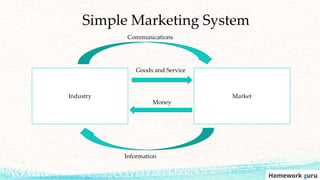
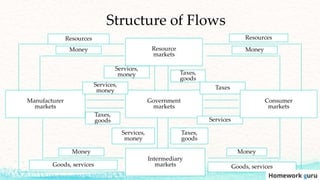
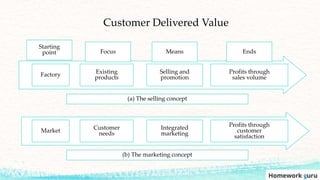
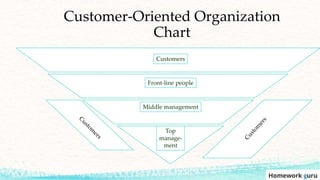
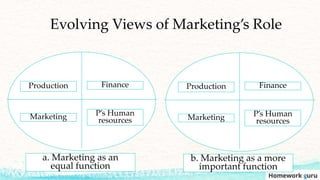
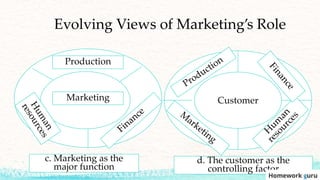
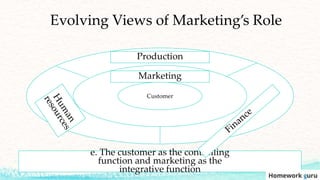
This document outlines the key topics covered in a marketing course, including the major concepts and tools of marketing such as segmentation, the marketing mix of product, price, place, and promotion, and different orientations like production and marketing concepts. It also discusses how the role of marketing has evolved to be more customer-centric, with the customer now seen as the controlling factor for the organization. The overall summary is that the document provides an overview of the key elements that will be covered in a marketing class, from fundamental concepts to frameworks to the changing role of marketing.