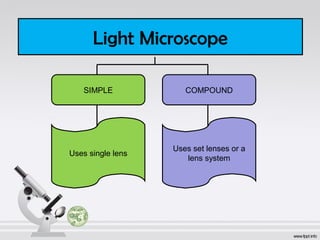
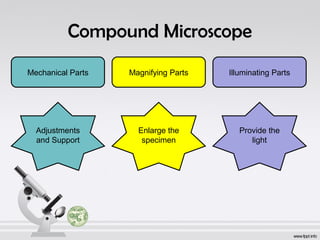
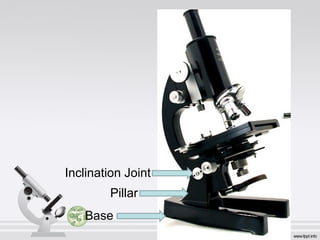
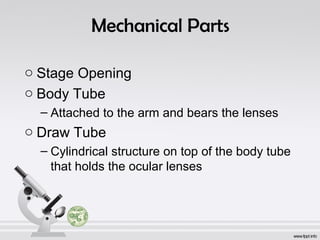
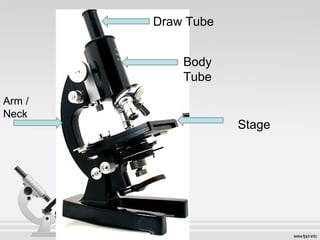
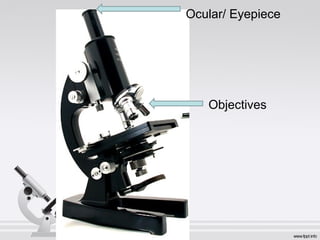
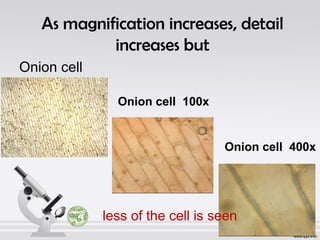
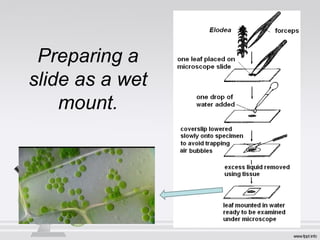
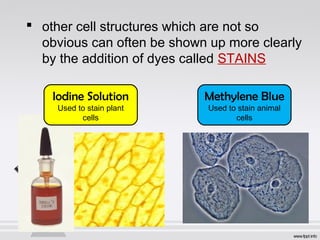
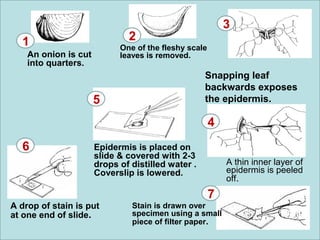
The document explains the structure and function of compound microscopes, including their various mechanical and magnifying parts. It details how to use and care for a microscope, as well as the process of preparing slides and using stains to enhance visibility of cell structures. Key parts include objectives, eyepieces, and adjustment knobs, which facilitate the magnification and focusing of small objects.