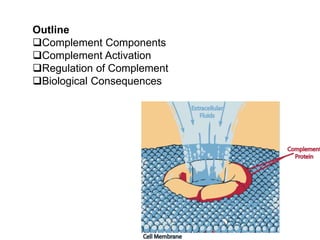
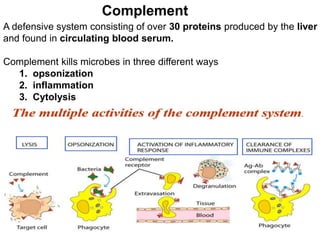
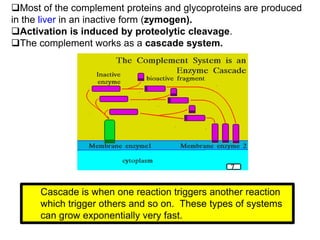
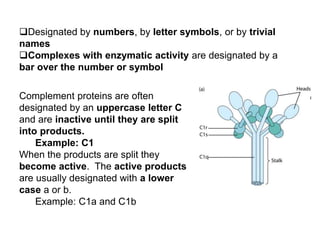
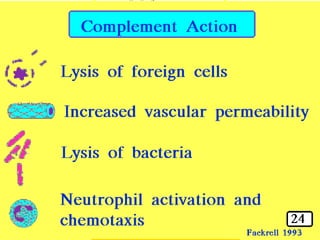
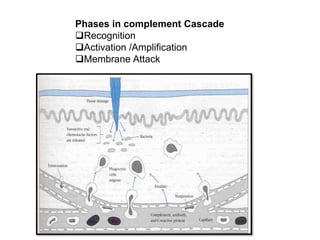
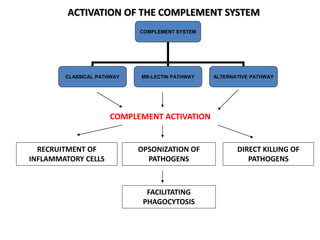
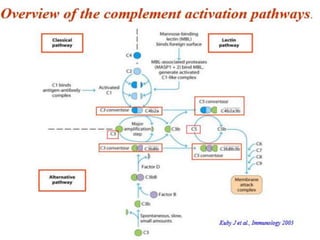
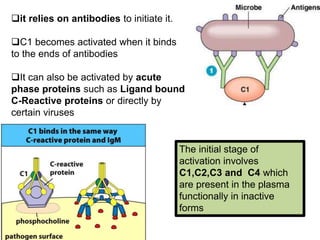
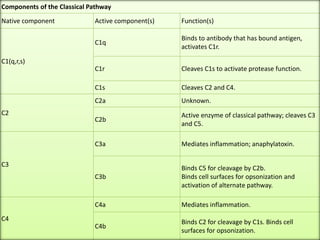
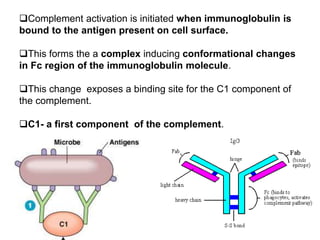
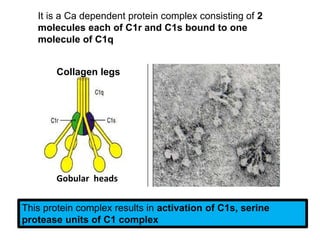
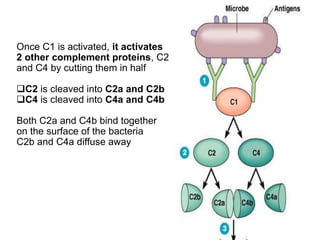
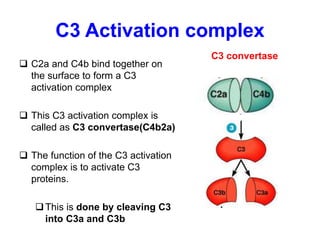
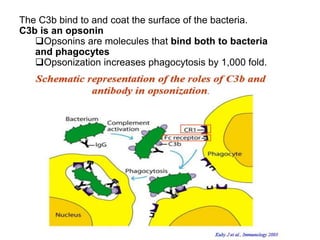
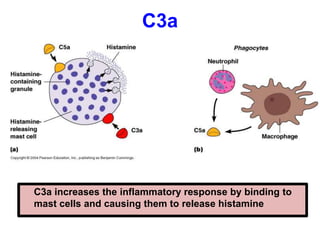
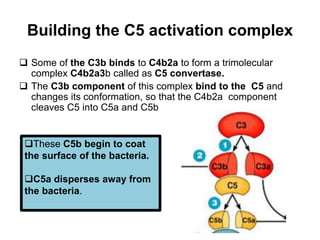
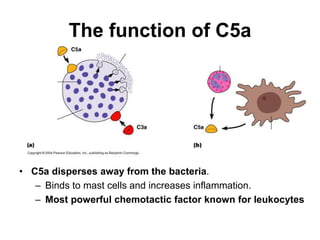
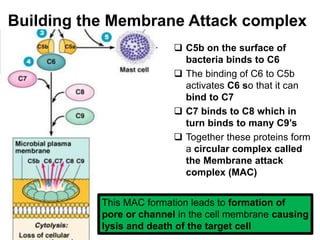
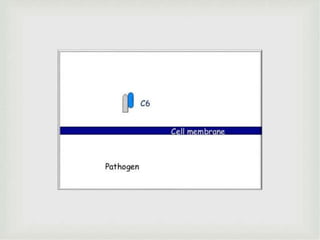
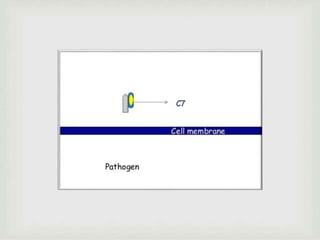
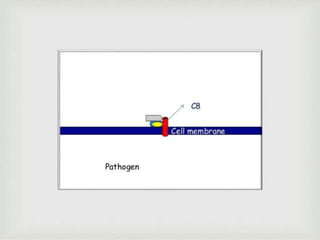
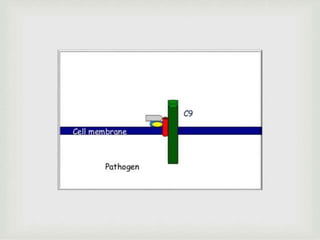
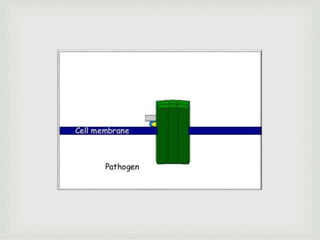
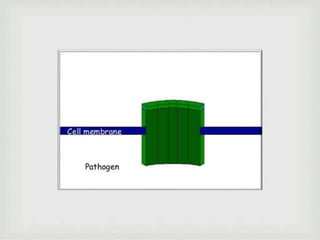
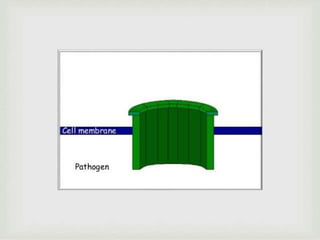
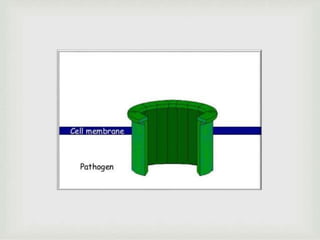
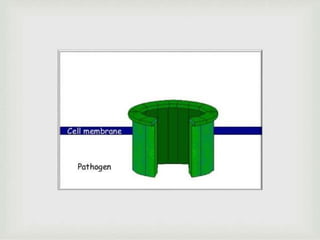
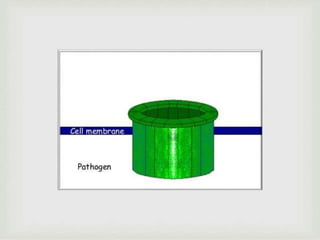
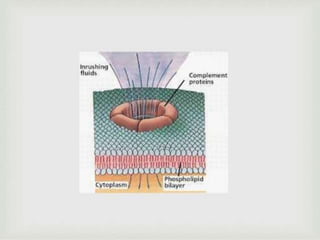
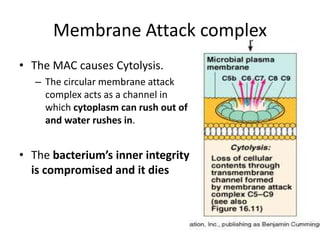
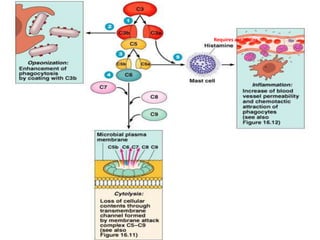
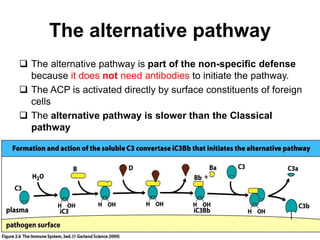
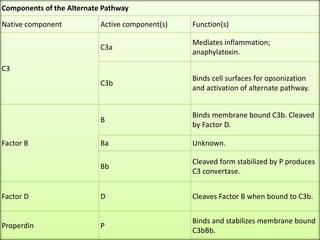
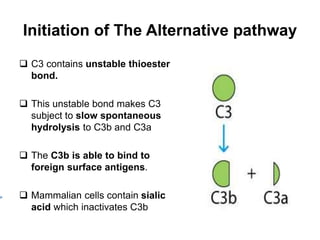
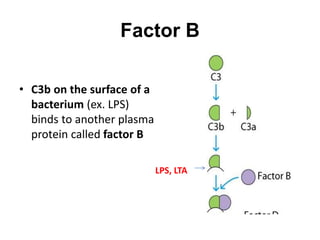
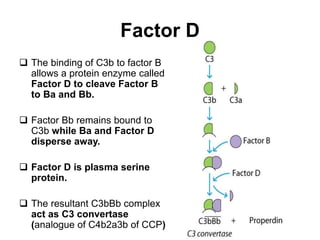
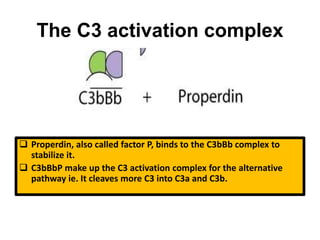
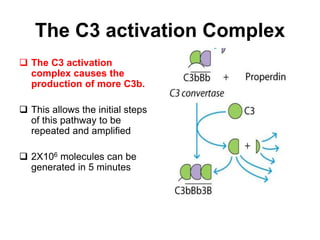
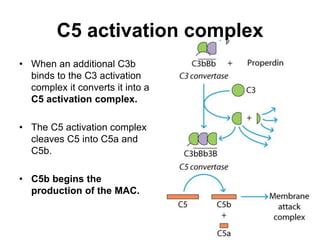
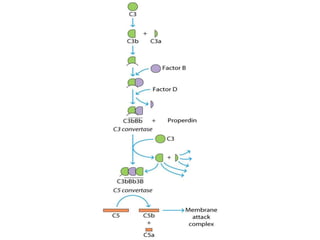
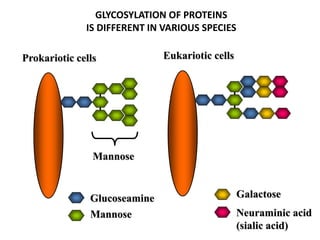
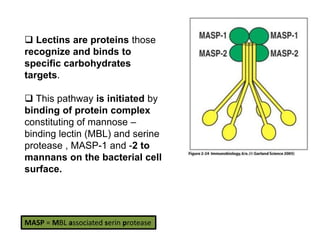
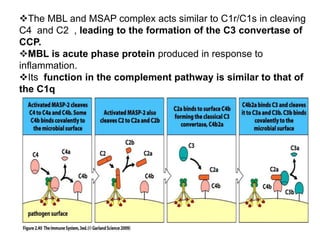
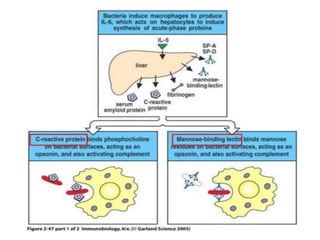
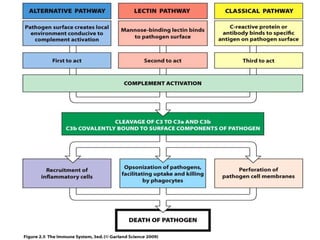
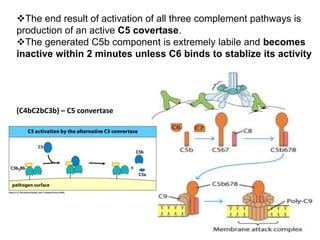
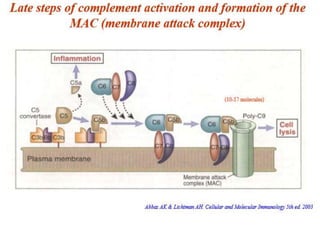
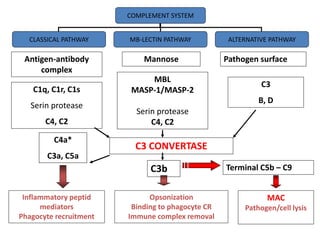
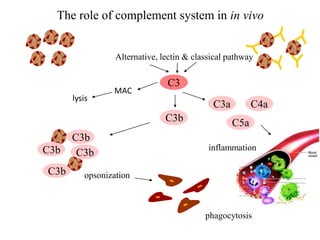
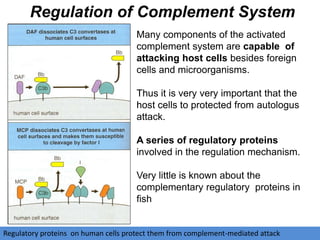
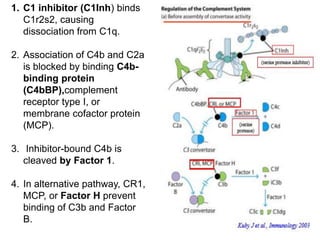
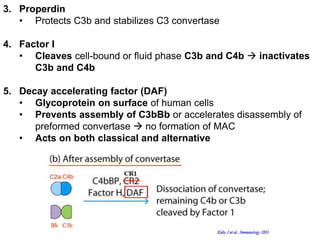
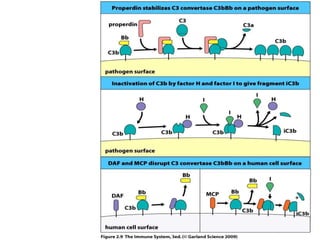
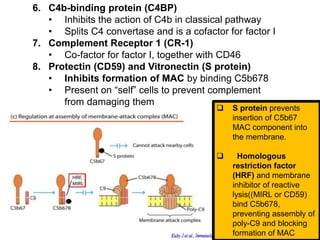
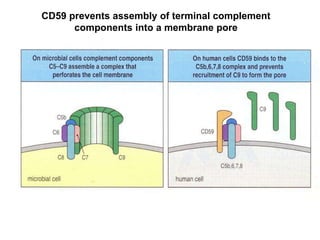
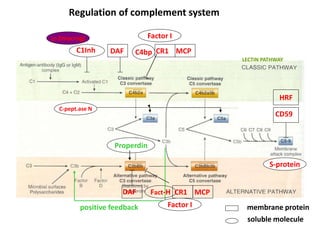
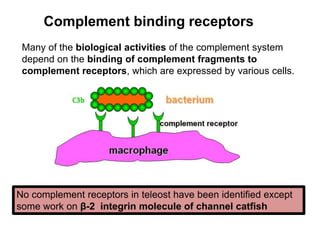
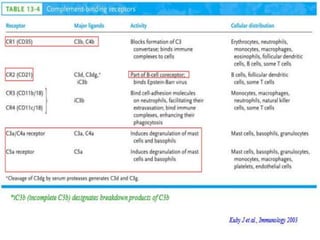
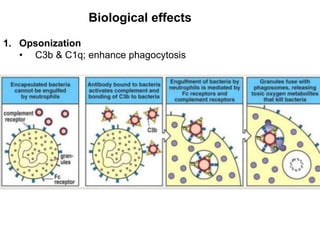
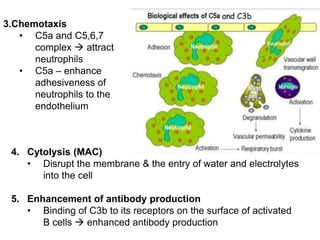
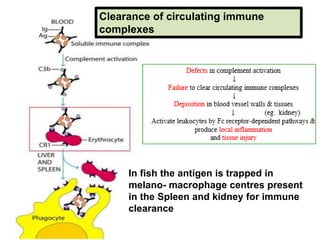
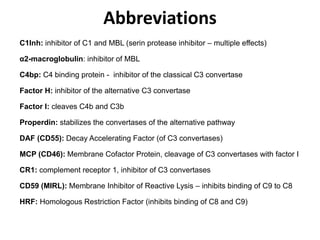
The document discusses the complement system of teleost fish. It has three pathways - the classical pathway, lectin pathway, and alternative pathway. All three pathways involve a cascade of complement components that ultimately lead to the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) on pathogen surfaces. The MAC forms pores that lyse pathogens. The complement system also opsonizes pathogens and generates inflammatory peptides like C3a and C5a. Strict regulation is needed to prevent damage to host cells, mediated by factors such as C1 inhibitor, factor H, decay accelerating factor, and CD59.