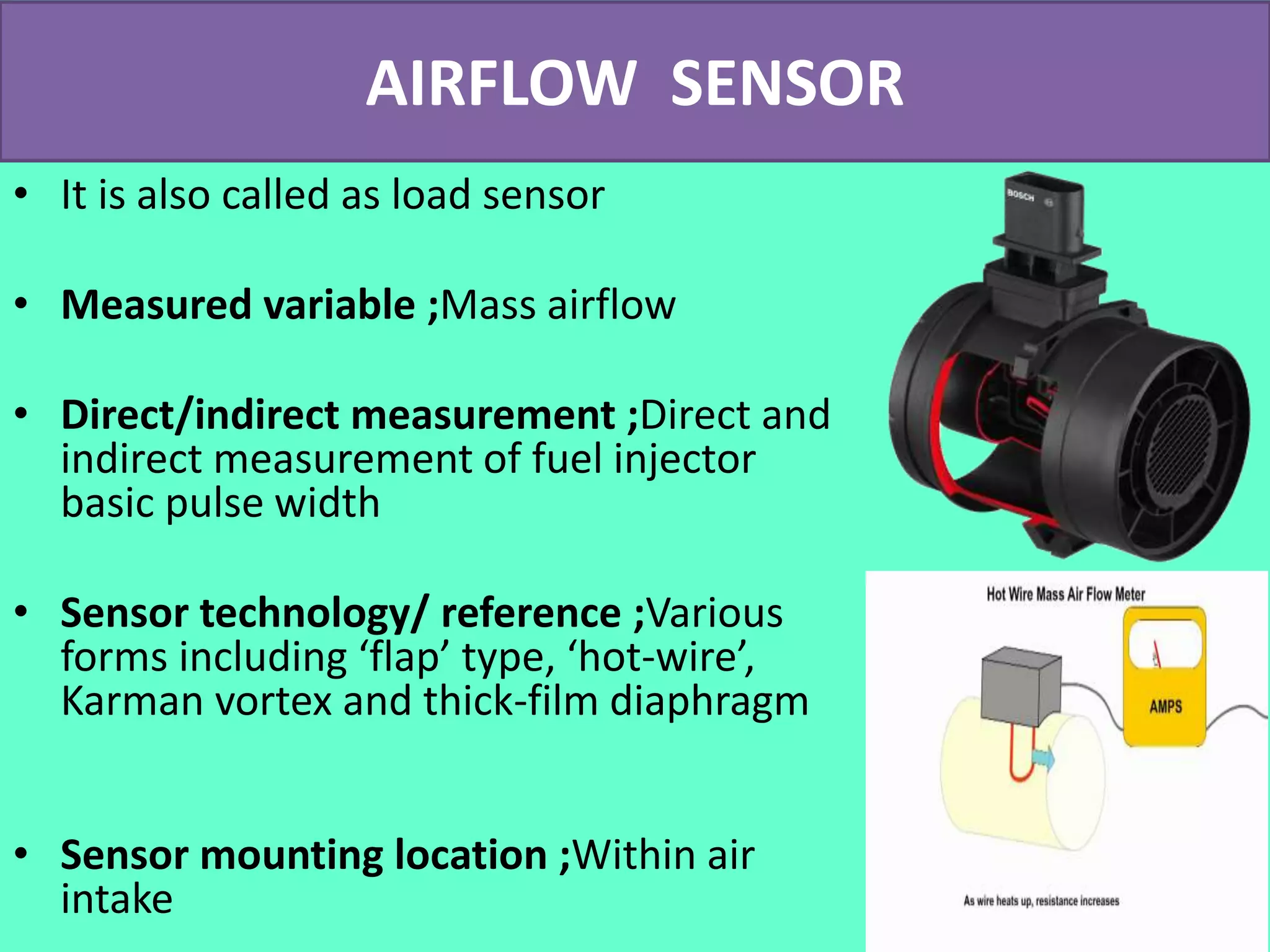
The document discusses the engine control unit (ECU) and its functions. The ECU uses sensors to monitor systems like the engine, emissions and safety and actuators to control functions like fuel injection. It allows for improved engine performance, emission control and safety compared to conventional systems. Modern vehicles have up to 75 ECUs working together over a network to precisely control and monitor various vehicle functions.