Cell Wall.pptx
- 1. Cell Wall Primary cell wall Secondary cell wall
- 2. Introduction • The cell wall is an outer protective membrane in many cells including plants, fungi, algae, and bacteria. Animal cells do not have a cell wall. • The main functions of the cell wall are to provide structure, support, and protection for the cell. • The cell wall in plants is composed mainly of cellulose and contains three layers in many plants. The three layers are the middle lamella, primary cell wall, and secondary cell wall. • Bacterial cell walls are composed of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer and gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer. The cell wall is the most characteristic feature of a plant cell
- 3. • Cell wall composition varies depending on the organism. • In plants, the cell wall is composed mainly of strong fibers of the carbohydrate polymer cellulose. Cellulose is the major component of cotton fiber and wood, and it is used in paper production. • Bacterial cell walls are composed of a sugar and amino acid polymer called peptidoglycan. • The main components of fungal cell walls are chitin, glucans, and proteins.
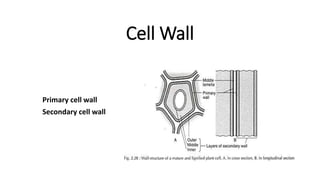
- 4. The middle lamella • The middle lamella is a pectin layer which functions to cement the two adjoining cells together of the cell wall. • This is essential to plants as it gives them stability, and allows that plants can form plasmodesmata between cells. • The middle lamella is the first layer that is formed, which is deposited at the time of cytokinesis. The cell plate that is molded during cell division is developed into lamellum or the middle lamella. • This layer is basically made up of calcium and magnesium pectates. • It is a common structure between adjacent cells and therefore, binds them with each other • The middle lamella remains unlignified in case of softer living tissues namely Parenchyma, collenchyma and arenchyma, but in woody tissues Sclerenchyma it becomes highly lignified
- 5. Primary cell wall • 1. Primary wall is laid inner to middle lamella. • 2. It is formed in young growing cell • 3. It is capable of extension. • 4. The wall grows by intussusception or addition of materials inside. • 5. It is single layered. • 6. Hydration is 60%. • 7. Cellulose content is comparatively low. • 8. Cellulose micro fibrils are shorter, wavy and loosely arranged. • 9. Protein content is high, up to 5%. • 10. Hemicellulose content is high, up to 50%. • 11. Lipid content is 5-10%. • 12. Additional chemicals like lignin are absent. • 13. Primary wall is thin (0.1-3 µm). • 14. Pits are usually absent in a primary wall
- 6. Secondary cell wall • 1. Secondary wall is laid inner to primary wall. • 2. Secondary wall is formed when the cell has stopped growing. • 3. Extensibility is usually absent. • 4. It grows by accretion or deposition of materials on the existing structure. • 5. Secondary wall is three or more layered known as S1 (outer), S2 (middle) and S3 (inner) • 6. Hydration is 30—40%. • 7. Cellulose content is comparatively high. • 8. Cellulose micro fibrils are longer, closely arranged, straight and parallel. • 9. Protein content is low, 1% or less. • 10. Hemicellulose content is 25% of the total. • 11. Lipid is absent or negligible. • 12. Lignin, suberin, etc. are present. • 13 .Secondary walls is quite thick (3-19 µm). • 14. Pits often occur in the secondary wall.